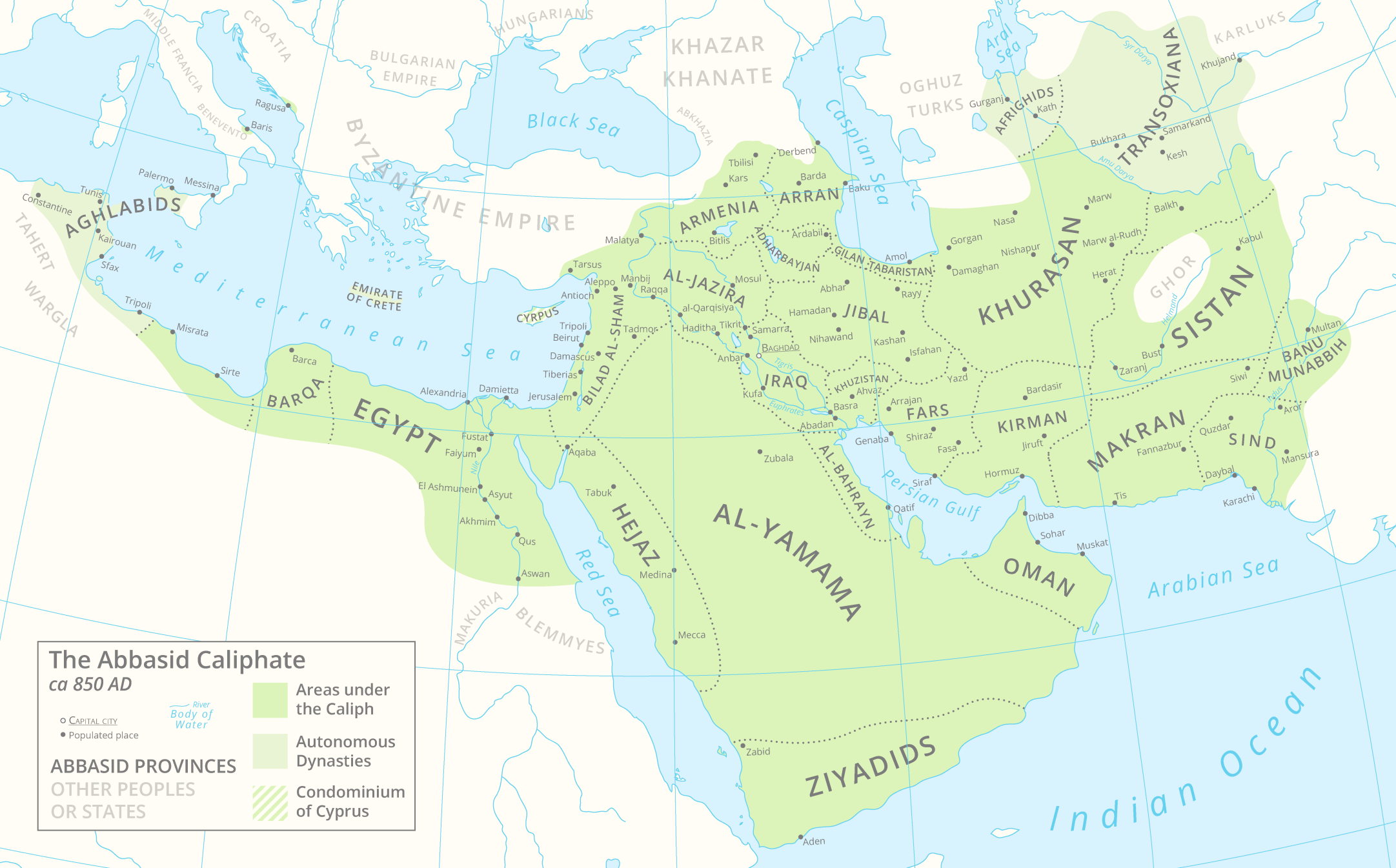
|
Maghariba (Abbasid Troops)
The Maghariba () were a regiment in the regular army of the Abbasid Caliphate. The unit was formed in the early ninth century A.D. and consisted of soldiers who were of Maghrebi origin. During their history, the Maghariba participated in several military campaigns and played a significant role in the politics of the central government. Characteristics The origin and composition of the Maghariba have been subject to debate. Historians have variously described the Maghariba as Berbers from North Africa, black slaves from East Africa, and Arab tribesmen from Egypt, with the last being the most widely accepted theory. According to the Muslim historian al-Mas'udi, the regiment was created by Caliph al-Mu'tasim (r. 833–842), who recruited troops from the Hawf districts of Egypt; this likely occurred before al-Mu'tasim's caliphate, when he and al-Afshin were serving in Egypt on behalf of the caliph al-Ma'mun (r. 813–833). After the succession of al-Mu'tasim to the caliphate in 833, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maghrebis
Maghrebis or Maghrebians () are the inhabitants of the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is a modern Arabic term meaning "Westerners", denoting their location in the western part of the Arab world. Maghrebis are predominantly of Arab and Berber origins. Name Maghrebis were known in ancient and medieval times as the Roman Africans or Moors. The word ''Moor'' is of Phoenician origin. The etymology of the word can be traced back to the Phoenician term , meaning "Westerners", from which the ancient Greeks derive , and from which Latin derives . The Arabic term ''maghrib'' () was given by the first Muslim Arab settlers to the recently conquered region located west of the Umayyad capital of Damascus in the 7th century AD. It initially referred to the area extending from Alexandria in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west. Religion Historic records of religion in the Maghreb region show its gradual inclusion in the Classical World, with coastal colonies established first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Samarra
Samarra is a city in central Iraq, which served as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate from 836 to 892. Founded by the caliph al-Mu'tasim, Samarra was briefly a major metropolis that stretched dozens of kilometers along the east bank of the Tigris, but was largely abandoned in the latter half of the 9th century, especially following the return of the caliphs to Baghdad. Due to the relatively short period of occupation, extensive ruins of Abbasid Samarra have survived into modern times. The layout of the city can still be seen via aerial photography, revealing a vast network of Urban planning, planned streets, houses, palaces and mosques. Studies comparing the archeological evidence with information provided by List of Muslim historians, Muslim historians have resulted in the identification of many of the toponyms within the former city. The archeological site of Samarra was named by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site in 2007, calling it "the best-preserved plan of an ancient large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishaq Ibn Isma'il
Ishaq b. Isma'il b. Shuab al-Tiflisi (before 833 – 853), also known as Sahak in Georgian sources, was the emir of Tbilisi between 833 and 853. He was married to a daughter of king of Sarir and followed his uncle Ali on the throne. Rule Under his rule, the emirate reached the apex of its power. He forced Georgian princes to pay tribute from Kakheti to Abkhazia. He tried to become independent from the Abbasid caliphate, stopped reversing the tribute, and allied himself with local nobility such as Samuel of Kakheti and Guaram Mampali. In retribution, the caliph Al-Mutawakkil sent an expedition against him led by Bugha al-Kabir (also known in Georgia as ''Bugha the Turk''), assisted by the Georgian noble Bagrationi family. In 853, they burnt and sacked Tbilisi, and killed the emir. He was replaced by Muhammad ibn Khalid al-Shaybani. References Sources * Suny, Ronald Grigor (1994), ''The Making of the Georgian Nation: 2nd edition'', p. 30. Indiana University Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Saudi Arabia. It is one of the oldest and most important places in Islamic history. The Holiest sites in Islam, second holiest city in Islam, the population as of 2022 is 1,411,599, making it the List of cities and towns in Saudi Arabia, fourth-most populous city in the country. Around 58.5% of the population are Saudi citizens and 41.5% are foreigners. Located at the core of the Medina Province in the western reaches of the country, the city is distributed over , of which constitutes the city's urban area, while the rest is occupied by the Hijaz Mountains, Hejaz Mountains, empty valleys, Agriculture in Saudi Arabia, agricultural spaces and older dormant volcanoes. Medina is generally considered to be the "cradle of Islamic culture and ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Sulaym
The Banu Sulaym () is an Arab tribe that dominated part of the Hejaz in the pre-Islamic era. They maintained close ties with the Quraysh of Mecca and the inhabitants of Medina, and fought in a number of battles against the Islamic prophet Muhammad before ultimately converting to Islam before his death in 632. They took part in the Muslim conquest of Syria, and established themselves in the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia), while part of the tribe remained in the Hejaz. During the early Muslim period, the tribe produced notable generals such as Safwan ibn Mu'attal, Abu'l-A'war and Umayr ibn al-Hubab. Those who remained in Arabia were largely absorbed by the Banu Harb of Yemen beginning in the 9th century, while those in Syria and the Jazira were expelled to Upper Egypt by the Fatimid Caliphs in the late 10th century for supporting the Qarmatians. In the mid-11th century, a prolonged famine in Egypt prompted the tribe to migrate westward with the Banu Hilal into Libya. There, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugha Al-Kabir
Bugha al-Kabir (), also known as Bugha al-Turki (), was a 9th-century Khazar general who served the Abbasid Caliphate. Biography He was of Khazar origin, and was acquired along with his sons as a military slave ('' ghulam'') by al-Mu'tasim in 819/820.Gordon (2001), p. 19 He is first mentioned in 825, and then again in 835, when he led reinforcements in the fight against the Khurramite rebels of Babak Khorramdin. Bugha also participated in Mu'tasim's Amorium campaign in 838, where he led the rearguard, and later served as the Caliph's chamberlain.Pipes (1981), pp. 155–156 In 844/845, he suppressed a revolt of the Bedouin tribes of central Arabia.Sourdel (1960), p. 1287 Next he played an important role in crushing the Armenian revolt of 850–855: in 852 he was entrusted by the Caliph al-Mutawakkil with its suppression. Setting out from his base at Diyar Bakr, he first focused on the southern half of Armenia, i.e. the regions of Vaspurakan and Lake Van, before moving nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Wathiq
Abū Jaʿfar Hārūn ibn Muḥammad al-Wathiq bi'Llah (; 18 April 81210 August 847), commonly known by his regnal name al-Wathiq bi'Llah (), was an Abbasid caliph who reigned from 842 until his death in 847. Al-Wathiq is described in the sources as well-educated, intellectually curious, but also a poet, who enjoyed the company of poets and musicians as well as scholars. His brief reign was one of continuity with the policies of his father, al-Mu'tasim (), as power continued to rest in the hands of the same officials whom al-Mu'tasim had appointed. The chief events of the reign were the suppression of revolts: Bedouin rebellions occurred in Syria in 842, the Hejaz in 845, and the Yamama in 846, Armenia had to be pacified over several years, and above all, an abortive uprising took place in Baghdad itself in 846, under Ahmad ibn Nasr al-Khuza'i. The latter was linked to al-Wathiq's continued support for the doctrine of Mu'tazilism, and his reactivation of the to root out oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itakh
Aytākh or Ītākh al-Khazarī () was a leading commander in the Turkic army of the Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim (r. 833-842 C.E.). As the '' nisba'' in his name suggests, he was a Khazar by origin, and is said to have been a slave working in the kitchen of Sallam al-Abrash al-Khadim—whence his nickname ''al-Tabbakh'', "the cook"—before he was purchased as a '' ghulām'' by al-Mu'tasim in 815. He rose to become one of the senior commanders in al-Mu'tasim's "Turkic" guard, and participated in several expeditions such as the Sack of Amorium. Under al-Mu'tasim, he served as ''sahib al-shurta'' at Samarra, and became commander of the Caliph's personal guard. By the time of the accession of al-Wathiq in 842, he was, along with the Turk Ashinas, the "mainstay of the caliphate". Al-Wathiq named him governor of the Yemen in 843/4. After the death of Ashinas, in 844/5, he was named governor of Egypt, but he appointed Harthamah ibn al-Nadr al-Jabali there in his stead. Ya'qubi further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sack Of Amorium
The siege of Amorium by the Abbasid Caliphate in mid-August 838 was one of the major events in the long history of the Arab–Byzantine Wars. The Abbasid campaign was led personally by the Caliph al-Mu'tasim (), in retaliation to a virtually unopposed expedition launched by the Byzantine emperor Theophilos (r. 829–842) into the Caliphate's borderlands the previous year. Mu'tasim targeted Amorium, an Eastern Roman city in western Asia Minor, because it was the birthplace of the ruling Byzantine dynasty and, at the time, one of Byzantium's largest and most important cities. The caliph gathered an exceptionally large army, which he divided in two parts, which invaded from the northeast and the south. The northeastern army defeated the Byzantine forces under Theophilos at Anzen, allowing the Abbasids to penetrate deep into Byzantine Asia Minor and converge upon Ancyra, which they found abandoned. After sacking the city, they turned south to Amorium, where they arrived on 1 Augu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasids Ninth Century
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 Common Era, CE), from whom the Abbasid dynasty, dynasty takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 anno Hegirae, AH), they ruled as caliphs based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad being their capital for most of their history. The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Greater Khorasan, Khurasan, far from the Levantine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of Science in the medieval Islamic world, science, Islamic culture, culture, Abbasid art, arts, and List of invent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirham
The dirham, dirhem or drahm is a unit of currency and of mass. It is the name of the currencies of Moroccan dirham, Morocco, the United Arab Emirates dirham, United Arab Emirates and Armenian dram, Armenia, and is the name of a currency subdivision in Jordanian dinar, Jordan, Libyan dinar, Libya, Qatari riyal, Qatar and Tajikistani somoni, Tajikistan. It was historically a silver coin. Unit of mass The dirham was a unit of mass used across North Africa, the Middle East, Persia and Ifat Sultanate, Ifat; later known as Adal Sultanate, Adal, with varying values. The value of Islamic dirham was 14 qirat. 10 dirham equals 7 mithqal (2.975 gm of silver). In the late Ottoman Empire (), the standard dirham was 3.207 gram, g; 400 dirhem equal one oka (measure), oka. The Ottoman dirham was based on the Sassanian, Sasanian drachm (in Middle Persian: 𐭦𐭥𐭦𐭭 ''drahm''), which was itself based on the Greek Ancient drachma, dram/drachma. In Egypt in 1895, it was equivalen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |