|
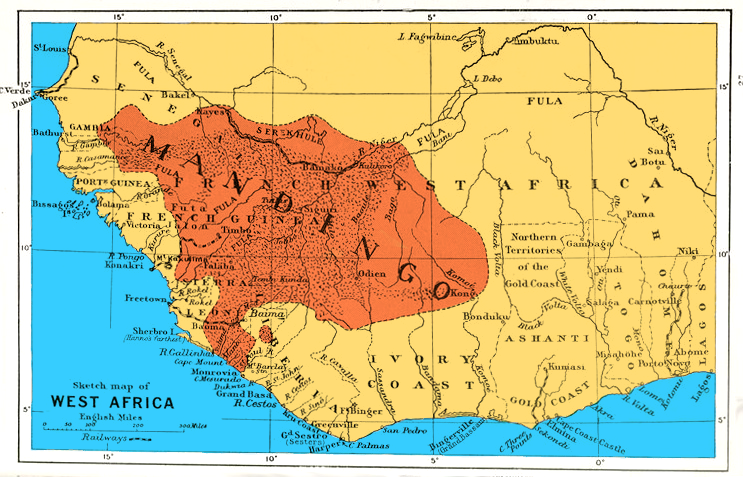
Manding Languages
The Manding languages (sometimes spelt Manden) are a dialect continuum within the Niger–Congo languages, Niger-Congo family spoken in West Africa. Varieties of Manding are generally considered (among native speakers) to be mutually intelligible – dependent on exposure or familiarity with dialects between speakers – and spoken by 9.1 million people in the countries Burkina Faso, Senegal, Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Mali, Liberia, Ivory Coast and The Gambia. Their best-known members are Mandinka language, Mandinka or Mandingo, the principal language of The Gambia; Bambara language, Bambara, the most widely spoken language in Mali; Maninka language, Maninka or Malinké, a major language of Guinea and Mali; and Dyula language, Jula, a trade language of Ivory Coast and western Burkina Faso. Manding is part of the larger Mande languages, Mandé family of languages. Subdivisions The Manding languages, the differences from one another and relationships among them are matter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom Overseas Territories, United Kingdom Overseas Territory).Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. The population of West Africa is estimated at around million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 were female and 192,309,000 male.United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2017). World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, custom data acquired via webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyula Language
Dyula (or Jula, Dioula, ''Julakan'' ߖߎ߬ߟߊ߬ߞߊ߲) is a language of the Mande language family spoken mainly in Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast and Mali, and also in some other countries, including Ghana, Guinea and Guinea-Bissau. It is one of the Manding languages and is most closely related to Bambara, being mutually intelligible with Bambara as well as Malinke. It is a trade language in West Africa and is spoken by millions of people, either as a first or second language. Similar to the other Mande languages, it uses tones. It may be written in the Latin, Arabic or N'Ko scripts. History Historically, Dyula ("jula" in the language) was not an ethonym, but rather a Manding language label literally meaning 'trader'. The term used to distinguish Muslim traders from the non-Muslim population living in the same area, mainly Senufo agricultors. It then became an exonym for Manding-speaking traders such as the Bambara or the Mandinka and their languages. At the same time, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sininkere Language
Sininkere (Silinkere) is a dialect of Soninke language of Burkina Faso Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 .... References Manding languages Languages of Burkina Faso {{Mande-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolon Language
Bolon is a Manding language of Burkina Faso Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 .... There are two dialects, White/Southern and Black/Northern; White Bolon is partially intelligible with Jula. References Manding languages Languages of Burkina Faso {{Mande-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marka Language
Marka, also called Dafing, is a Manding language of West Africa, spoken in northwest Burkina Faso Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 .... References Manding languages Languages of Burkina Faso {{Mande-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahanka Language
Jahanka is a Manding language of Guinea-Bissau and Guinea. It is partially intelligible with Mandinka. (The Jahanka of Senegal and Guinea-Bissau Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, its north and Guinea to Guinea–Guinea-Bissau b ... is a dialect of Kassonke). References Manding languages {{Mande-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kita Maninka Language
Kita Maninkakan, or Central Malinke, is a Manding language spoken by about a million people in Mali Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ..., where it is a national language. About 10% are ethnically Fula. The Kagoro variety is 86% lexically similar according to ''Ethnologue'', and is being replaced by Bambara. References Manding languages Languages of Mali {{Mande-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassonke Language
The Kassonke (Khassonké) language, ''Xaasongaxango (Xasonga)'', or Western Maninka (Malinke), is a Manding language spoken by the Khassonké and Malinke of western Mali and by the Malinke of eastern Senegal. Kassonke is an official language An official language is defined by the Cambridge English Dictionary as, "the language or one of the languages that is accepted by a country's government, is taught in schools, used in the courts of law, etc." Depending on the decree, establishmen ... in Mali. Western and Eastern Maninka are 90% mutually intelligible, though distinct from the Mandinka (Malinke) of southern Senegal, which is a national language there. Phonology Consonants Vowels See also * Bafoulabé * Kayes References Further reading * * Manding languages Languages of the Gambia Languages of Mali Languages of Senegal {{Mande-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Vowel
A nasal vowel is a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the soft palate (or velum) so that the air flow escapes through the nose and the mouth simultaneously, as in the French vowel /ɑ̃/ () or Amoy []. By contrast, oral vowels are produced without nasalization. Nasalized vowels are vowels under the influence of neighbouring sounds. For instance, the [] of the word ''hand'' is affected by the following nasal consonant. In most languages, vowels adjacent to nasal consonants are produced partially or fully with a lowered velum in a natural process of assimilation and are therefore technically nasal, but few speakers would notice. That is the case in English: vowels preceding nasal consonants are nasalized, but there is no phonemic distinction between nasal and oral vowels, and all vowels are considered phonemically oral. Some languages contrast oral vowels and nasalized vowels phonemically. Linguists make use of minimal pairs to decide whether or not the nasality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowels
A vowel is a speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract, forming the nucleus of a syllable. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (length). They are usually voiced and are closely involved in prosodic variation such as tone, intonation and stress. The word ''vowel'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "vocal" (i.e. relating to the voice). In English, the word ''vowel'' is commonly used to refer both to vowel sounds and to the written symbols that represent them (, , , , , and sometimes and ). Definition There are two complementary definitions of vowel, one phonetic and the other phonological. *In the phonetic definition, a vowel is a sound, such as the English "ah" or "oh" , produced with an open vocal tract; it is median (the air escapes along the middle of the tongue), oral (at least some of the airflow must escape through the mouth), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonetic
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds or, in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech are phoneticians. The field of phonetics is traditionally divided into three sub-disciplines on questions involved such as how humans plan and execute movements to produce speech (articulatory phonetics), how various movements affect the properties of the resulting sound (acoustic phonetics) or how humans convert sound waves to linguistic information (auditory phonetics). Traditionally, the minimal linguistic unit of phonetics is the phone (phonetics), phone—a speech sound in a language which differs from the phonological unit of phoneme; the phoneme is an abstract categorization of phones and it is also defined as the smallest unit that discerns meaning between sounds in any given language. Phonetics deals with two aspects of human speech: production ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the List of ethnic groups of Africa, largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. They are predominantly Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |