|
Magnapinna Sp. B
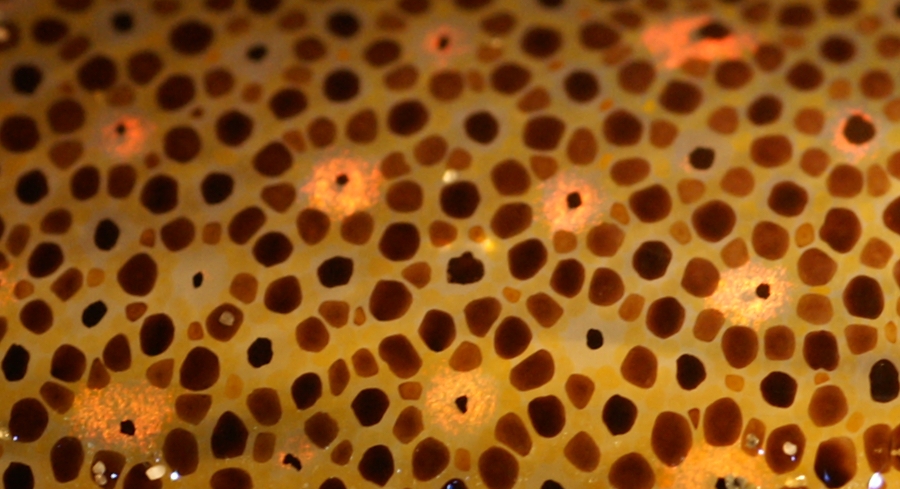
''Magnapinna'' sp. B is an undescribed species of bigfin squid known only from a single immature specimen collected in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Description It is characterised by its dark epidermal pigmentation, which is epithelial, as opposed to the chromatophoral pigmentation found in other ''Magnapinna'' species. Discovery The only known specimen of ''Magnapinna'' sp. B is a juvenile male of mantle length (ML) held in the Bergen Museum The University Museum of Bergen () is a university museum in Bergen, Norway. The museum features material related to anthropology, archaeology, botany, geology, zoology, art, and cultural history. History The University Museum of Bergen was fo .... It was caught by the R/V G.O. SARS (MAR-ECO cruise super station 46, local station 374) on July 11, 2004, at . References *Vecchione, M. & Young, R. E. (2006)"The squid family Magnapinnidae (Mollusca; Cephalopoda) in the North Atlantic with a description of ''Magnapinna atlantica'', n. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undescribed Species
In taxonomy, an undescribed taxon is a taxon (for example, a species) that has been discovered, but not yet formally described and named. The various Nomenclature Codes specify the requirements for a new taxon to be validly described and named. Until such a description has been published, the taxon has no formal or official name, although a temporary, informal name is often used. A published scientific name may not fulfil the requirements of the Codes for various reasons. For example, if the taxon was not adequately described, its name is called a ''nomen nudum''. It is possible for a taxon to be "undescribed" for an extensive period of time, even if unofficial descriptions are published. An undescribed species may be referred to with the genus name, followed by "sp.", but this abbreviation is also used to label specimens or images that are too incomplete to be identified at the species level. In some cases, there is more than one undescribed species in a genus. In this case, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigfin Squid
Bigfin squids are a group of rarely seen cephalopods with a distinctive Morphology (biology), morphology. They are placed in the genus ''Magnapinna'' and family (biology), family Magnapinnidae. Although the family was described only from larval, paralarval, and juvenile specimens, numerous video observations of much larger squid with similar morphology are assumed to be adult specimens of the same family. The arms and tentacles of the squid are both extremely long, estimated at . These appendages are held perpendicular to the body, creating "elbows". How the squid feeds is yet to be discovered. ''Magnapinna'' is thought to be the deepest-occurring squid genus, with sightings as deep as below the surface, making it the only squid known to inhabit the hadal zone. Taxonomy ''Magnapinna'' is the sister group to ''Joubiniteuthis portieri, Joubiniteuthis'', another little-known deep-sea squid with an unusual body plan and long arms. Both ''Magnapinna'' and ''Joubiniteuthis'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse colonization of North America, Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an Age of Discovery, age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopod A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...s. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for animal coloration, coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye color, eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescence, iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle (also known by the Latin language, Latin word pallium meaning mantle, robe or cloak, adjective pallial) is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsum (biology), dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself. In many species of molluscs the Epidermis (skin), epidermis of the mantle secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin, and creates a mollusc shell, shell. In sea slugs there is a progressive loss of the shell and the mantle becomes the dorsal surface of the animal. The words mantle and pallium both originally meant ‘cloak’ or ‘cape’; see mantle (vesture). This anatomical structure in molluscs often resembles a cloak because in many groups the edges of the mantle, usually referred to as the ''mantle margin'', extend far beyond the main part of the body, forming flaps, double-layered structures which have been adapted for many different uses, including for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergen Museum
The University Museum of Bergen () is a university museum in Bergen, Norway. The museum features material related to anthropology, archaeology, botany, geology, zoology, art, and cultural history. History The University Museum of Bergen was founded in 1825 by Wilhelm Frimann Koren Christie, at the time president of the Storting. Founded under the name University Museum of Bergen with the intent of building large collections in the fields of culture and natural history, it became the grounds for most of the academic activity in the city, a tradition which has prevailed since the museum became part of the University of Bergen. The University Museum of Bergen is divided into two departments, the Natural History Collections and the Cultural History Collections and Public Outreach and exhibitions. It is also the caretaker of the museum garden, formerly the botanical garden, surrounding the natural history building, and the city's arboretum. This was the first dedicated museum build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigfin Squid
Bigfin squids are a group of rarely seen cephalopods with a distinctive Morphology (biology), morphology. They are placed in the genus ''Magnapinna'' and family (biology), family Magnapinnidae. Although the family was described only from larval, paralarval, and juvenile specimens, numerous video observations of much larger squid with similar morphology are assumed to be adult specimens of the same family. The arms and tentacles of the squid are both extremely long, estimated at . These appendages are held perpendicular to the body, creating "elbows". How the squid feeds is yet to be discovered. ''Magnapinna'' is thought to be the deepest-occurring squid genus, with sightings as deep as below the surface, making it the only squid known to inhabit the hadal zone. Taxonomy ''Magnapinna'' is the sister group to ''Joubiniteuthis portieri, Joubiniteuthis'', another little-known deep-sea squid with an unusual body plan and long arms. Both ''Magnapinna'' and ''Joubiniteuthis'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |