|
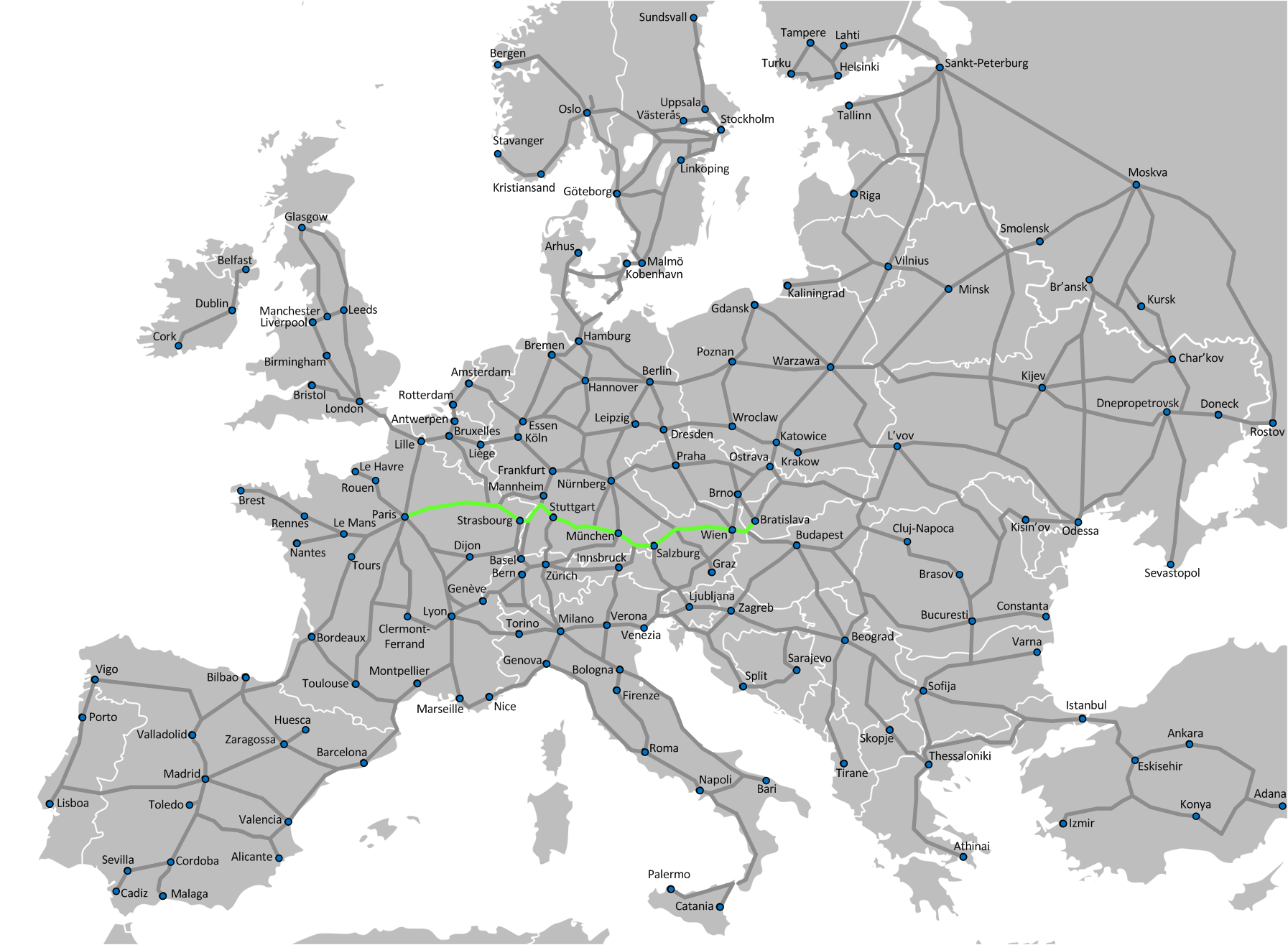
Main Line For Europe
The Magistrale for Europe (German: ''Magistrale für Europa''; French: ''Magistrale européenne'') or Main Line for Europe is a Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T) project for the creation of a high-speed railway line between Paris and Bratislava, with a branch-off to Budapest. It was listed as TEN project No. 17 (Paris—Bratislava) by the European Commission in 1995, and is already under way. The project was planned to be completed by 2020, however the entire project has not been delivered on time, with only some of the sections running. It will link 34 million people in five European countries. The overall length of the route from Paris to Budapest is . Sections Parts of the route were formerly served by Orient Express trains, which ceased operations in 2009. Today TGV rail connections exist from Paris to Stuttgart or at longest Munich. The Austrian Federal Railways (ÖBB) currently provide direct Railjet and EuroNight connections between Munich and Budapest in addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGV Est Européenne
The Ligne à Grande Vitesse Est européenne (East European High Speed Line), typically shortened to LGV Est, is a French high-speed rail line that connects Vaires-sur-Marne (near Paris) and Vendenheim (near Strasbourg). The line halved the travel time between Paris and Strasbourg and provides fast services between Paris and the principal cities of Eastern France as well as Luxembourg and Germany. The LGV Est is a segment of the Main Line for Europe project to connect Paris with Budapest with high-speed rail service. The line was built in two phases. Construction on the from Vaires-sur-Marne to Baudrecourt (near Metz and Nancy) began in 2004; the first phase entered into service in June 2007. Construction on the second phase from Baudrecourt to Vendenheim began in June 2010; the second phase opened to commercial service on 3 July 2016. Opening of the second phase was delayed after a train derailed near Eckwersheim on 14 November 2015 during commissioning trials, resulting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannheim–Stuttgart High-speed Railway
The Mannheim–Stuttgart high-speed railway is a long railway line in Germany, connecting the cities of Mannheim and Stuttgart. The line was officially opened on 9 May 1991, and Intercity-Express service began on 2 June. The Hanover–Würzburg high-speed railway also opened at the same time. The line cost about DM 4.5 billion to build and has 15 tunnels and more than 90 bridges. Planning Planning for a new line between Mannheim and Stuttgart (the two largest cities of Baden-Württemberg) began in 1970. The railway lines that it replaced followed the terrain and followed rivers and valleys, resulting in steep gradients and sharp curves and thus not suitable for high-speed trains. The 1973 federal transport plan incorporated the following minimum requirements for mixed traffic to accommodate heavy, slow goods trains and light fast passenger trains: *maximum grade of 1.25% (occasionally 2.0%) *curves with small superelevation and minimum radii of *maximum line speed of *av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rastatt
Rastatt () is a town with a Baroque core, District of Rastatt, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located in the Upper Rhine Plain on the Murg river, above its junction with the Rhine and has a population of around 51,000 (2022). Rastatt was an important place of the War of the Spanish Succession ( Treaty of Rastatt) and the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states. History Until the end of the 17th century, Rastatt held little influence, but after its destruction by the French in 1689, it was rebuilt on a larger scale by Louis William, Margrave of Baden, the Imperial General in the Great Turkish War known popularly as ''Türkenlouis''. It then remained the residence of the Margraves of Baden-Baden until 1771. It was the location of the First and Second Congress of Rastatt, the former giving rise to the Treaty of Rastatt while the second ended in failure in 1799. In the 1840s, Rastatt was surrounded by fortifications to form the Fortress of Rastatt. For about 20 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruchsal Rollenberg Junction
Bruchsal (; South Franconian: ''Brusl'') is a city at the western edge of the Kraichgau, approximately 20 km northeast of Karlsruhe in the state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is located on Bertha Benz Memorial Route. Bruchsal is the largest city in the district of Karlsruhe and is known for being Europe's largest asparagus producer and one of the economic centers of the region of Karlsruhe. The Bruchsal area also includes the cities and towns of Bad Schönborn, Forst, Hambrücken, Karlsdorf-Neuthard, Kraichtal, Kronau, Oberhausen-Rheinhausen, Östringen, Philippsburg, Ubstadt-Weiher and Waghäusel. Until 1972 Bruchsal was the seat of the district of Bruchsal, which was merged into the district of Karlsruhe as a result of the district reform, effective January 1, 1973. Bruchsal's population passed the 20,000 mark around 1955. When the new Body of Municipal Law for Baden-Württemberg went into effect on April 1, 1956, the city was therefore immediately awarded Große ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannheim–Karlsruhe–Basel Railway
The Mannheim–Karlsruhe–Basel railway is a double-track electrified mainline railway in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It runs from Mannheim via Heidelberg, Bruchsal, Karlsruhe, Rastatt, Baden-Baden, Offenburg and Freiburg to Basel, Switzerland. It is also known as the Rhine Valley Railway () or the Upper Rhine Railway (''Oberrheinbahn''). The line was built as part of the Baden Mainline (''Badische Hauptbahn''). Between Mannheim and Rastatt it runs parallel to the Baden Rhine Railway (''Rheinbahn''). The Karlsruhe–Basel high-speed railway, called the ''Ausbau- und Neubaustrecke Karlsruhe–Basel'' in German (literally: "Upgraded and new line Karlsruhe–Basel"), has been under construction since April 1987. This includes upgrading the current line to four-tracks in places and the construction of new line elsewhere. It was originally envisaged as being completed in 2008. The new construction work will be completed by 2035. The existing Rhine Valley Railway will the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appenweier
Appenweier () is a Municipalities of Germany, municipality in western Baden-Württemberg, Germany in the district of Ortenau. Geography Appenweier consists of the main municipal Appenweier (4,075 inhabitants), Urloffen (4,301 inhabitants), known for horseradish-growing, and Nesselried (1,383 inhabitants). The Nesselried district runs through the Wannenbach valley, while Urloffen lies north of Appenweier. References External links Appenweier Web Page (in German)Appenweier history, places of interest, destination (in German) Ortenaukreis {{Ortenaukreis-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine Bridge, Kehl
The first railway bridge at Kehl across the Rhine was opened in May 1861. Since then the bridge has been partially or fully destroyed more than once. The Kehl railway bridge constructed in 1956, was a single track railway bridge between Strasbourg and Kehl, crossing in the process both the Rhine and the frontier between Germany and France. A replacement double track railway bridge was first used on 10 October 2010 and formally opened in December 2010 in order to permit trains to cross the river more rapidly. The speed limit on the new bridge is 160 km/h (100 mph). The 1861 bridge Under the terms of an international convention dated 2 July 1857 between Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden and the Second French Empire, French government it was agreed that a railway bridge should be constructed across the Rhine between Kehl and Strasbourg. This would be the first permanent bridge across the Upper Rhine. The structure would comprise a twin track bridge long, with a central trus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appenweier–Strasbourg Railway
The Appenweier–Strasbourg railway is a major railway line linking the French TGV station at Strasbourg with the German Rhine Valley Railway (''Rheintalbahn'') and the Karlsruhe–Basel high-speed railway (between Offenburg and Baden-Baden stations). It is almost entirely double-tracked and fully electrified. The section between Kehl and Appenweier is undergoing modernisation with the goal of a maximum speed of 200 km/h. The French section is owned by SNCF; the German section is owned by Deutsche Bahn (, ; abbreviated as DB or DB AG ) is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). DB was fou .... References External links Railway lines in Baden-Württemberg Railway lines in Grand Est Cross-border railway lines in France Buildings and structures in Ortenaukreis Cross-border railway lines in Germany France– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gare De Strasbourg
Strasbourg-Ville station ( French: ''Gare de Strasbourg-Ville'') is the main railway station in the city of Strasbourg, Bas-Rhin, France. It is the eastern terminus of the Paris-Est–Strasbourg-Ville railway. The current core building, an example of historicist architecture of the Wilhelminian period, replaced a previous station inaugurated in 1852, later turned into a covered market and ultimately demolished. With nearly 24 million passengers in 2023, Strasbourg-Ville is one of the busiest railway stations in France outside of the Île-de-France. Previous history Strasbourg's first railway station was inaugurated on 19 September 1841 with the opening of the Strasbourg–Basel railway. It was situated far from the city center, in the district of Koenigshoffen. On 11 July 1846, it was moved to the city center; a new building was designed (as a terminus station) by the French architect Jean-André Weyer (1805–??) and inaugurated on 18 July 1852 by Président Bonapart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gare De Paris-Est
The Gare de l'Est (; English: "Station of the East" or "East station"), officially Paris Est, is one of the seven large mainline railway station termini in Paris, France. It is located in the 10th arrondissement, not far southeast from the Gare du Nord, facing the Boulevard de Strasbourg, part of the north–south axis of Paris created by Georges-Eugène Haussmann. Opened in 1849, it is currently the fifth-busiest of the six main railway stations in Paris before the Gare d'Austerlitz. The Gare de l'Est is the western terminus of the Paris–Strasbourg railway and Paris–Mulhouse railway which then proceeds to Basel, Switzerland. History The Gare de l'Est was opened in 1849 by the Compagnie du Chemin de Fer de Paris à Strasbourg (Paris–Strasbourg Railway Company) under the name "Strasbourg platform" (''Embarcadère de Strasbourg''); an official inauguration with President Louis Napoléon Bonaparte took place the next year. The platform corresponds today with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departments of France, department and the Seat of the European Parliament in Strasbourg, official seat of the European Parliament. The city has about three hundred thousand inhabitants, and together Eurométropole de Strasbourg, Greater Strasbourg and the arrondissement of Strasbourg have over five hundred thousand. Strasbourg's functional area (France), metropolitan area had a population of 860,744 in 2020, making it the eighth-largest metro area in France and home to 14% of the Grand Est region's inhabitants. The transnational Eurodistrict Strasbourg-Ortenau Eurodistrict, Strasbourg-Ortenau had a population of roughly 1,000,000 in 2022. Strasbourg is one of the ''de facto'' four main capitals of the European Union (alongside Brussels, Luxembourg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |