|
Malton And Driffield Junction Railway
The Malton and Driffield Junction Railway, later known as the ''Malton and Driffield branch'' was a railway line in Yorkshire that ran between the towns of Malton, North Yorkshire and Driffield in the East Riding of Yorkshire. The line was formally opened on 19 May 1853 with full public services starting on 1 June 1853. It became part of the North Eastern Railway (United Kingdom), North Eastern Railway (1854), then London and North Eastern Railway (1923), becoming part of British Railways in 1948. Passenger services on the line gained the nickname the ''Malton Dodger''. Between the 1920s and 1950s the line saw use transporting chalk from the Burdale and Wharram quarries. Passenger services ended on 5 June 1950; the Burdale quarry closed in 1955, and the line closed on 20 October 1958. A short section of the original line reopened on 24 May 2015 as a heritage attraction operating as the Yorkshire Wolds Railway. There are plans to further extend the heritage railway. History Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ) is an area of Northern England which was History of Yorkshire, historically a county. Despite no longer being used for administration, Yorkshire retains a strong regional identity. The county was named after its county town, the city of York. The south-west of Yorkshire is densely populated, and includes the cities of Leeds, Sheffield, Bradford, Doncaster and Wakefield. The north and east of the county are more sparsely populated, however the north-east includes the southern part of the Teesside conurbation, and the port city of Kingston upon Hull is located in the south-east. York is located near the centre of the county. Yorkshire has a Yorkshire Coast, coastline to the North Sea to the east. The North York Moors occupy the north-east of the county, and the centre contains the Vale of Mowbray in the north and the Vale of York in the south. The west contains part of the Pennines, which form the Yorkshire Dales in the north-west. The county was historically borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle And Darlington Junction Railway (Thirsk And Malton Branches) Act 1846
The York, Newcastle and Berwick Railway (YN&BR) was an English railway company formed in 1847 by the amalgamation of the York and Newcastle Railway as well as the Newcastle and Berwick Railway. Both companies were part of the group of business interests controlled by George Hudson, the so-called ''Railway King''. In collaboration with the York and North Midland Railway and other lines he controlled, he planned that the YN&BR would form the major part of a continuous railway between London and Edinburgh. At this stage the London terminal was Euston Square (nowadays called Euston) and the route was through Normanton. This was the genesis of the East Coast Main Line, but much remained to be done before the present-day route was formed, and the London terminus was altered to King's Cross. The YN&BR completed the plans of its predecessors, including building a central passenger station in Newcastle, the High Level Bridge across the River Tyne, and the viaduct across the River Tweed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Settrington Railway Station
Settrington railway station was a railway station on the Malton & Driffield Railway in North Yorkshire North Yorkshire is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in Northern England.The Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas of City of York, York and North Yorkshire (district), North Yorkshire are in Yorkshire and t ..., England. It opened on 19 May 1853, and served the village of Settrington. It closed for passengers on 5 June 1950 and goods on 20 October 1958. References * * External links Settrington station on navigable 1947 O. S. map Disused railwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abeyance
Abeyance (from the Old French ' meaning "gaping") describes a state of temporary dormancy or suspension. In law, it can refer to a situation where the ownership of property, titles, or office is not currently Vesting, vested in any specific person, but is awaiting the appearance or determination of the rightful owner. This typically applies to future estates that have not yet vested, and may never vest. For example, an estate is granted to A for life, with the remainder to the heir of B upon A's death. if B is still alive, the remainder is held in abeyance because B can have no legal heir until B's own death. The term hold in abeyance is used in lawsuits and court cases when a case is temporarily put on hold. English peerage law History The most common use of the term is in the case of English peerage dignities. Most such peerages pass to heirs-male, but the ancient baronies created by writ, as well as some very old earldoms, pass instead to heirs-general (by cognatic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Mania
Railway Mania was a stock market bubble in the rail transportation industry of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in the 1840s. It followed a common pattern: as the price of railway shares increased, speculators invested more money, which further increased the price of railway shares, until the share price collapsed. The mania reached its zenith in 1846, when 263 Acts of Parliament for setting up new railway companies were passed, with the proposed routes totalling . About a third of the railways authorised were never built—the companies either collapsed because of poor financial planning, were bought out by larger competitors before they could build their line, or turned out to be fraudulent enterprises to channel investors' money into other businesses. Causes The world's first recognizably modern inter-city railway, the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (the L&M), opened in 1830 and proved to be successful for transporting both passengers and freight. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
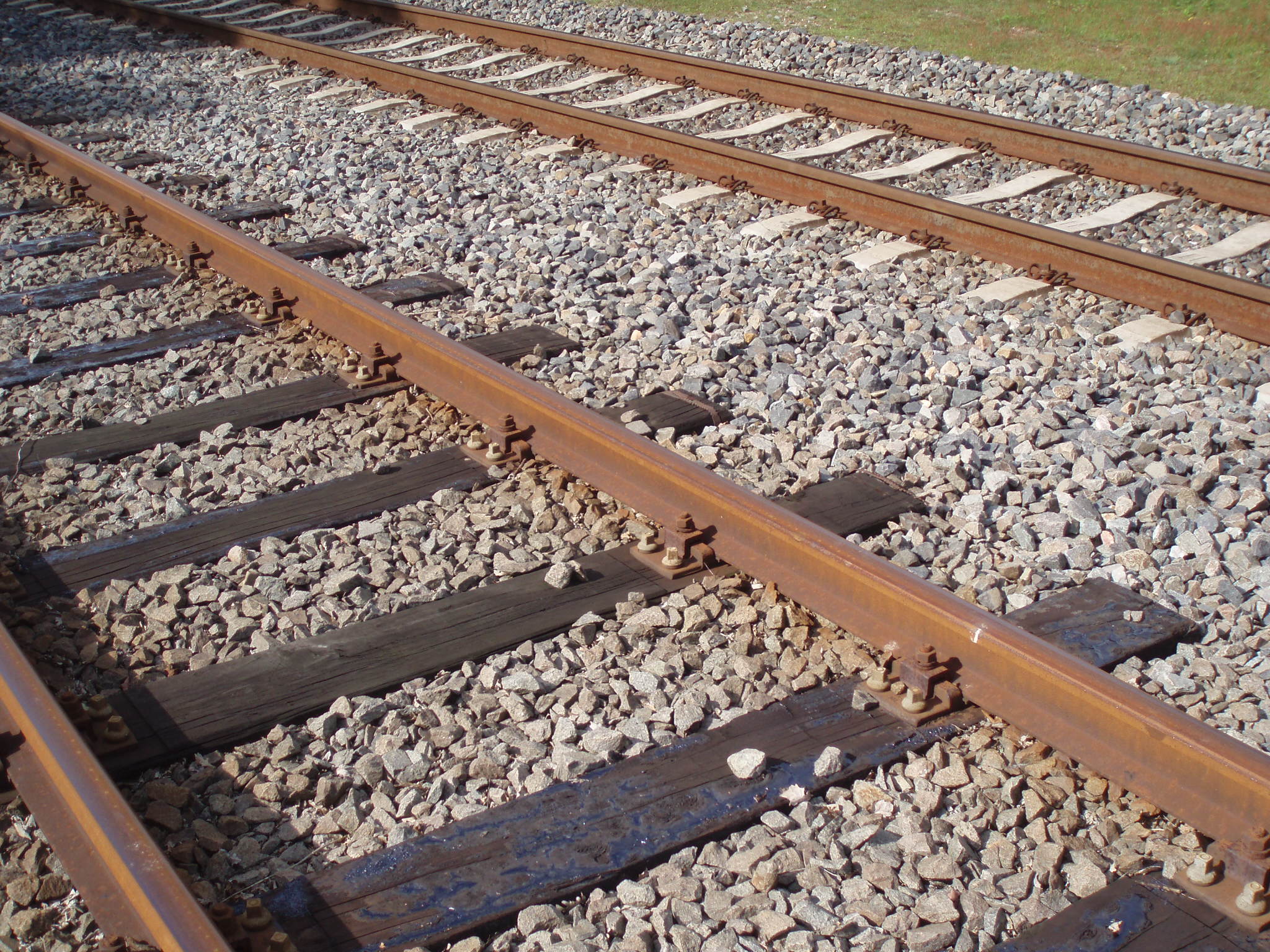
Railroad Tie
A railroad tie, crosstie (American English), railway tie (Canadian English) or railway sleeper ( Australian and British English) is a rectangular support for the rails in railroad tracks. Generally laid perpendicular to the rails, ties transfer loads to the track ballast and subgrade, hold the rails upright and keep them spaced to the correct gauge. Railroad ties are traditionally made of wood, but prestressed concrete is now also widely used, especially in Europe and Asia. Steel ties are common on secondary lines in the UK; plastic composite ties are also employed, although far less than wood or concrete. As of January 2008, the approximate market share in North America for traditional and wood ties was 91.5%, the remainder being concrete, steel, azobé (red ironwood) and plastic composite. Tie spacing may depend on the type of tie, traffic loads and other requirements, for example on North American mainline railroads to on London, Midland and Scottish Railway joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Profile
The rail profile is the cross-sectional shape of a Railway track#Rail, rail as installed on a railway or railroad, perpendicular to its length. Early rails were made of wood, cast iron or wrought iron. All modern rails are hot rolled steel with a cross section Profile (engineering), (profile) approximate to an I-beam, but asymmetric about a horizontal axis (however see #Grooved rail, grooved rail below). The head is profiled to resist wear and to give a good ride, and the foot profiled to suit the fixing system. Unlike some other uses of iron and steel, railway rails are subject to very high stresses and are made of very high quality steel. It took many decades to improve the quality of the materials, including the change from iron to steel. Minor flaws in the steel that may pose no problems in other applications can lead to broken rails and dangerous derailments when used on railway tracks. By and large, the heavier the rails and the rest of the track work, the heavier an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Railway Curve Radius
The minimum railway curve radius is the shortest allowable design radius for the centerline of railway tracks under a particular set of conditions. It has an important bearing on construction costs and operating costs and, in combination with superelevation (difference in elevation of the two rails) in the case of train tracks, determines the maximum safe speed of a curve. The minimum radius of a curve is one parameter in the design of railway vehicles as well as trams; monorails and automated guideways are also subject to a minimum radius. History The first proper railway was the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, which opened in 1830. Like the tram roads that had preceded it over a hundred years, the L&M had gentle curves and gradients. Reasons for these gentle curves include the lack of strength of the track, which might have overturned if the curves were too sharp causing derailments. The gentler the curves, the greater the visibility, thus boosting safety via increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Hull
The River Hull is a navigable river in the East Riding of Yorkshire in Northern England. It rises from a series of springs to the west of Driffield, and enters the Humber Estuary at Kingston upon Hull. Following a period when the Archbishops of York charged tolls for its use, it became a free navigation. The upper reaches became part of the Driffield Navigation from 1770, after which they were again subject to tolls, and the section within the city of Hull came under the jurisdiction of the Port of Hull, with the same result. Most of its course is through low-lying land that is at or just above sea level, and regular flooding has been a long-standing problem along the waterway. Drainage schemes to alleviate it were constructed on both sides of the river. The Holderness Drainage scheme to the east was completed in 1772, with a second phase in 1805, and the Beverley and Barmston Drain to the west was completed in 1810. Since 1980, the mouth of the river has been protected by a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Driffield
Driffield, also known as Great Driffield (neighbouring Little Driffield), is a market town and civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The civil parish is formed by the town of Driffield and the village of Little Driffield. By road, it is north-east of Leeds, east of York and north of Hull. Driffield, being near the centre of the Yorkshire Wolds, is named ''The Capital of the Wolds''. According to the 2011 UK census, Driffield parish had a population of 13,080, an increase on the 2001 UK census figure of 11,477. The town was listed in the 2019 ''Sunday Times'' report on the Best Places to Live in northern England. History Driffield is of Anglo-Saxon origin, and the name is first attested in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' where King Aldfrith of Northumbria died on 14 December 705. It is also found in the Domesday Book of 1086, meaning "dirty (manured) field". A Bronze Age mound outside Driffield was excavated in the 19th century, the contents of which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York To Scarborough Line
York is a cathedral city in North Yorkshire, England, with Roman Britain, Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Foss, Foss. It has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a York Minster, minster, York Castle, castle and York city walls, city walls, all of which are Listed building, Grade I listed. It is the largest settlement and the administrative centre of the wider City of York district. It is located north-east of Leeds, south of Newcastle upon Tyne and north of London. York's built-up area had a recorded population of 141,685 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census. The city was founded under the name of Eboracum in AD 71. It then became the capital of Britannia Inferior, a province of the Roman Empire, and was later the capital of the kingdoms of Deira, Northumbria and Jórvík, Scandinavian York. In the England in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages it became the Province of York, northern England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Lamert Dickens
Alfred Lamert Dickens (March 1822 – 27 July 1860) was an English railway engineer and the younger brother of the Victorian novelist Charles Dickens. Biography As a boy Alfred, nicknamed Enrique by friends, attended a school in Hampstead with his brother Frederick Dickens for two years, until his father John Dickens could no longer afford the fees. At the end of the school day the boys would be collected by their older brother, Charles. On 20 February 1824, John Dickens was imprisoned in the Marshalsea Debtors' Prison for debt under the Insolvent Debtors Act 1813, because he owed a baker, James Kerr, £40 and 10 shillings."Why Dickens had a conscience" BBC News, 3 December 2004. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |