|
Magnetic Pulsations
Magnetic pulsations are extremely low frequency disturbances in the Earth's magnetosphere driven by its interactions with the solar wind. These variations in the planet's magnetic field can oscillate for multiple hours when a solar wind driving force strikes a resonance. This is a form of Kelvin–Helmholtz instability. The intensity, frequency, and orientation of these variations is measured by Intermagnet. In 1964, the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy The International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA) is an international scientific association that focuses on the study of terrestrial and planetary magnetism and space physics. IAGA is one of the eight associations of the Interna ... (IAGA) proposed a classification of magnetic pulsations into continuous pulsations (Pc) and irregular pulsations (Pi). References Magnetospheres Magnetism in astronomy Earth Solar phenomena {{Astronomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extremely Low Frequency
Extremely low frequency (ELF) is the ITU designation for electromagnetic radiation (radio waves) with frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz, and corresponding wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 kilometers, respectively. In atmospheric science, an alternative definition is usually given, from 3 Hz to 3 kHz.Liemohn, Michael W. and A. A. CHAN,Unraveling the Causes of Radiation Belt Enhancements. . EOS, TRANSACTIONS, AMERICAN GEOPHYSICAL UNION, Volume 88, Number 42, 16 October 2007, pages 427–440. Republished by NASA and accessed online, 8 February 2010. Adobe File, page 2. In the related magnetosphere science, the lower-frequency electromagnetic oscillations (pulsations occurring below ~3 Hz) are considered to lie in the ULF range, which is thus also defined differently from the ITU radio bands. ELF radio waves are generated by lightning and natural disturbances in Earth's magnetic field, so they are a subject of research by atmospheric scientist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo theory, dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body with a dipole magnetic field such as Earth, the field lines resemble a simple magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma (physics), plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation. Interactions of particles and atmospheres with magnetospheres are studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics, and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert (astronomer), W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
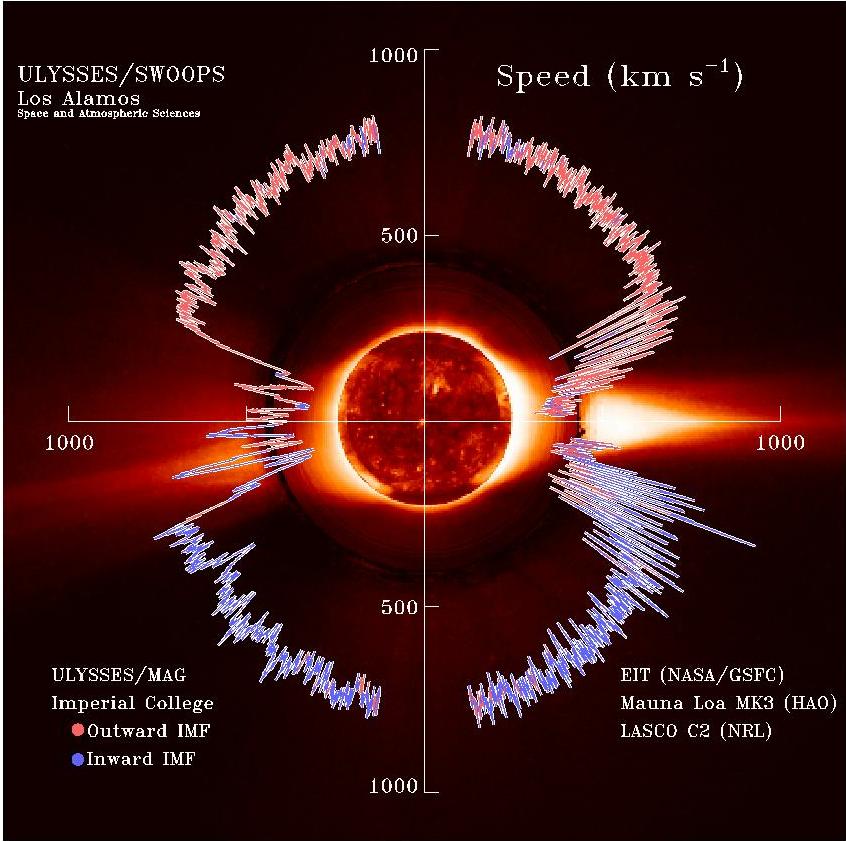
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of Chemical element, elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over Solar coordinate systems#Heliographic, solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin–Helmholtz Instability
The Kelvin–Helmholtz instability (after Lord Kelvin and Hermann von Helmholtz) is a fluid instability that occurs when there is shear velocity, velocity shear in a single continuum mechanics, continuous fluid or a velocity difference across the interface between two fluids. Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities are visible in the atmospheres of planets and moons, such as in List of cloud types, cloud formations on Earth or the Great Red Spot#Great Red Spot, Red Spot on Jupiter, and the Stellar atmosphere, atmospheres of the Sun and other stars. Theory overview and mathematical concepts Fluid dynamics predicts the onset of instability and transition to turbulent flow within fluids of different density, densities moving at different speeds. If surface tension is ignored, two fluids in parallel motion with different velocities and densities yield an interface that is unstable to short-wavelength perturbations for all speeds. However, surface tension is able to stabilize the short w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermagnet
The International Real-time Magnetic Observatory Network (INTERMAGNET) is a world-wide consortium of institutes operating ground-based magnetometers recording the absolute level of the Earth's time-varying magnetic field, to an agreed set of standards. INTERMAGNET has its roots in discussions held at the Workshop on Magnetic Observatory Instruments in Ottawa, Canada, in August 1986 and at the Nordic Comparison Meeting in Chambon La Foret, France, in May 1987. A pilot scheme between USGS and BGS was described in the sessions of Division V of the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy at the 19th General Assembly of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics in Vancouver, Canada, in August 1987. This scheme used the GOES East satellite to successfully transfer geomagnetic data between the two organisations. INTERMAGNET was founded soon after in order to extend the network of observatories communicating in this way. 62 different institutes are now members of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Association Of Geomagnetism And Aeronomy
The International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA) is an international scientific association that focuses on the study of terrestrial and planetary magnetism and space physics. IAGA is one of the eight associations of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics. It is a non-governmental body funded through the subscriptions paid to IUGG by its member countries. IAGA have been responsible for developing and maintaining the International Geomagnetic Reference Field, a reference for the magnetic field of the Earth that was adopted in 1968 and is updated every five years. The most recent version is IGRF-12. History IAGA has a long history and can trace its origins to the Commission for Terrestrial Magnetism and Atmospheric Electricity, part of the World Meteorological Organization originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), which was founded in 1873. At the First IUGG General Assembly (Rome, 1922), the Section de Magnétisme et Elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetospheres
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynamo. In the space environment close to a planetary body with a dipole magnetic field such as Earth, the field lines resemble a simple magnetic dipole. Farther out, field lines can be significantly distorted by the flow of electrically conducting plasma, as emitted from the Sun (i.e., the solar wind) or a nearby star. Planets having active magnetospheres, like the Earth, are capable of mitigating or blocking the effects of solar radiation or cosmic radiation. Interactions of particles and atmospheres with magnetospheres are studied under the specialized scientific subjects of plasma physics, space physics, and aeronomy. History Study of Earth's magnetosphere began in 1600, when William Gilbert discovered that the magnetic field on the surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetism In Astronomy
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, magnetism is one of two aspects of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys. All substances exhibit some type of magnetism. Magnetic materials are classified according to their bulk susceptibility. Ferromagnetism is responsible for most of the effects of magnetism encountered in everyday life, but there are actually several types of magnetism. Paramagnetic substances, such as aluminium and oxygen, are weakly attracted to an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |