|
Manual Command To Line Of Sight
Manual command to line of sight (MCLOS or MACLOS) is a method for guiding guided missiles. With an MCLOS missile, the operator must track the missile and the target simultaneously and guide the missile to the target. Typically the missile is steered with a joystick, and its path is observed through a periscope-type telescopic sight. The missiles are usually equipped with a magnesium flare in the base that automatically ignites on launch and allows the gunner to visually track the fast-moving missile in a manner similar in concept to tracer ammunition. MCLOS requires considerable training and practice to master, since even a minor disruption in the gunner's concentration would likely cause a miss. These guidance systems have marginal accuracy on tank-sized targets, even with perfect line-of-sight by the gunner, due to erratic flight paths requiring timely manual corrections. As demonstrated by the Israeli Army under fire from Soviet-armed Arab states, responding to the distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Guided Missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of Propulsion, self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor. Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this usage is still recognized today with any unguided jet- or rocket-propelled weapons generally described as rocket artillery. Airborne explosive devices without propulsion are referred to as shell (projectile), shells if fired by an artillery piece and Aerial bomb, bombs if dropped by an aircraft. Missiles are also generally missile guidance, guided towards specific targets termed as guided missiles or guided Rocket (weapon), rockets. Missile systems usually have five system components: targeting (warfare), targeting, guidance system, flight system, engine, and warhead. Missiles are primarily classified into different types based on firing source and target such as surface-to-surface missile, surface-to-surface, air-to-surface missi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Azon
AZON (or Azon), from "azimuth only", was one of the world's first guided weapons, deployed by the Allies and contemporary with the German Fritz X. Officially designated VB-1 ("Vertical Bomb 1"), it was invented by Major Henry J. Rand and Thomas J. O'Donnell during the latter stages of World War II as the answer to the difficult problem of destroying the narrow wooden bridges that supported much of the Burma Railway. AZON was essentially a general-purpose AN-M65 bomb with a quadrilateral 4-fin style radio controlled tail fin design as part of a "tail package" to give the desired guidance capability, allowing adjustment of the vertical trajectory in the yaw axis, giving the Azon unit a lateral steering capability (meaning it could only steer left and right, and could not alter its pitch or rate of fall). This lack of any pitch control meant that the bombardier still had to accurately release it with a bombsight to ensure it could not fall short of or beyond the target. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
SSM-A-23 Dart
The XSSM-A-23 Dart was an anti-tank-guided missile developed for the United States Army in the 1950s. After protracted development, the missile, similar in design to the French SS.10, was cancelled in favor of purchasing the SS.11 missile. Design and development The initial requirement for a guided anti-tank missile, intended for the replacement of recoilless rifles and Bazookas in the role,Ordway and Wakeford 1960, p.USA4 was issued by the U.S. Army in 1951; that November,Hunnicutt 1999, p.176. the Aerophysics Development Corporation responded with a proposal for a wire-guided missile, similar in concept and configuration to the SS.10 missile being developed in France.Jacobs and Whitney 1962, p.44. After evaluating the SS.10 in 1952–53,Parsch 2003 the Army issued a contract for the full development of the Aerophysics Development missile, designated SSM-A-23 Dart, in April 1953. The SSM-A-23 was of conventional configuration for an anti-tank missile of the time, having cruci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Rb 05
The Saab RB05 (abbreviation of Swedish: robot 05, "missile 05"), initially named Saab 305 (RB 305) or AT 3 internally, was a short-range air-to-surface missile with that was developed in the 1960s by the Swedish company Saab-Scania, Missiles and Electronics for the Swedish Air Force. History The RB 05 was developed as a ground attack missile for the Saab 37 Viggen fighter-bomber and Saab 105 trainer aircraft in 1967. The missile was tracer guided using radio controlled manual command to line of sight (MCLOS), which meant that aiming had to be done separate to piloting, either requiring a two-seat cockpit with a dedicated missile gunner, as per the Saab 105, or a central computer which could control the aircraft during guidance, as present on the Saab 37 Viggen. During development, Saab used a variety of Saab 35 Draken prototypes for testing. Saab 35 prototypes with tandem trainer cockpits were used for many of the firing trials, as the guidance equipment could be easily re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
3M6 Shmel
The 3M6 (; ) is an MCLOS wire-guided anti-tank missile of the Soviet Union. Its GRAU designation is "3M6" and its NATO reporting name is AT-1 Snapper. Too large to be manportable, it was typically deployed from specialised vehicles or helicopters. The missile was intended to supplement traditional anti-tank weapons, like the 100 mm anti-tank gun whose accuracy beyond 1,500 m is poor. The missile's accuracy in contrast remained high as far as its maximum range of 2,000 m. However, the system's bulk, slow speed and poor combat accuracy drove development of later SACLOS systems, like the 9M113 Konkurs. Development The 3M6 began development through Decree No. 7 on May 27, 1957. Development would be spread across several bureaus and research institutes, with the missile complex and rocket being designed by SKB-4, led by Boris Shavyrin under the leadership of the to-be famous Sergey Nepobedimy, being based on the Nord Aviation SS.10. Teams from , led by Zinovy Moiseevich Persi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Blowpipe Missile
The Shorts Blowpipe is a man-portable (MANPADS) surface-to-air missile that was in use with the British Army and Royal Marines from 1975 to 1985. It also saw service in other military forces around the world. Most examples were retired by the mid-1990s. It is unique among MANPADS in that it is manually guided to its target with a small joystick, sending guidance corrections to the missile over a radio control link. Blowpipe underwent a protracted and controversial development between the programme's initial conception in 1966 and 1975 when it finally entered service. It had its first use during active combat in the Falklands War in 1982 when it was used by both sides of the conflict. Its demonstrated performance was poor, with only two confirmed kills. As a result of the poor performance of the system, an improved version offering semi-automatic guidance was introduced as Javelin. This was further improved with a laser designator system in Javelin S15, which was later renamed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
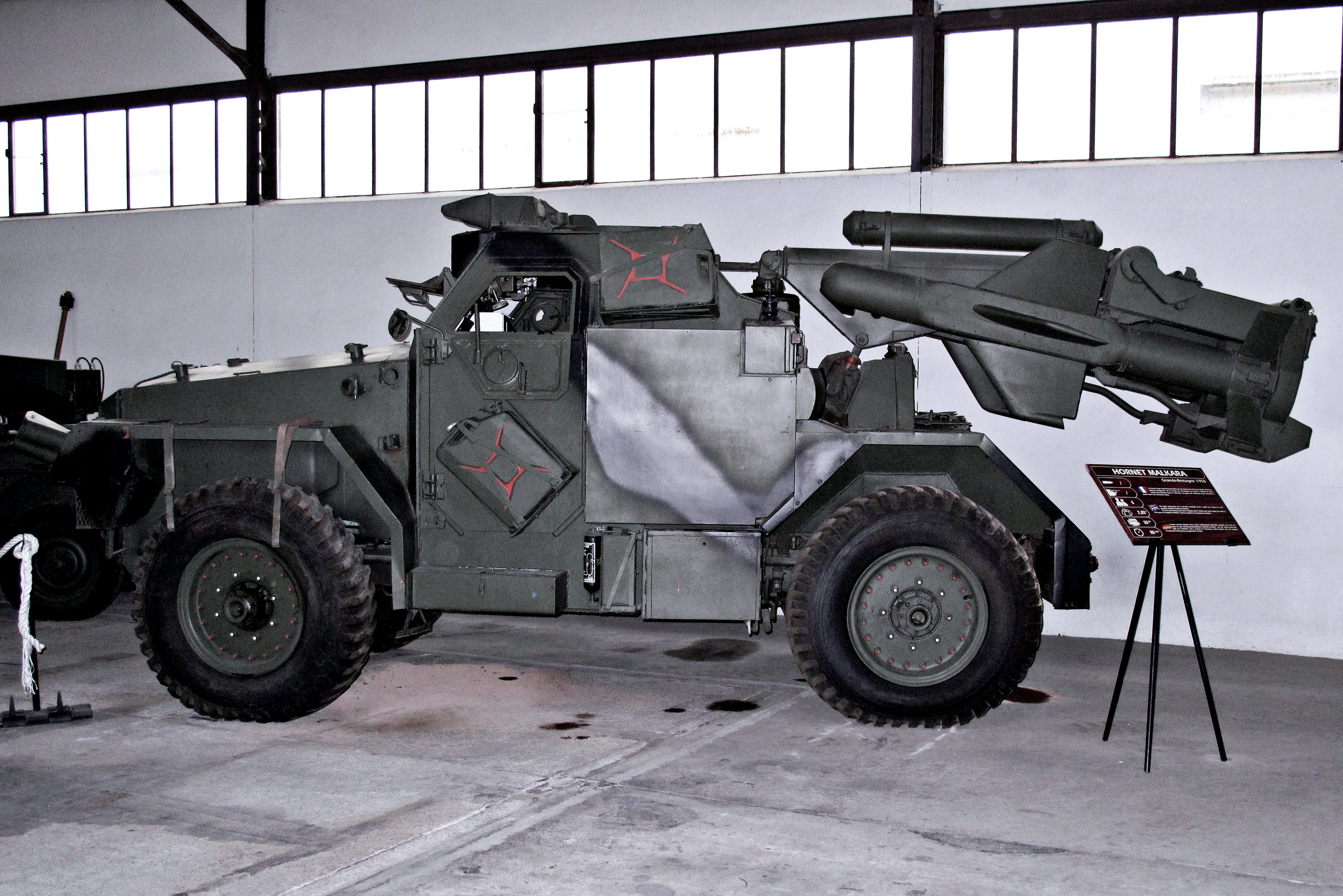 |
Malkara (missile)
The Malkara (from an Aboriginal word for "shield") was one of the earliest guided anti-tank missiles (ATGMs). It was jointly developed by Australia and the United Kingdom between 1951 and 1954, and was in service from 1958 until gradually replaced by the Vickers Vigilant missile in the late 1960s. It was intended to be light enough to deploy with airborne forces, yet powerful enough to knock out any tank then in service. The basic form was later adapted for the short-range surface-to-air role as the Seacat and influenced the development of the Ikara. Development and operations Design was principally undertaken at the Australian Government Aeronautical Research Laboratory, and this phase was also one of the first examples of computer simulation in engineering design. Development testing was carried out at Woomera Prohibited Area, and approval testing at the tank training range at Lulworth Cove, Dorset. Although testing at Dorset apparently achieved an impressive 90% Pkill, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
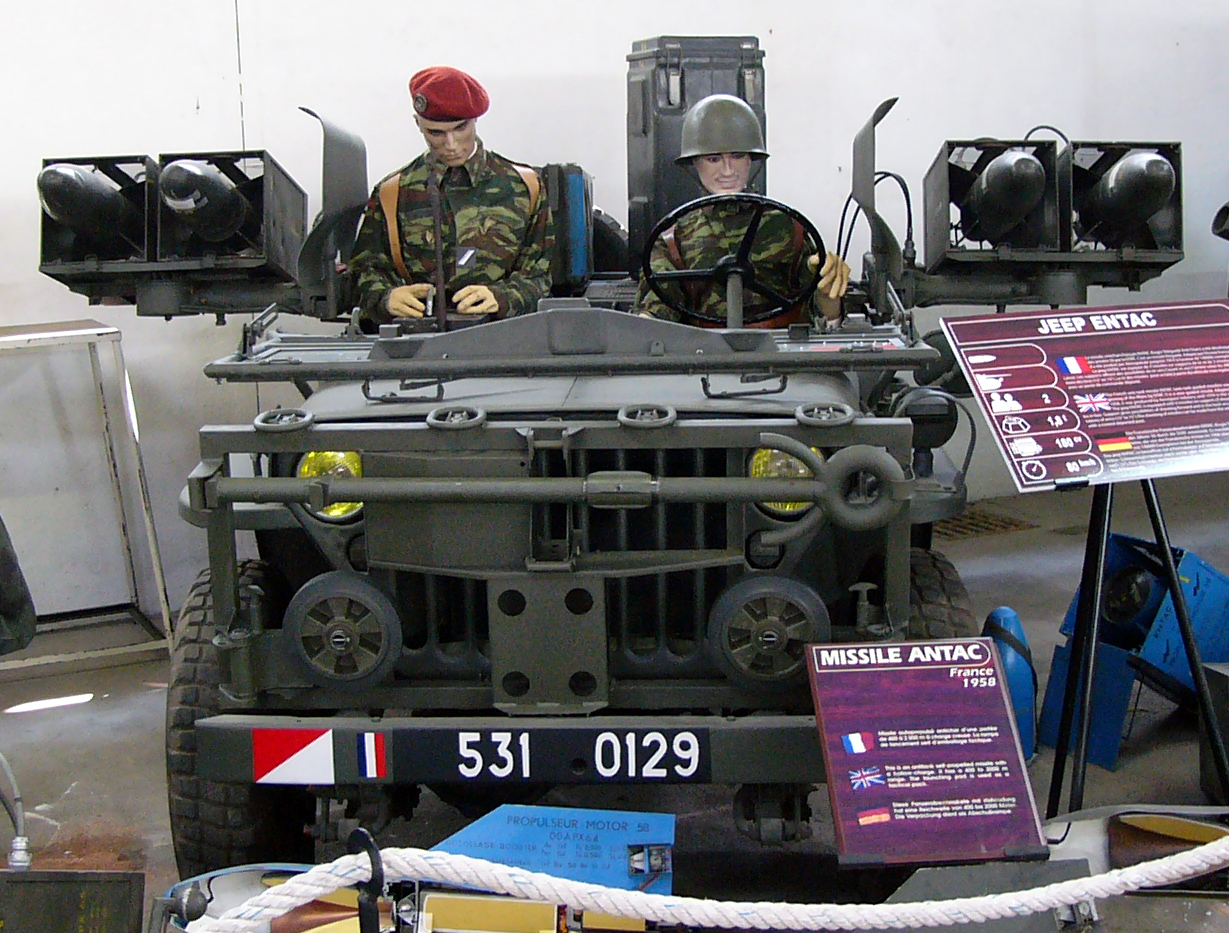 |
ENTAC
ENTAC ("Engin Téléguidé Anti-Char") or MGM-32A was a French MCLOS Wire-guided missile, wire-guided anti-tank missile. Developed in the early 1950s, the weapon entered service with the French Army in 1957. Production ended in 1974 after approximately 140,000 had been built. Development The missile was developed by the French Government agency - DTAT (''Direction Technique des Armements Terrestres'') at the same time as the private industry SS.10. Development time for the ENTAC was longer than the SS.10, so it did not enter service until 1957. It proved to be a great improvement over the SS.10, which had entered production five years earlier. Once fully developed and tested, production of the ENTAC was given to the firm of Aerospatiale. The ENTAC was designed to be a man-portable weapon or operated from a small vehicle like the Jeep, replacing the Nord SS.10 in French service. Design The missile is launched from a simple metal box, which is connected to an operator station. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Wasserfall
The ("Waterfall remote-controlled anti-aircraft rocket") was a German guided supersonic surface-to-air missile project of World War II. Development was not completed before the end of the war and it was not used operationally. The system was based on many of the technologies developed for the V-2 rocket program, including the rocket itself, which was essentially a much scaled-down version of the V-2 airframe. Significant additional development was required, including design and test of an effective guidance system to allow interception of an air target, adoption of hypergolic fuels to allow the missile to stand ready for launch for days or weeks, and the development of a reliable Proximity Fuse. :234 Technical characteristics was essentially an anti-aircraft development of the V-2 rocket, sharing the same general layout and shaping. Since the missile had to fly only to the altitudes of the attacking bombers, and needed a far smaller warhead to destroy these, it could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ruhrstahl X-4
The Ruhrstahl Ru 344 X-4 or Ruhrstahl-Kramer RK 344 was a Wire-guided missile, wire-guided air-to-air missile designed by Germany during World War II. The X-4 did not see operational service and thus was not proven in combat but inspired considerable post-war work around the world, and was the basis for the development of several ground-launched anti-tank missiles. History During 1943, the Royal Air Force, RAF's RAF Bomber Command, Bomber Command and the US Air Force mounted a series of heavy raids against Germany. Despite heavy bomber losses, these prompted ''Luftwaffe'' research into considerably more powerful anti-bomber weaponry in order to reduce the cost in lost fighter aircraft and aircrew. A massive development effort resulted in a number of heavy-calibre autocannon designs, air-to-air rockets, Surface-to-air missile, SAMs, and the X-4. Work on the X-4 began in June 1943, by Dr Max Kramer at . The idea was to build a missile with enough range to allow it to be fired f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
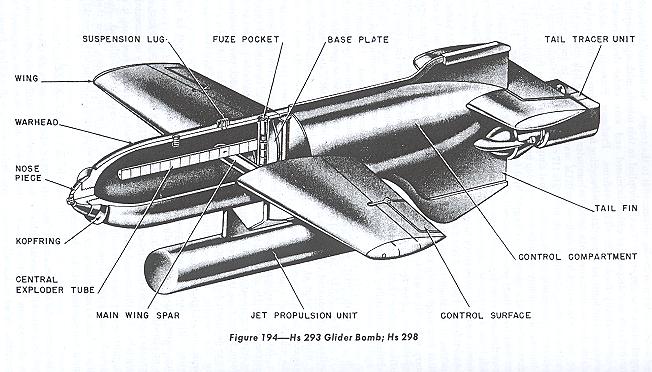 |
Henschel Hs 293
The Henschel Hs 293 was a World War II Nazi Germany, German Command guidance, radio-guided glide bomb. It is the first operational anti-shipping missile, first used unsuccessfully on 25 August 1943 and then with increasing success over the next year, damaging or sinking at least 25 ships. Allied efforts to jam the radio control link were increasingly successful despite German efforts to counter them. The weapon remained in use through 1944 when it was also used as an air-to-ground weapon to attack bridges to prevent the Allied breakout after D-Day, but proved almost useless in this role. Development The Hs 293 project started in 1940, based on the "Gustav Schwartz Propellerwerke" pure glide bomb designed in 1939. The Schwartz design did not have a terminal guidance system; instead, it used an autopilot to maintain a straight course. It was intended to be launched from a bomber at sufficient distance to keep the aircraft out of range of anti-aircraft artillery, anti-aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Henschel Hs 117
The Henschel Hs 117 ''Schmetterling'' (German for ''Butterfly'') was a radio-guided German surface-to-air missile project developed during World War II. There was also an air-to-air version, the Hs 117H. The operators used a telescopic sight and a joystick to guide the missile by radio control, which was detonated by Acoustics, acoustic and Photoelectric effect, photoelectric proximity fuses, at . Development In 1941, Professor Herbert A. Wagner (who was previously responsible for the Henschel Hs 293 anti-ship missile) invented the Schmetterling missile and submitted it to the Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Reich Air Ministry (RLM), who rejected the design because there was no need for more anti-aircraft weaponry. However, by 1943 the Defence of the Reich, large-scale bombing of Germany caused the RLM to change its mind, and Henschel was given a contract to develop and manufacture it. The team was led by Professor Wagner, and it produced a weapon somewhat resembling a bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |