|
MAMBA
Mambas are fast-moving, highly venomous snakes of the genus ''Dendroaspis'' (which literally means "tree asp") in the family Elapidae. Four extant species are recognised currently; three of those four species are essentially arboreal and green in colour, whereas the black mamba, ''Dendroaspis polylepis'', is largely terrestrial and generally brown or grey in colour. All are native to various regions in sub-Saharan Africa and all are feared throughout their ranges, especially the black mamba. In Africa there are many legends and stories about mambas. also at/ref> Behaviour The three green species of mambas are arboreal, whereas the black mamba is largely terrestrial. All four species are active diurnal hunters, preying on birds, lizards, and small mammals. At nightfall some species, especially the terrestrial black mamba, shelter in a lair. A mamba may retain the same lair for years. Resembling a cobra, the threat display of a mamba includes rearing, opening the mouth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Mamba
The black mamba (''Dendroaspis polylepis'') is a species of highly venomous snake belonging to the family Elapidae. It is native to parts of sub-Saharan Africa. First formally species description, described by Albert Günther in 1864, it is the second-longest venomous snake after the king cobra; mature specimens generally exceed and commonly grow to . Specimens of have been reported. It varies in colour from grey to dark brown. Juvenile black mambas tend to be more pale in colour than adults, and darken with age. Despite the common name, the black mamba is not black; the colour name describes rather the inside of its mouth, which it displays when feeling threatened. The species is both terrestrial animal, terrestrial (ground-living) and arboreal (tree-living); it inhabits savannah, woodland, rocky slopes and in some regions, dense forest. It is Diurnality, diurnal and is known to prey on birds and small mammals. Over suitable surfaces, it can move at speeds up to for short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter used at the neuromuscular junction. In other words, it is the chemical that motor neurons of the nervous system release in order to activate muscles. This property means that drugs that affect cholinergic systems can have very dangerous effects ranging from paralysis to convulsions. Acetylcholine is also a neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system, both as an internal transmitter for both the sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system, and as the final product released by the parasympathetic nervous system. Acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter of the parasympathet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasciculin
Fasciculins are a class of toxic proteins found in certain snake venoms, notably some species of mamba. Investigations have revealed distinct forms in some green mamba venoms, in particular FAS1 and FAS2 Fasciculins are so called because they cause intense fasciculation in muscle fascicles of susceptible organisms, such as the preferred prey of the snakes. This effect helps to incapacitate the muscles, either killing the prey, or paralysing it so that the snake can swallow it. Fundamental mechanism of action The mechanism of action of FAS proteins is associated with attachment to molecules within muscular acetylcholinesterase, and at neuromuscular junctions, thus conferring their ability to interfere with neuromodulatory inhibition. Molecular nature and physiological effect Fasciculins from mambas inhibit mammalian and fish acetylcholinesterases intensely, but are less active against the corresponding enzymes in insects, reptiles and birds. As one might expect of fast-acting ven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiotoxin
Cardiotoxicity is the occurrence of heart dysfunction as electric or muscle damage, resulting in heart toxicity. This can cause heart failure, arrhythmia, myocarditis, and cardiomyopathy in patients. Some effects are reversible, while in others, permanent damage requiring further treatment may arise. The heart becomes weaker and is not as efficient in pumping blood. Cardiotoxicity may be caused by chemotherapy (a usual example is the class of anthracyclines) treatment and/or radiotherapy; complications from anorexia nervosa; adverse effects of heavy metals intake; the long-term abuse of or ingestion at high doses of certain strong stimulants such as cocaine; or an incorrectly administered drug such as bupivacaine. Mechanism Many mechanisms have been used to explain cardiotoxicity. While many times, differing etiologies share the same mechanism, it generally depends on the agent inducing cardiac damage. For example, the primary mechanism is thought to be oxidative stress on cardia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrotoxin
Dendrotoxins are a class of presynaptic neurotoxins produced by mamba snakes ('' Dendroaspis'') that block particular subtypes of voltage-gated potassium channels in neurons, thereby enhancing the release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions. Because of their high potency and selectivity for potassium channels, dendrotoxins have proven to be extremely useful as pharmacological tools for studying the structure and function of these ion channel proteins. Dendrotoxins have been shown to block particular subtypes of voltage-gated potassium (K+) channels in neuronal tissue. In the nervous system, voltage-gated K+ channels control the excitability of nerves and muscles by controlling the resting membrane potential and by repolarizing the membrane during action potentials. Dendrotoxin has been shown to bind the nodes of Ranvier of motor neurons and to block the activity of these potassium channels. In this way, dendrotoxins prolong the duration of action potentials and increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called ''envenomation''. Venom is often distinguished from ''poison'', which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and ''toxungen'', which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism. Venom has evolved in terrestrial and marine environments and in a wide variety of animals: both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrosis, necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; myotoxins, which damage muscles; and Hemotoxin, haemotoxins, which disrupt Thrombus, blood clotti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
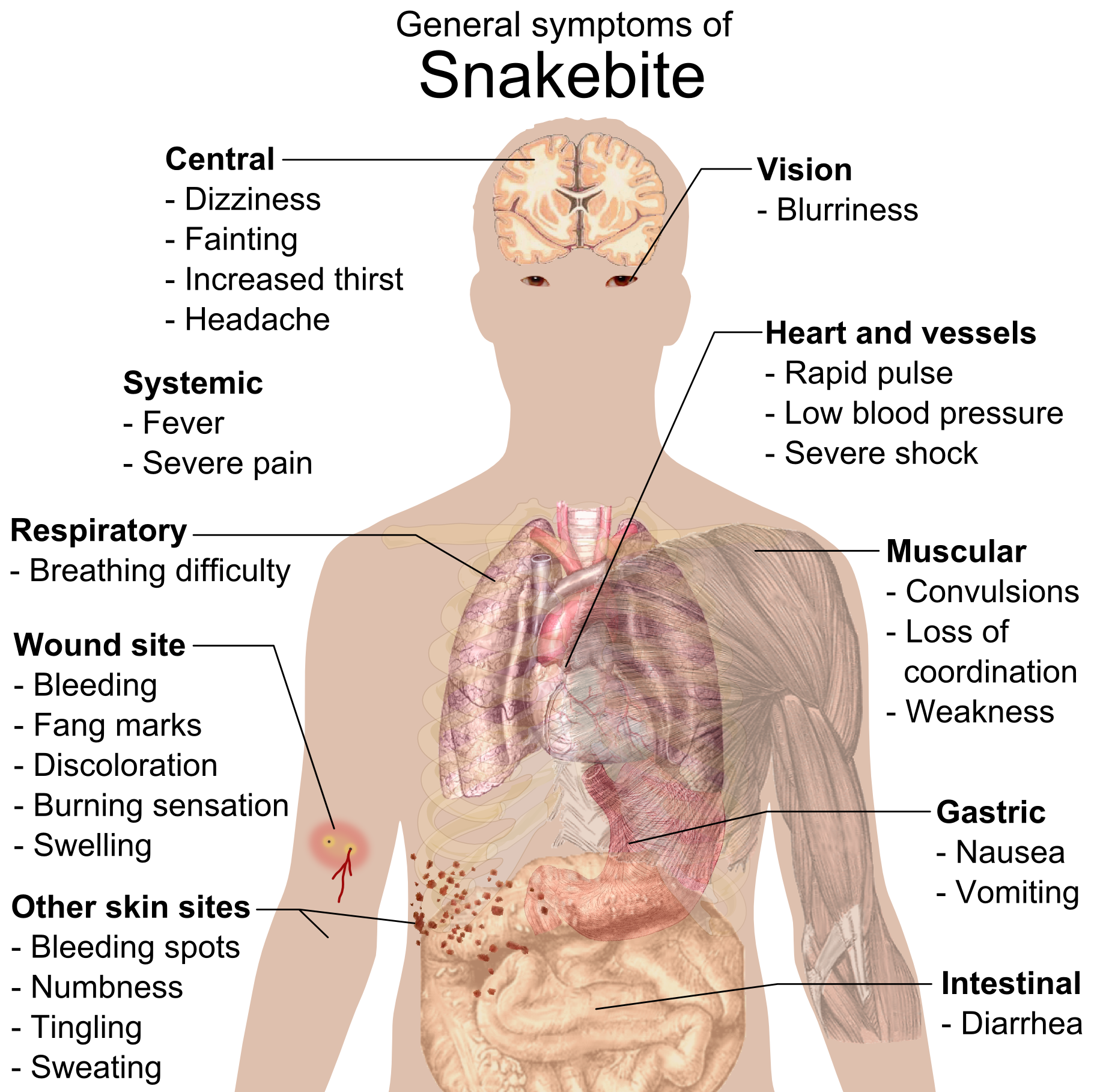
Snakebites
A snakebite is an injury caused by the bite of a snake, especially a venomous snake. A common sign of a bite from a venomous snake is the presence of two puncture wounds from the animal's fangs. Sometimes venom injection from the bite may occur. This may result in redness, swelling, and severe pain at the area, which may take up to an hour to appear. Vomiting, blurred vision, tingling of the limbs, and sweating may result. Most bites are on the hands, arms, or legs. Fear following a bite is common with symptoms of a racing heart and feeling faint. The venom may cause bleeding, kidney failure, a severe allergic reaction, tissue death around the bite, or breathing problems. Bites may result in the loss of a limb or other chronic problems or even death. The outcome depends on the type of snake, the area of the body bitten, the amount of snake venom injected, the general health of the person bitten, and whether or not anti-venom serum has been administered by a doctor in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Envenomation
Envenomation is the process by which venom is injected by the bite or sting of a venomous animal. Many kinds of animals, including mammals (e.g., the northern short-tailed shrew, ''Blarina brevicauda''), reptiles (e.g., many snakes), spiders, insects (e.g., wasps) and other arthropods, and fish (e.g., stone fish) employ venom for hunting and for self-defense. In particular, snakebite is considered to be a neglected tropical disease causing over 100,000 deaths and maiming over 400,000 people per year. Mechanisms Some venoms are applied externally, especially to sensitive tissues such as the eyes, but most venoms are administered by piercing the skin of the victim. Venom in the saliva of the Gila monster and some other reptiles enters prey through bites of grooved teeth. More commonly animals have specialized organs such as hollow teeth (fangs) and tubular stingers that penetrate the prey's skin, whereupon muscles attached to the attacker's venom reservoir squirt venom deep wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threat Display
Deimatic behaviour or startle display means any pattern of bluffing behaviour in an animal that lacks strong defences, such as suddenly displaying conspicuous eyespots, to scare off or momentarily distract a predator, thus giving the prey animal an opportunity to escape. The term deimatic or dymantic originates from the Greek δειματόω (deimatóo), meaning "to frighten". Deimatic display occurs in widely separated groups of animals, including moths, butterflies, mantises and phasmids among the insects. In the cephalopods, different species of octopuses, squids, cuttlefish and the paper nautilus are deimatic. Displays are classified as deimatic or aposematic by the responses of the animals that see them. Where predators are initially startled but learn to eat the displaying prey, the display is classed as deimatic, and the prey is bluffing; where they continue to avoid the prey after tasting it, the display is taken as aposematic, meaning the prey is genuinely distast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |