|
Magnetic Anomaly
In geophysics, a magnetic anomaly is a local variation in the Earth's magnetic field resulting from variations in the chemistry or magnetism of the rocks. Mapping of variation over an area is valuable in detecting structures obscured by overlying material. The magnetic variation (geomagnetic reversals) in successive bands of ocean floor parallel with mid-ocean ridges was important evidence for seafloor spreading, a concept central to the theory of plate tectonics. Measurement Magnetic anomalies are generally a small fraction of the magnetic field. The total field ranges from 25,000 to 65,000 nanoteslas (nT). To measure anomalies, magnetometers need a sensitivity of 10 nT or less. There are three main types of magnetometer used to measure magnetic anomalies: # The fluxgate magnetometer was developed during World War II to detect submarines. It measures the component along a particular axis of the sensor, so it needs to be oriented. On land, it is often oriented vertically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangui Anomaly
The Bangui magnetic anomaly is a local variation in the Earth's magnetic field centered at Bangui, the capital of the Central African Republic. The magnetic anomaly is roughly ellipse, elliptical, about , and covers most of the country, making it one of the "largest and most intense crustal magnetic anomalies on the African continent". The anomaly was discovered in the late 1950s, explored in the 1970s, and named in 1982. Its origin remains unclear. History In 1962, Raymond Godivier and Lucien Le Donche reported on a magnetic anomaly in the Central African Republic, which they identified by analyzing their surface magnetic activity data of 1956. These results were confirmed and built upon by the high-altitude aeromagnetic surveys carried out by the Naval Oceanographic Office, US Naval Oceanographic Office, as well as by the satellite measurements conducted in 1964 with Cosmos 49 and in the 1970s with the Orbiting Geophysical Observatory at altitudes. This data was combined in 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magsat
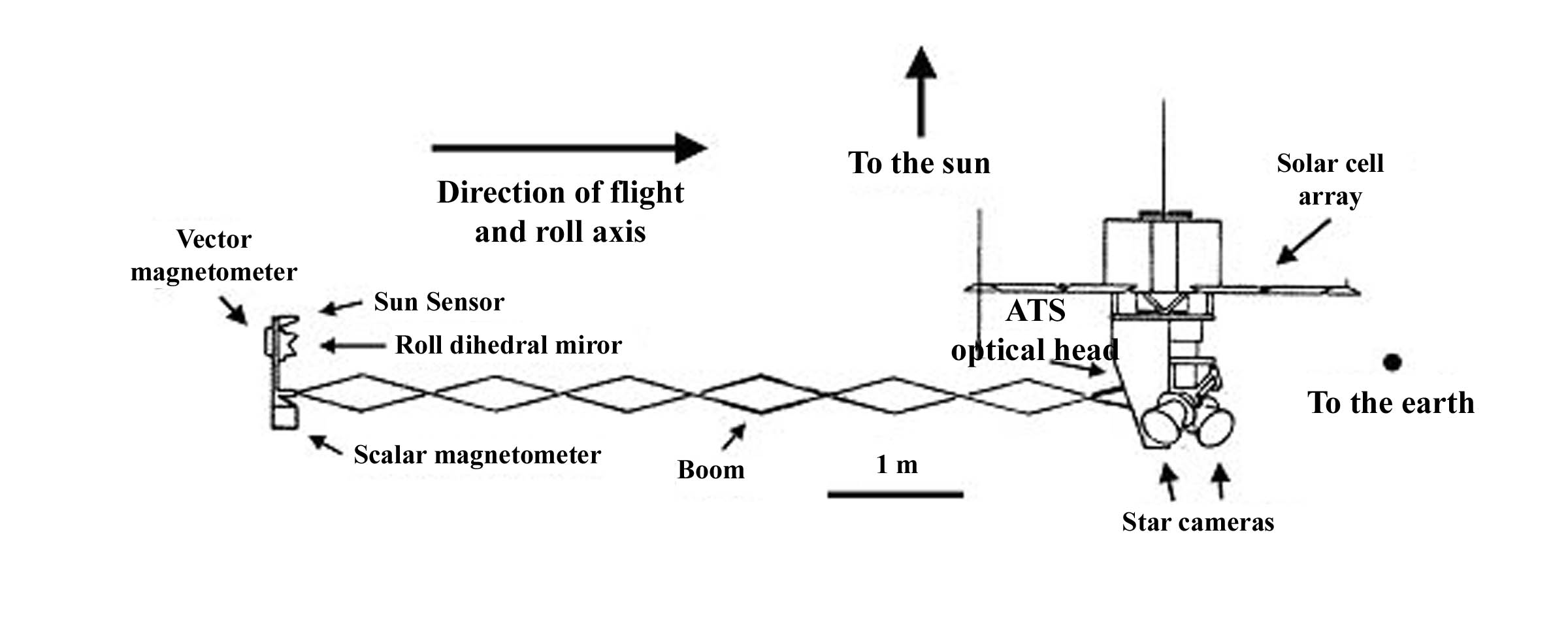
Magsat (Magnetic field Satellite, Applications Explorer Mission-C or AEM-C or Explorer 61) was a NASA / United States Geological Survey, USGS (United States Geological Survey) spacecraft, launched on 30 October 1979. The mission was to map the Earth's magnetic field, the satellite had two magnetometers. The scalar (Caesium, Cesium vapor) and vector magnetometers gave Magsat a capability beyond that of any previous spacecraft. Extended by a telescoping boom, the magnetometers were distanced from the magnetic field created by the satellite and its electronics. The satellite carried two magnetometers, a three-axis fluxgate magnetometer for determining the strength and direction of magnetic fields, and an ion-vapor/vector magnetometer for determining the magnetic field caused by the vector magnetometer itself. Magsat is considered to be one of the more important Science/Earth-orbiting satellites launched; the data it accumulated is still being used, particularly in linking new satell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstones
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains, cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar, because they are the most resistant minerals to the weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be imparted any color by impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Because sandstone beds can form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have become strongly identified with certain regions, such as the red rock deserts of Arches National Park and other areas of the American Southwest. Rock formations composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestones
Limestone is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limestone co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Anomaly
The gravity anomaly at a location on the Earth's surface is the difference between the observed value of gravity and the value predicted by a theoretical model. If the Earth were an ideal oblate spheroid of uniform density, then the gravity measured at every point on its surface would be given precisely by a simple algebraic expression. However, the Earth has a rugged surface and non-uniform composition, which distorts its gravitational field. The theoretical value of gravity can be corrected for altitude and the effects of nearby terrain, but it usually still differs slightly from the measured value. This gravity anomaly can reveal the presence of subsurface structures of unusual density. For example, a mass of dense ore below the surface will give a positive anomaly due to the increased gravitational attraction of the ore. Different theoretical models will predict different values of gravity, and so a gravity anomaly is always specified with reference to a particular model. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geomagnetic Reference Field
The International Geomagnetic Reference Field (IGRF) is a standard mathematical description of the large-scale structure of the Earth's main magnetic field and its secular variation. It was created by fitting parameters of a mathematical model of the magnetic field to measured magnetic field data from surveys, observatories and satellites across the globe. The IGRF has been produced and updated under the direction of the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA) since 1965. The IGRF model covers a significant time span, and so is useful for interpreting historical data. (This is unlike the World Magnetic Model, which is intended for navigation in the next few years.) It is updated at 5-year intervals, reflecting the most accurate measurements available at that time. The current 13th edition of the IGRF model (IGRF-13) was released in December 2019 and is valid from 1900 until 2025. For the interval from 1945 to 2015, it is "definitive" (a "DGRF"), meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient plasma and magnetic field structures that originate on or near the Sun. The structures that produce geomagnetic storms include interplanetary coronal mass ejections (CME) and corotating interaction regions (CIR). The former often originate from solar active regions, while the latter originate at the boundary between high- and low-speed streams of solar wind. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. During solar maxima, geomagnetic storms occur more often, with the majority driven by CMEs. When these structures reach Earth, the increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth's magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both intera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. Travel through this layer also impacts GPS signals, resulting in effects such as deflection in their path and delay in the arrival of the signal. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Wind
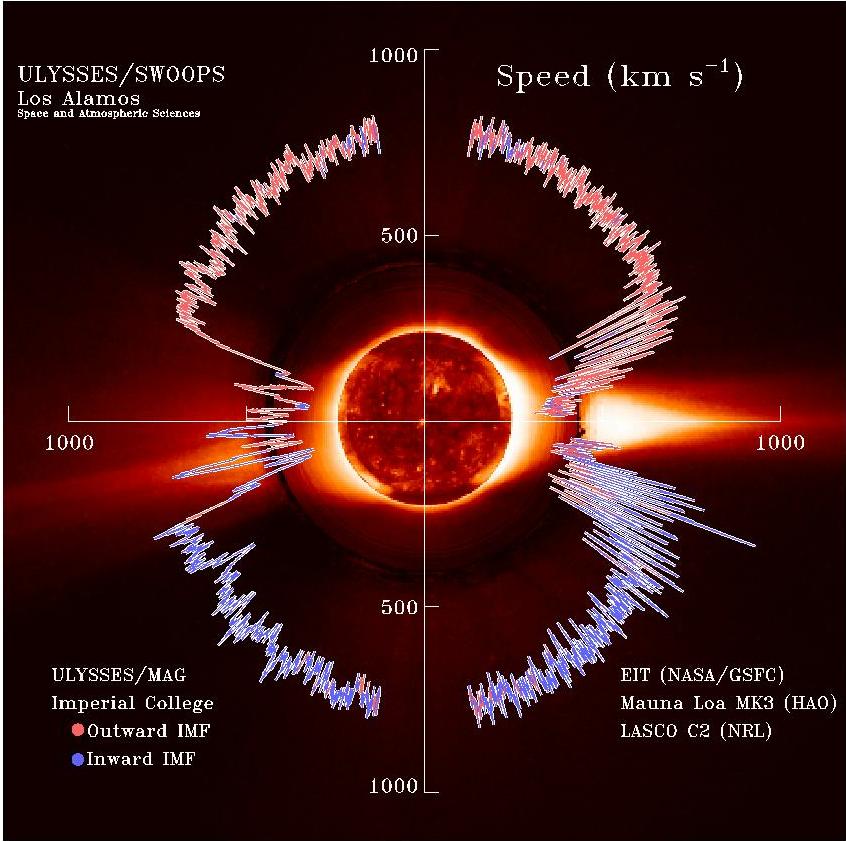
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of Chemical element, elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over Solar coordinate systems#Heliographic, solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 in the context of European integration. Its 2025 annual budget was ÔéČ7.7 billion. The ESA Human and Robotic Exploration programme includes human spaceflight (mainly through participation in the International Space Station programme); as well as the launch and operation of missions to Mars and Moon. Further activities include science missions to Jupiter, Mercury, the Sun, Earth observation, Asteroid impact avoidance and Telecommunications missions, designing launch vehicles; and maintaining Europe's Spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou (French Guiana). Further programmes include space safety, satellite navigation, applications and commercialisation. The main European launch vehicle Ariane 6 is operated through Arianespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swarm (spacecraft)
Swarm is a European Space Agency (ESA) mission to study the Earth's magnetic field. High-precision and high-resolution measurements of the strength, direction and variations of the Earth's magnetic field, complemented by precise navigation, accelerometer and electric field measurements, will provide data for modelling the geomagnetic field and its interaction with other physical aspects of the Earth system. The results offer a view of the inside of the Earth from space, enabling the composition and processes of the interior to be studied in detail and increase our knowledge of atmospheric processes and ocean circulation patterns that affect climate and weather. Overview The overall objective of the Swarm mission is to build on the experience from the ├śrsted and CHAMP missions and to provide the best ever survey of the geomagnetic field (multi-point measurements) and its temporal evolution, to gain new insights into the Earth system by improving our understanding of the Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
├śrsted (satellite)
├śrsted is an Earth science satellite launched in 1999 to study the Earth's geomagnetic field. It is Denmark's first satellite, named after Hans Christian ├śrsted (1777ÔÇô1851), a Danish physicist and professor at the University of Copenhagen, who discovered electromagnetism in 1820. Objectives The spacecraft's primary science objectives are to perform highly accurate and sensitive measurements of the geomagnetic field and to perform global monitoring of the high energy charged particle environment. Instruments The instrumentation consisted of two magnetometers ( proton precession and fluxgate), a star imager for attitude determination, a solid-state charged particle detector package, and a GPS receiver. The Science Instrument Team is responsible for the design of the instruments, while the Science Team is responsible for the science mission planning and international science participation. The science data obtained during the planned one-year mission will be used to derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |