|
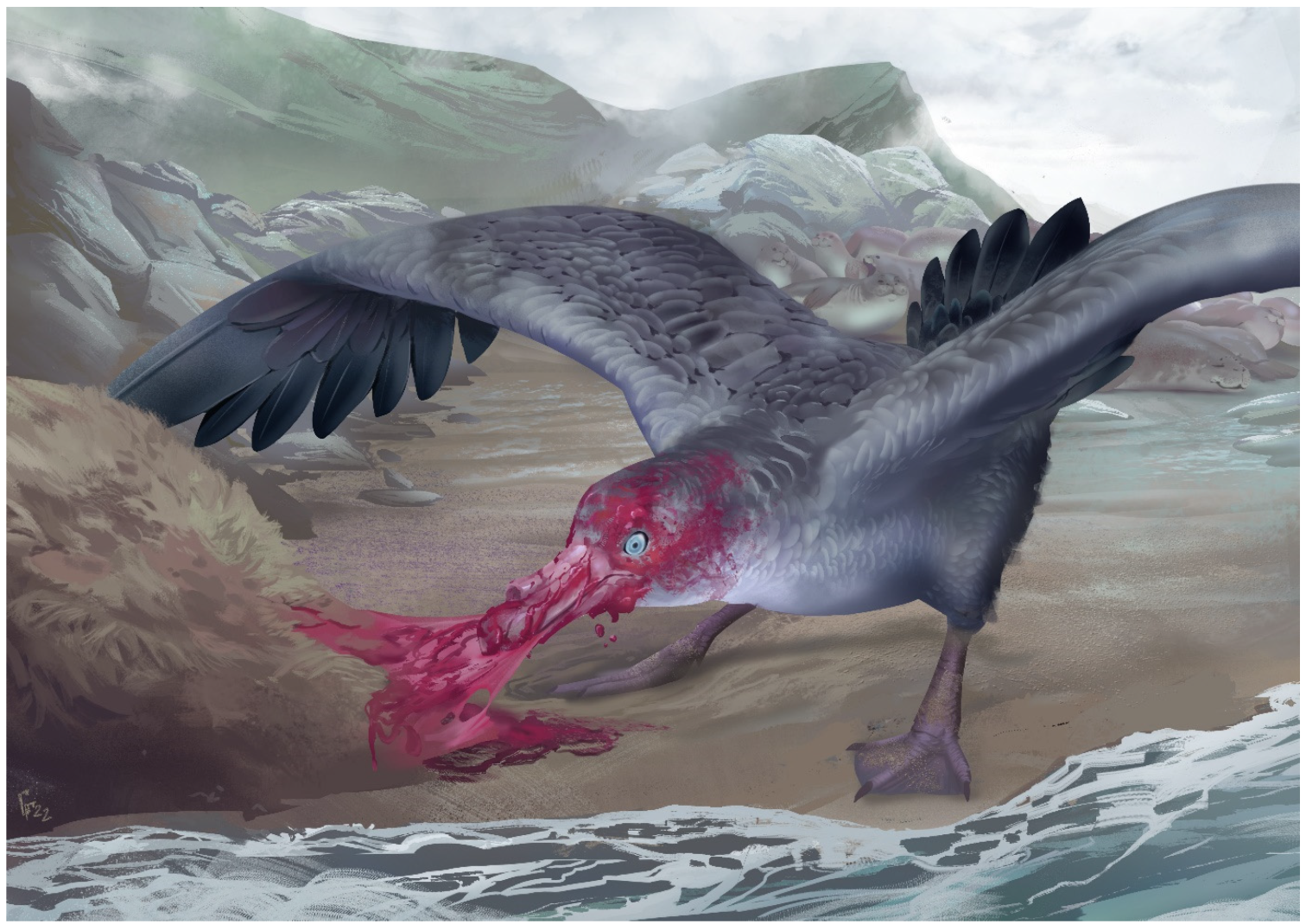
Macronectes Tinae
''Macronectes tinae'' is an extinct species of giant petrel from the Pliocene of New Zealand. Although clearly belonging to the genus ''Macronectes'', this species was notably smaller and less robust than either of the modern forms, possibly due to its more ancestral nature or due to the warmer climate of its environment. Like modern giant petrels it likely scavenged and hunted, feeding on the carcasses of seals and penguins as well as the chicks of other seabirds. History and naming The bones of ''Macronectes tinae'' were discovered in the marine sediments of the Pliocene Tangahoe Formation, located within the Whanganui Basin of New Zealand's North Island. Both the holotype specimen, a complete skull, as well as the paratype humerus, are kept at the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa. The fusion of the individual elements suggest that both belonged to adult individuals, however the distance between them makes it unlikely that they belonged to a single individual, instead rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.59 to 1.81 Ma, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well-identified but the exact dates of the start a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Giant Petrel
The southern giant petrel (''Macronectes giganteus''), also known as the Antarctic giant petrel, giant fulmar, stinker, and stinkpot, is a large seabird of the southern oceans. Its distribution overlaps broadly with the similar northern giant petrel, though it overall is centered slightly further south. Adults of the two species can be distinguished by the colour of their bill-tip: greenish in the southern and reddish in the northern. Taxonomy The southern giant petrel was formally described in 1789 by the German naturalist Johann Friedrich Gmelin. He placed it with all the other petrels in the genus ''Procellaria'' and coined the binomial name ''Procellaria gigantea''. Gmelin cited the "giant petrel" that had been described and illustrated in 1785 by the English ornithologist John Latham in his ''A General Synopsis of Birds''. The southern giant petrel is now placed with the northern giant petrel in the genus '' Macronectes'' that was introduced in 1905 by the American orni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2023
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Birds
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the |
Procellariidae
The family (biology), family Procellariidae is a group of seabirds that comprises the fulmarine petrels, the gadfly petrels, the diving petrels, the prion (bird), prions, and the shearwaters. This family is part of the bird order (biology), order Procellariiformes (or tubenoses), which also includes the albatrosses and the storm petrels. The procellariids are the most numerous family of tubenoses, and the most diverse. They range in size from the giant petrels with a wingspan of around , that are almost as large as the albatrosses, to the diving petrels with a wingspan of around that are similar in size to the little auks or dovekies in the family Alcidae. Male and female birds are identical in appearance. The plumage color is generally dull, with blacks, whites, browns and grays. The birds feed on fish, squid and crustacea, with many also taking Discards, fisheries discards and carrion. Whilst agile swimmers and excellent in water, petrels have weak legs and can only shuffle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bird Species Described In The 2020s ...
: ''See also parent article Bird species new to science'' This list shall only include newly recognized species and subspecies of birds (living as well as extinct) whose formal description was first published during the period from to . By default, the table was sorted by the "publ-date" and alphabetically by the scientific name. List of species ;Legend to the BGR column See also * List of bird species described in the 2000s * List of bird species described in the 2010s Notes References {{Reflist 2020s The 2020s (pronounced "twenty-twenties" or "two thousand ndtwenties"; shortened to "the '20s" and also known as "The Twenties") is the current decade that began on 1 January 2020, and will end on 31 December 2029. The 2020s began with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrels
Petrels are tube-nosed seabirds in the phylogenetic order Procellariiformes. Description Petrels are a monophyletic group of marine seabirds, sharing a characteristic of a nostril arrangement that results in the name "tubenoses". Petrels encompass three of the four extant families within the Procellariiformes order, namely Procellariidae (fulmarine petrels, gadfly petrels, diving petrels, prions, and shearwaters), Hydrobatidae (northern storm petrels), and Oceanitidae (austral storm petrels). The remaining family in Procellariiformes is the albatross family, Diomedeidae. Etymology The word ''petrel'' (first recorded in that spelling 1703) comes from earlier (''ca.'' 1670) ''pitteral''; the English explorer William Dampier wrote the bird was so called from its way of flying with its feet just skimming the surface of the water, recalling Saint Peter's walk on the sea of Galilee (Matthew xiv.28); if so, it likely was formed in English as a diminutive of Peter (< Old (?) < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldiomedes Angustirostris
''Aldiomedes'' is an extinct genus of albatross that lived in New Zealand during the Piacenzian stage. It is a monotypic genus containing the species A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ... ''A. angustirostris''. References Prehistoric bird genera Fossil taxa described in 2020 Diomedeidae {{paleo-bird-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albatross
Albatrosses, of the biological family Diomedeidae, are large seabirds related to the procellariids, storm petrels, and diving petrels in the order Procellariiformes (the tubenoses). They range widely in the Southern Ocean and the North Pacific. They are absent from the North Atlantic, although fossil remains of short-tailed albatross show they lived there up to the Pleistocene, and occasional vagrants are found. Great albatrosses are among the largest of flying birds, with wingspans reaching up to and bodies over in length. The albatrosses are usually regarded as falling into four genera, but disagreement exists over the number of species. Albatrosses are highly efficient in the air, using dynamic soaring and slope soaring to cover great distances with little exertion. They feed on squid, fish, and krill by either scavenging, surface seizing, or diving. Albatrosses are colonial, nesting for the most part on remote oceanic islands, often with several species nesting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagornithidae
The Pelagornithidae, commonly called pelagornithids, pseudodontorns, bony-toothed birds, false-toothed birds or pseudotooth birds, are a prehistoric family (biology), family of large seabirds. Their fossil remains have been found all over the world in rocks dating between the Early Paleocene and the Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary. Most of the common names refer to these bird, birds' most notable trait: tooth-like points on their beak, beak's edges, which, unlike true teeth, contained Volkmann's canals and were outgrowths of the premaxillary and mandible, mandibular bones. Even "small" species of pseudotooth birds were the size of albatrosses; the largest ones had wingspans estimated at 5–6 metres (15–20 ft) and were among the largest flying birds ever to live. They were the dominant seabirds of most oceans throughout most of the Cenozoic, and modern humans apparently missed encountering them only by a tiny measure of evolutionary time: the last known pelagornithids were co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudyptes Atatu
''Eudyptes atatu'' is an extinct species of crested penguin that lived during the Pliocene epoch around 3.2 million years ago. It is considered the first stem species of the crested penguin genus. ''Eudyptes atatu'' is thought to have inhabited what is now New Zealand. The bird's existence has been cited as evidence supporting the idea that penguins originated in Zealandia before spreading across the Southern Hempishere. Etymology The generic term ''Eudyptes'' derives from Ancient Greek, and translates to "fine diver" in English. The species name ''atatu'' is a contraction between the words "ata" and "tū" from the Te Reo Maori language, meaning "dawn". "Dawn" refers to the species' place within the fossil record, representing the beginning of the crested penguin lineage in New Zealand. Description ''Eudyptes atatu'' was close in size to the modern erect-crested penguin, which measures at around 60 cm long. As with other crested penguins, sexual dimorphism is fairly promin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |