|
Mali Empire
The Mali Empire (Manding languages, Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or ''Manden Duguba''; ) was an empire in West Africa from 1226 to 1610. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita () and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa (Musa Keita). At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of Manding languages, its language, laws, and customs. The empire began as a small Mandinka people, Mandinka kingdom at the upper reaches of the Niger River, centered around the Manding region. It began to develop during the 11th and 12th centuries as the Ghana Empire, or Wagadu, declined and trade epicentres shifted southward. The Pre-imperial Mali, history of the Mali Empire before the 13th century is unclear, as there are conflict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postclassical Era
In world history, post-classical history refers to the period from about 500 CE to 1500 CE, roughly corresponding to the European Middle Ages. The period is characterized by the expansion of civilizations geographically and the development of trade networks between civilizations.The Post‐Classical Era by Joel Hermansen This period is also called the medieval era, post-antiquity era, post-ancient era, pre-modernity era, or pre-modern era. In , the spread of Islam created a series of |
Elective Monarchy
An elective monarchy is a monarchy ruled by a monarch who is elected, in contrast to a hereditary monarchy in which the office is automatically passed down as a family inheritance. The manner of election, the nature of candidate qualifications, and the electors vary from case to case. Historically, it was common for elective monarchies to transform into hereditary ones (whether legally or ''de facto'') by repeated election of the previous rulers' children, or for hereditary monarchies to acquire elective or semi-elective succession laws, particularly following dynastic crises. Evolution Many kingdoms were officially elective historically, though the candidates were typically only from the family of the deceased monarch. Eventually, however, most elected monarchies introduced hereditary succession, guaranteeing that the title and office stayed within the royal family and specifying, more or less precisely, the order of succession. Today, almost all monarchies are hereditary mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keita Dynasty
The Keita dynasty ruled pre-imperial and imperial Mali from the 11th century into the early 17th century. It was a Muslim dynasty, and its rulers claimed descent from Bilal ibn Rabah. The early history is entirely unknown, outside of legends and myths. The first Keita ''mansa'' was Sundiata Keita. This is when Mari Jata is crowned and Keita becomes a clan name. A couple of generations after him, his great-nephew, Mansa Musa Keita I of Mali, made a celebrated pilgrimage to Mecca. The dynasty remained a major power in West Africa from the early 13th century until the breakup of the Mali Empire around 1610. Rivals from within the clan founded smaller kingdoms within contemporary Mali and Guinea. Of the members of these modern "daughter dynasties", the late politician Modibo Keita and the musician Salif Keita are arguably the most famous. Legendary Ancestors According to Muslim tradition, Bilal ibn Rabah was a freed slave, possibly of Abyssinian descent, who accepted Islam and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griot
A griot (; ; Manding languages, Manding: or (in N'Ko script, N'Ko: , or in French spelling); also spelt Djali; or / ; ) is a West African historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet, and/or musician. Griots are masters of communicating stories and history orally, which is an African tradition. Instead of writing history books, List of oral repositories, oral historians tell stories of the past that they have memorized. Sometimes there are families of historians, and the oral histories are passed down from one generation to the next. Telling a story out loud allows the speaker to use poetic and musical conventions that entertain an audience. This has contributed to many oral histories surviving for hundreds of years without being written down. Through their storytelling, griots preserve and pass on the values of a tribe or people, such as the Senegalese, who are Muslims. The Wolof people in Senegal, many of whom cannot read or write, depend on griots to learn abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-imperial Mali
The history of the Mali Empire begins when the first Mande people entered the Manding region during the period of the Ghana Empire. After its fall, the various tribes established independent chiefdoms. In the 12th century, these were briefly conquered by the Sosso Empire under Soumaoro Kante. He was in turn defeated by a Mande coalition led by Sundiata Keita, who founded the Mali Empire. The Keita dynasty ruled the Empire for its entire history, with the exception of the third mansa, Sakura, who was a freed slave who took power from one of Sundiata's sons. Upon his death, the Keita line was re-established, and soon led the empire to the peak of its wealth and renown under Mansa Musa. His pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324 became legendary for the vast sums of gold that he gave as gifts and alms, to the point where it created an inflationary crisis in Egypt. Mansa Musa also extended the empire to its greatest territorial extent, re-annexing the city of Gao in the east. After Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire (), also known as simply Ghana, Ghanata, or Wagadu, was an ancient western-Sahelian empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali. It is uncertain among historians when Ghana's ruling dynasty began. The first identifiable mention of the imperial dynasty in written records was made by Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī in 830. Further information about the empire was provided by the accounts of Cordoban scholar al-Bakri when he wrote about the region in the 11th century. After centuries of prosperity, the empire began its decline in the second millennium, and would finally become a vassal state of the rising Mali Empire at some point in the 13th century. Despite its collapse, the empire's influence can be felt in the establishment of numerous urban centers throughout its former territory. In 1957, the British colony of the Gold Coast, under the leadership of Kwame Nkrumah named itself Ghana upon independence. Etymology The word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
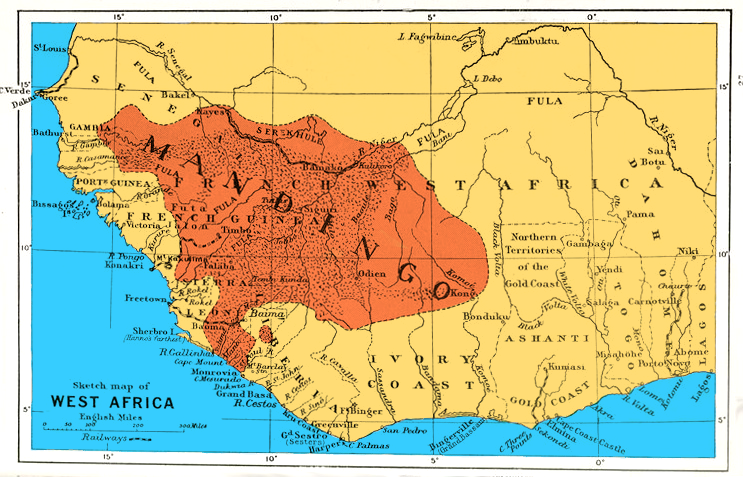
Manding Region
Manding, Manden or even Mandé is a region located in West Africa, a space between southern Mali and eastern Guinea. It is the historic home of the Manding languages, Mandinka community. The Malinke people, Malinke are at the origin of the foundation of the largest empires in West Africa. Among the many groups linked to or originating from Manding, there are the Bambara people, Bambara, the Dyula people, Dyula, the Khassonké people, Khassonke, the Konianké, the Mahou, Koyaka, the Dafing, the Bobo-Dioula and the Kuranko people, Kuranko. Toponymy According to Camara Laye, transcribing the words of griot Babou Condé, the name "Mandén" means "child of the hippopotamus" ("Man" meaning "hippopotamus" or "manatee" and "den" "child"). Geography The climate of Mande is called Sudanese. It is characterized by the alternation of seasons: a rainy season and a dry season. It is the domain of the savannah which is distinguished by shrub vegetation. This region is characterized by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through a massive River delta, delta, known as the Niger Delta, into the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean. The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa, exceeded by the Nile and the Congo River. Its main tributary is the Benue River. Etymology The Niger has different names in the different languages of the region: * Fula language, Fula: ''Maayo Jaaliba'' * Manding languages, Manding: ''Jeliba'' or ''Joliba'' "great river" * Tuareg languages, Tuareg: ''Eġərəw n-Igərǝwăn'' "river of rivers" * Songhay languages, Songhay: ''Isa'' "the river" * Zarma language, Zarma: ''Isa Beeri'' "great river" * Hausa language, Hausa: ''Kwara'' *Nupe language, Nupe: ''Èdù'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the List of ethnic groups of Africa, largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. They are predominantly Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom Overseas Territories, United Kingdom Overseas Territory).Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. The population of West Africa is estimated at around million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 were female and 192,309,000 male.United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2017). World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, custom data acquired via webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) has political control over the peripheries. Within an empire, different populations may have different sets of rights and may be governed differently. The word "empire" derives from the Roman concept of . Narrowly defined, an empire is a sovereign state whose head of state uses the title of "emperor" or Empress-regnant, "empress"; but not all states with aggregate territory under the rule of supreme authorities are called "empires" or are ruled by an emperor; nor have all self-described empires been accepted as such by contemporaries and historians (the Central African Empire of 1976 to 1979, and some Anglo-Saxon kingdoms in early England being examples). There have been "ancient and modern, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansa (title)
''Mansa'' (; ''mansaw'') is a Maninka and Mandinka language, Mandinka word for a hereditary ruler, commonly translated as "king". It is particularly known as the title of the rulers of the Mali Empire, such as Mansa Musa, and in this context is sometimes translated as "emperor". It is also a title held by traditional village rulers, and in this context is translated as "chief". ''Mansa'' contrasts with another Manding word for ruler, ''faama''. ''Faama'' emphasizes the military, coercive authority of a ruler, and can be translated as "tyrant", whereas ''mansa'' refers to a hereditary ruler whose authority is derived from tradition and mystical power. A ruler can be both a ''faama'' and a ''mansa'', but a ''mansa'' was not necessarily a ''faama''. The word ''mansa'' () was recorded in Arabic during the 14th century by North African writers such as Ibn Battuta and Ibn Khaldun, who explained it as meaning "sultan". Cognates of ''mansa'' exist in other Mandé languages, such as S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |