|
MAN Lion's Chassis
MAN Lion's Chassis is a series of modular chassis made to replace most of MAN's rear-engined low-entry, intercity and coach chassis. It was first introduced at the IAA Commercial Vehicles 2008 in Hanover. MAN prospected both two- and tri-axle low-entry, two-axle intercity and two- and tri-axle coach versions. The first of the intercity version appeared in 2008, the two-axle low-entry version in 2009 and both coach versions in 2010. The tri-axle low-entry version may have been abandoned. The models that the Lion's Chassis was set to replace weren't discontinued until the end of 2013. All chassis versions can be delivered as either a rolling chassis with shortened wheelbase for transport or as CIB ("Chassis in the box" — partly assembled kit). MAN CO 19.xxx MAN CO 19.xxx is the two-axle 19.7 tonnes GVW coach version replacing the ''MAN 18.xxx HOCL'' (R33). Internal codes are ''RR2'' for the normal version and ''RR3'' for the CIB version. It is available as CO 19.350 and CO 19. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beulas
Beulas SAU is a coachbuilder based in Arbúcies, Catalonia, Spain. The company builds a range of coach bodies on a variety of chassis. Their products are sold throughout Europe. History The company was established in 1934 by Ramón Beulas and Narcís Pujol in Arbúcies, a village in the Selva county of the province of Girona, Catalonia, Spain. It was (after Indcar and Ayats) the third coachbuilding company to be founded in this small town, which offered the advantage of being in the midst of a densely forested area ("Selva" means "forest" in Catalan), useful since the bodyworks were still made of wood at the time. During the Spanish Civil War, Beulas built ambulance bodies for the army. For the next three decades, Beulas remained a small coachbuilder which hand-crafted each bodywork to order, making 6–10 per year. During the 1960s, the company grew steadily and components began to be standardized, allowing for an increase in production volume. In the 1970s and 1980s the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coach (bus)
A coach (or coach bus/motorcoach) is a type of bus built for longer-distance service, in contrast to transit buses that are typically used within a single metropolitan region. Often used for touring, intercity, and international bus service, coaches are also used for private charter for various purposes. Coaches are also related and fall under a specific category/type of RVs. Deriving the name from horse-drawn carriages and stagecoaches that carried passengers, luggage, and mail, modern motor coaches are almost always high-floor buses, with separate luggage hold mounted below the passenger compartment. In contrast to transit buses, motor coaches typically feature forward-facing seating, with no provision for standing. Other accommodations may include onboard restrooms, televisions, and overhead luggage space. History Background Horse-drawn chariots and carriages ("coaches") were used by the wealthy and powerful where the roads were of a high enough standard from p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus Chassis
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for charter purposes, or through private ownership. Although the average bus carries between 30 and 100 passengers, some buses have a capacity of up to 300 passengers. The most common type is the single-deck rigid bus, with double-decker and articulated buses carrying larger loads, and midibuses and minibuses carrying smaller loads. Coaches are used for longer-distance services. Many types of buses, such as city transit buses and inter-city coaches, charge a fare. Other types, such as elementary or secondary school buses or shuttle buses within a post-secondary education campus, are free. In many jurisdictions, bus drivers require a special large vehicle licence above and beyond a regular driving licence. Buses may be used for sche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAN Buses
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the father. Sex differentiation of the male fetus is governed by the SRY gene on the Y chromosome. During puberty, hormones which stimulate androgen production result in the development of secondary sexual characteristics, thus exhibiting greater differences between the sexes. These include greater muscle mass, the growth of facial hair and a lower body fat composition. Male anatomy is distinguished from female anatomy by the male reproductive system, which includes the penis, testicles, sperm duct, prostate gland and the epididymis, and by secondary sex characteristics, including a narrower pelvis, narrower hips, and smaller breasts without mammary glands. Throughout human history, traditional gender roles have often defined an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro III
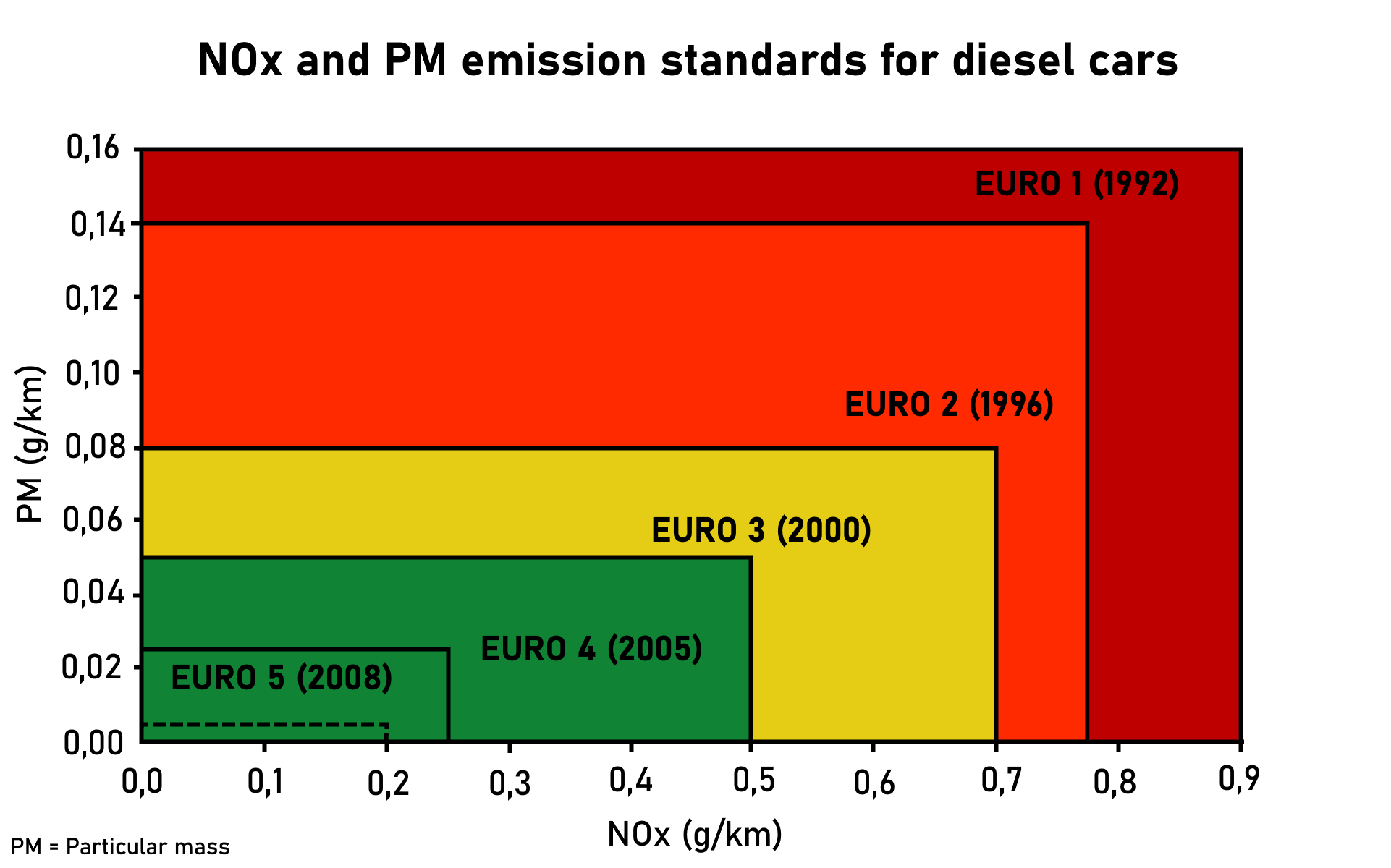
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards for pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and EEA member states and the UK, and ships in EU waters. The standards are defined in a series of European Union directives staging the progressive introduction of increasingly stringent standards. , the standards do not include non-exhaust emissions such as particulates from tyres and brakes. Details of Euro 7 have been postponed to 12 October 2022. Background In the European Union, emissions of nitrogen oxides (), total hydrocarbon (THC), non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate matter (PM) are regulated for most vehicle types, including cars, trucks (lorries), locomotives, tractors and similar machinery, barges, but excluding seagoing ships and aeroplanes. For each vehicle type, different standards apply. Compliance is determined by running the engine at a standardised test cycle. Non-comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating
Vehicle weight is a measurement of wheeled motor vehicles; either an actual measured weight of the vehicle under defined conditions or a gross weight rating for its weight carrying capacity. Curb or kerb weight Curb weight (U.S. English) or kerb weight (British English) is the total mass of a vehicle with standard equipment and all necessary operating consumables such as motor oil, transmission oil, brake fluid, coolant, air conditioning refrigerant, and sometimes a full tank of fuel, while not loaded with either passengers or cargo. The gross vehicle weight is larger and includes the maximum payload of passengers and cargo. This definition may differ from definitions used by governmental regulatory agencies or other organizations. For example, many European Union manufacturers include the weight of a driver and luggage to follow European Directive 95/48/EC. Organizations may also define curb weight with fixed levels of fuel and other variables to equalize the value for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling Chassis
A rolling chassis is the chassis without bodywork of a motor vehicle (car, truck, bus, or other vehicle), assembled with suspension and wheels. Heavy vehicles Separate chassis remain in use for almost all heavy vehicles ranging from pickup trucks to the biggest trucks and commercial passenger carrying vehicles. The rolling chassis is delivered to the commercial body maker, coachbuilder, or bulk transporter on its own wheels, under its own power. Automobiles Rolling chassis was a stage of manufacture of every vehicle. Mass produced cars were supplied complete from the factory, but luxury cars like Rolls-Royce were supplied as a chassis from the factory to several bespoke coachbuilders like J Gurney Nutting & Co who would supply a body to the customer's order (or build a car which was sold from their showroom). Automobile construction methods changed when unibody or monocoque combined chassis and body structures gradually replaced chassis. Restoration In restoration circl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany after Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen. Hanover's urban area comprises the towns of Garbsen, Langenhagen and Laatzen and has a population of about 791,000 (2018). The Hanover Region has approximately 1.16 million inhabitants (2019). The city lies at the confluence of the River Leine and its tributary the Ihme, in the south of the North German Plain, and is the largest city in the Hannover–Braunschweig–Göttingen–Wolfsburg Metropolitan Region. It is the fifth-largest city in the Low German dialect area after Hamburg, Dortmund, Essen and Bremen. Before it became the capital of Lower Saxony in 1946, Hannover was the capital of the Principality of Calenberg (1636–1692), the Electorate of Hanover (1692–1814), the Kingdom of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercity Bus
An intercity bus service (North American English) or intercity coach service (British English and Commonwealth English), also called a long-distance, express, over-the-road, commercial, long-haul, or highway bus or coach service, is a public transport service using coaches to carry passengers significant distances between different cities, towns, or other populated areas. Unlike a transit bus service, which has frequent stops throughout a city or town, an intercity bus service generally has a single stop at one location in or near a city, and travels long distances without stopping at all. Intercity bus services may be operated by government agencies or private industry, for profit and not for profit. Intercity coach travel can serve areas or countries with no train services, or may be set up to compete with trains by providing a more flexible or cheaper alternative. Intercity bus services are of prime importance in lightly populated rural areas that often have little or no publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothenburg
Gothenburg (; abbreviated Gbg; sv, Göteborg ) is the second-largest city in Sweden, fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and capital of the Västra Götaland County. It is situated by the Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has a population of approximately 590,000 in the city proper and about 1.1 million inhabitants in the metropolitan area. Gothenburg was founded as a heavily fortified, primarily Dutch, trading colony, by royal charter in 1621 by King Gustavus Adolphus. In addition to the generous privileges (e.g. tax relaxation) given to his Dutch allies from the ongoing Thirty Years' War, the king also attracted significant numbers of his German and Scottish allies to populate his only town on the western coast. At a key strategic location at the mouth of the Göta älv, where Scandinavia's largest drainage basin enters the sea, the Port of Gothenburg is now the largest port in the Nordic countries. Gothenburg is home to many students, as the city incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAN 18
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the father. Sex differentiation of the male fetus is governed by the SRY gene on the Y chromosome. During puberty, hormones which stimulate androgen production result in the development of secondary sexual characteristics, thus exhibiting greater differences between the sexes. These include greater muscle mass, the growth of facial hair and a lower body fat composition. Male anatomy is distinguished from female anatomy by the male reproductive system, which includes the penis, testicles, sperm duct, prostate gland and the epididymis, and by secondary sex characteristics, including a narrower pelvis, narrower hips, and smaller breasts without mammary glands. Throughout human history, traditional gender roles have often defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)

