|
Macrosomia Adiposa Congenita
Large for gestational age (LGA) is a term used to describe infants that are born with an abnormally high weight, specifically in the 90th percentile or above, compared to other babies of the same developmental age. Macrosomia is a similar term that describes excessive birth weight, but refers to an absolute measurement, regardless of gestational age. Typically the threshold for diagnosing macrosomia is a body weight between , or more, measured at birth, but there are difficulties reaching a universal agreement of this definition. Evaluating an infant for macrosomia or LGA can help identify risks associated with their birth, including labor complications of both the parent and the child, potential long-term health complications of the child, and infant mortality. Signs and symptoms Fetal macrosomia and LGA often do not present with noticeable patient symptoms. Important signs include large fundal height (uterus size) and excessive amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios). Fundal height c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms. Obesity increases the rate of pre-eclampsia, cesarean sections, and embryo macrosomia, as well as gestational diabetes. Babies born to individuals with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of macrosomia, of having hypoglycemia after birth, and of jaundice. If untreated, diabetes can also result in stillbirth. Long term, children are at higher risk of being overweight and of developing type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes can occur during pregnancy because of insulin resistance or reduced production of insulin. Risk factors include being overweight, previously having gestational diabetes, a family history of type 2 diabetes, and having polycystic ovarian syndrome. Diagnosis is by blood tests. For those at normal risk, Screening (medicine), screening is recommended betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Weight Gain
right Gestational weight gain is defined as the amount of weight gain a woman experiences between conception and birth of an infant. Recommendations The Institute of Medicine (IOM) recommendations for gestational weight gain are based on body mass index (BMI) of women prior to pregnancy. However, early first trimester BMI appears to be a valid proxy for pre-conception BMI. BMI is split up into four categories: underweight (<18.5 kg/m^2), normal weight (18.5-24.9 kg/m^2), overweight (25-29.9 kg/m^2), and obese (≥30.0 kg/m^2). The IOM has recommended the ranges of weight gain to be 12.5–18 kg, 11.5–16 kg, 7-11.5 kg, and 5–9 kg respectively. That is, the smaller the BMI pre pregnancy, the more weight a woman is expected to gain during her pregnancy. Contributing factors Excessive GWG (eGWG) has been shown to adversely affect maternal and baby health ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Needed To Treat
The number needed to treat (NNT) or number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) is an epidemiology, epidemiological measure used in communicating the effectiveness of a health-care intervention, typically a treatment with medication. The NNT is the average number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one additional bad outcome. It is defined as the inverse of the absolute risk reduction, and computed as 1/(I_u - I_e), where I_u is the incidence in the control (unexposed) group, and I_e is the incidence in the treated (exposed) group. This calculation implicitly assumes monotonicity, that is, no individual can be harmed by treatment. The modern approach, based on counterfactual conditional, counterfactual conditionals, relaxes this assumption and yields bounds on NNT. A type of effect size, the NNT was described in 1988 by McMaster University's Laupacis, Sackett and Roberts. While theoretically, the ideal NNT is 1, where everyone improves with treatm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American College Of Obstetricians And Gynecologists
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) is a professional association of physicians specializing in obstetrics and gynecology in the United States. Several Latin American countries are also represented within Districts of the organization. It is a 501(c) organization, 501(c)(6) organization with a membership of more than 60,000 obstetrician-gynecologists and women's health care professionals. It was founded in 1951. __TOC__ Background A companion 501(c)(6) organization, the American ''Congress'' of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, was founded in 2008 and became operational in 2010. The two organizations coexist, and member individuals automatically belong to both. Both are nonprofit organization, not-for-profit. The College as a 501(c)(3) focuses on education (with limited political work), whereas the Congress as a 501(c)(6) is allowed to advocate for members' interests in terms of the business of medicine (BOM) through lobbying and other political work. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold's Maneuvers
In obstetrics, Leopold maneuvers are a common and systematic way to determine the position of a fetus inside the woman's uterus. They are named after the gynecologist Christian Gerhard Leopold. They are also used to estimate term fetal weight. The maneuvers consist of four distinct actions, each helping to determine the position of the fetus. The maneuvers are important because they help determine the position and lie of the fetus, which in conjunction with correct assessment of the shape of the maternal pelvis can indicate whether the delivery is going to be complicated, or whether a caesarean section is necessary. The examiner's skill and practice in performing the maneuvers are the primary factor in whether the fetal lie is correctly ascertained. Alternately, position can be determined by ultrasound performed by a sonographer or physician. Performing the maneuvers Leopold maneuvers are difficult to perform on obese women and women who have polyhydramnios. The palpation can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetric Ultrasonography
Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of Pregnancy, prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus. The International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG) recommends that pregnant women have routine Obstetrics, obstetric ultrasounds between 18 weeks' and 22 weeks' Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age (the anatomy scan) in order to confirm pregnancy dating, to measure the fetus so that growth abnormalities can be recognized quickly later in pregnancy, and to assess for congenital malformations and Multiple birth, multiple pregnancies (twins, etc). Additionally, the ISUOG recommends th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
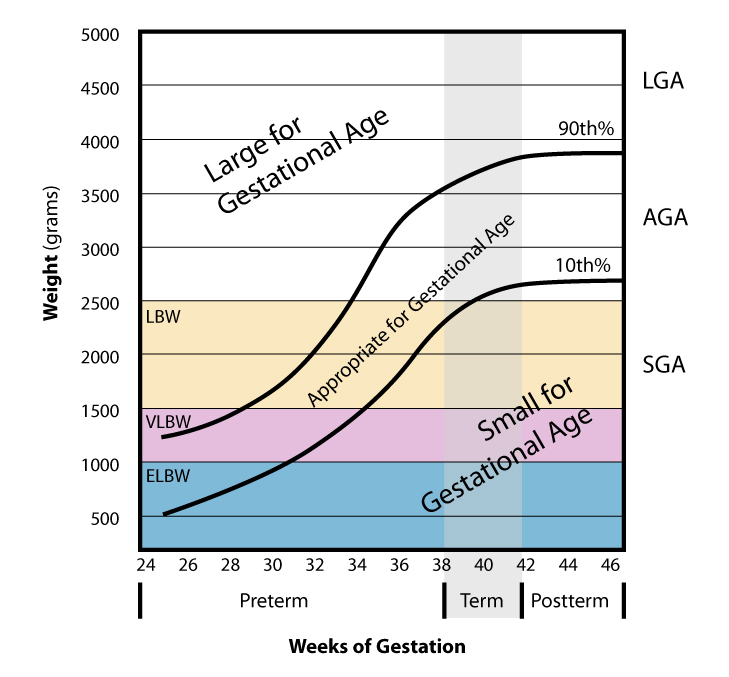
Weight Vs Gestational Age
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is a quantity associated with the gravitational force exerted on the object by other objects in its environment, although there is some variation and debate as to the exact definition. Some standard textbooks define weight as a vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar quantity, the magnitude of the gravitational force. Yet others define it as the magnitude of the reaction force exerted on a body by mechanisms that counteract the effects of gravity: the weight is the quantity that is measured by, for example, a spring scale. Thus, in a state of free fall, the weight would be zero. In this sense of weight, terrestrial objects can be weightless: so if one ignores air resistance, one could say the legendary apple falling from the tree, on its way to meet the ground near Isaac Newton, was weightless. The unit of measurement for weight is that of force, which in the International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroides Plebeius
''Phocaeicola plebeius'', formerly ''Bacteroides plebeius'', is a microbe found in the Human digestive system, human gut, most commonly in Japanese people, Japan natives. It is able to digest porphyran, a polysacchide from ''Porphyra'' seaweed (nori) that humans cannot digest on their own. The porphyranase-encoding gene Bp1689 is believed to have been derived from the microbe ''Zobellia galactanivorans'' via horizontal gene transfer, as part of a gene cluster containing other CAZy, carbohydrate-active enzymes. Composition of red algae ''Porphyra'' ''Porphyra'' is a genus of red seaweed. The two main ''Porphyra'' used in Japanese dishes are ''Porphyra yezoensis, P. yezoensis'' and ''Porphyra tenera, P. tenera'' which are commonly used in sushi. ''Porphyra spp.'' also known as nori in Japan contains compounds such porphyrans and agaroses that are indigestible to people lacking ''P. plebius''. Rhodophyta, the phylum of red algae, has a cell wall composed of sulfated galactans. Agar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simpson–Golabi–Behmel Syndrome
Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome (SGBS) is a rare inherited congenital disorder that can cause craniofacial, skeletal, vascular, cardiac, and renal abnormalities. There is a high prevalence of cancer associated in those with SGBS which includes wilms tumors, neuroblastoma, tumors of the adrenal gland, liver, lungs and abdominal organs. The syndrome is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. Females that possess one copy of the mutation are considered to be carriers of the syndrome but may still express varying degrees of the phenotype, suffering mild to severe malady. Males experience a higher likelihood of fetal death. Types There are two types of SGBS, each associated with mutations on a different gene: SGBS is also considered to be an overgrowth syndrome (OGS). OGS is characterized by a two to three standard deviation increase in weight, height, or head circumference above the average for sex and age. One of the most noted features of OGS is the increased risk of neopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perlman Syndrome
Perlman syndrome (PS), also known as nephroblastomatosis-fetal ascites-macrosomia-Wilms tumor syndrome, is a rare overgrowth syndrome caused by Dominance (genetics), autosomal recessive mutations in the ''DIS3L2'' gene. PS is characterized by macrocephaly, neonatal macrosomia, nephromegaly, renal dysplasia, dysmorphic facial features, and increased risk for Wilms' tumor. The syndrome is associated with high neonatal mortality. Signs and symptoms Perlman syndrome may be detected as early as Gestational age, gestational week 18 by Obstetric ultrasonography, prenatal ultrasound. In the first Pregnancy#Trimesters, trimester, cystic hygroma and thickened nuchal scan, nuchal translucency may be observed. Macrosomia, macrocephaly, enlarged kidneys, macroglossia, cardiac abnormalities, and visceromegaly may become evident by the second and third trimesters. Polyhydramnios is frequently observed. Characteristic facial features of Perlman syndrome include a Hypotonia, hypotonic appearance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |