|
Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) is a rodent-borne viral infectious disease that presents as aseptic meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Its causative agent is lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), a member of the family '' Arenaviridae''. The name was coined by Charles Armstrong in 1934. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) is "a viral infection of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord and of the cerebrospinal fluid". Lasker, Jill S. "Lymphocytic choriomeningitis". The name is based on the tendency of an individual to have abnormally high levels of lymphocytes during infection. Choriomeningitis is "cerebral meningitis in which there is marked cellular infiltration of the meninges, often with a lymphocytic infiltration of the choroid plexuses". Signs and symptoms LCMV infection manifests itself in a wide range of clinical symptoms, and may even be asymptomatic for immunocompetent individuals. CDC. "Information for Pet Owners: Reducing the Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease (specialty)
Infectious diseases (ID), also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of infections. An infectious diseases specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial ( healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections. An ID specialist investigates and determines the cause of a disease (bacteria, virus, parasite, fungus or prions). Once the cause is known, an ID specialist can then run various tests to determine the best drug to treat the disease. While infectious diseases have always been around, the infectious disease specialty did not exist until the late 1900s after scientists and physicians in the 19th century paved the way with research on the sources of infectious disease and the development of vaccines. Scope Infectious diseases specialists typically serve as consultants to other physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immunodeficiency. Although many co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
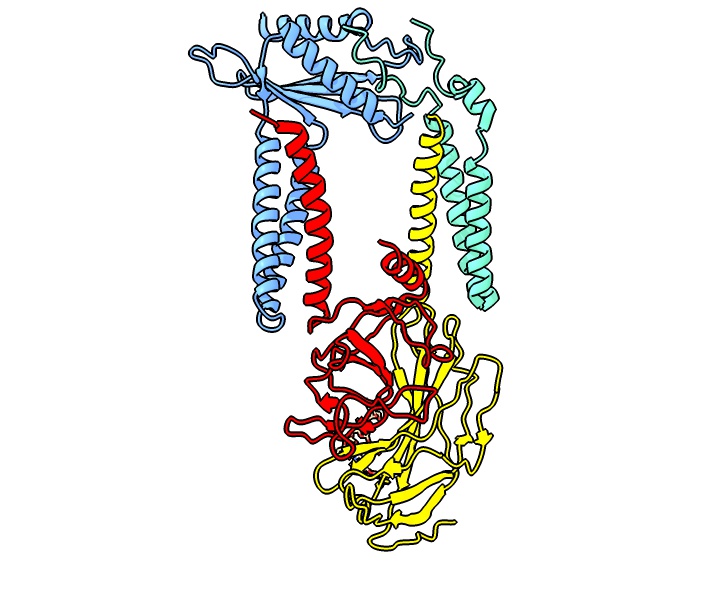
Nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MHC Restriction
In immunology, MHC-restricted antigen recognition, or MHC restriction, refers to the fact that a T cell can interact with a self-major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule and a foreign peptide bound to it, but will only respond to the antigen when it is bound to a particular MHC molecule. Background When foreign proteins enter a cell, they are broken into smaller pieces called peptides. These peptides, also known as antigens, can derive from pathogens such as viruses or intracellular bacteria. Foreign peptides are brought to the surface of the cell and presented to T cells by proteins called the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). During T cell development, T cells go through a selection process in the thymus to ensure that the T cell receptor (T cell receptor, TCR) will not recognize Major histocompatibility complex, MHC molecule presenting self-antigens, i.e that its affinity is not too high. High affinity means it will be autoreactive, but no affinity means it will no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arenavirus
An arenavirus is a bi- or trisegmented ambisense RNA virus that is a member of the family ''Arenaviridae''. These viruses infect rodents and occasionally humans. A class of novel, highly divergent arenaviruses, properly known as reptarenaviruses, have also been discovered which infect snakes to produce inclusion body disease, mostly in boa constrictors. At least eight arenaviruses are known to cause human disease. The diseases derived from arenaviruses range in severity. Aseptic meningitis, a severe human disease that causes inflammation covering the brain and spinal cord, can arise from the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Viral hemorrhagic fever, Hemorrhagic fever syndromes, including Lassa fever, are derived from infections such as Guanarito virus, Junin virus, Lassa virus, Lujo virus, Machupo virus, Sabia virus, or Whitewater Arroyo virus. Because of the epidemiological association with rodents, some arenaviruses and bunyaviruses are designated as roboviruses. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribonucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Institute Of Bioinformatics
The SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics is an academic not-for-profit foundation which federates bioinformatics activities throughout Switzerland. The institute was established on 30 March 1998 and its mission is to provide core bioinformatics resources to the national and international life science research community in fields such as genomics, proteomics and systems biology as well as to lead and coordinate the field of bioinformatics in Switzerland. In particular, it promotes research, develops databanks and computer technologies, and is involved in teaching and service activities. History The institute was originally created to provide a framework for stable long-term funding for both the Swiss-Prot database and the Swiss EMBnet node. Swiss-Prot in particular went through a major funding crisis in 1996, which led the leaders of the five research groups active in bioinformatics in Geneva and Lausanne, Ron Appel, Amos Bairoch, Philipp Bucher, Victor Jongeneel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MBTPS1
Membrane-bound transcription factor site-1 protease, or site-1 protease (S1P) for short, also known as subtilisin/kexin-isozyme 1 (SKI-1), is an enzyme (EC 3.4.21.112) that in humans is encoded by the MBTPS1 gene. S1P cleaves the endoplasmic reticulum loop of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) transcription factors. Function This gene encodes a member of the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family, which includes proteases that process protein and peptide precursors trafficking through regulated or constitutive branches of the secretory pathway. The encoded protein undergoes an initial autocatalytic processing event in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to generate a heterodimer which exits the ER and sorts to the cis/medial- Golgi where a second autocatalytic event takes place and the catalytic activity is acquired. It encodes a type 1 membrane bound protease which is ubiquitously expressed and regulates cholesterol or lipid homeostasis via cleavage of substrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Glycoprotein
The term viral protein refers to both the products of the genome of a virus and any host proteins incorporated into the viral particle. Viral proteins are grouped according to their functions, and groups of viral proteins include structural proteins, nonstructural proteins, regulatory proteins, and accessory proteins. Viruses are non-living and do not have the means to reproduce on their own, instead depending on their host cell's machinery to do this. Thus, viruses do not code for most of the proteins required for their replication and the translation of their mRNA into viral proteins, but use proteins encoded by the host cell for this purpose. Viral structural proteins Most viral structural proteins are components for the capsid and the envelope of the virus. Capsid The genetic material of a virus is stored within a viral protein structure called the capsid. The capsid is a "shield" that protects the viral nucleic acids from getting degraded by host enzymes or other types of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins into membrane-bound Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and Endocytosis, endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. The Golgi apparatus was identified in 1898 by the Italian biologist and pathologist Camillo Golgi. The organelle was later named after him in the 1910s. Discovery Because of its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Peptidase
Signal peptidases are enzymes that convert secretory and some membrane proteins to their mature or pro forms by cleaving their signal peptides from their N-termini. Signal peptidases were initially observed in endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived membrane fractions isolated from mouse myeloma cells. The key observation by César Milstein and colleagues was that immunoglobulin light chains were produced in a higher molecular weight form, which became processed by the ER membrane fraction. This finding was directly followed by the discovery of the translocation machinery. Signal peptidases are also found in prokaryotes A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' ... as well as the protein import machinery of mitochondria and chloroplasts. All signal peptidases described s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Peptide
A signal peptide (sometimes referred to as signal sequence, targeting signal, localization signal, localization sequence, transit peptide, leader sequence or leader peptide) is a short peptide (usually 16–30 amino acids long) present at the N-terminus (or occasionally nonclassically at the C-terminus or internally) of most newly synthesized proteins that are destined toward the secretory pathway. These proteins include those that reside either inside certain organelles (the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi or endosomes), secreted from the cell, or inserted into most cellular membranes. Although most type I membrane-bound proteins have signal peptides, most type II and multi-spanning membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which biochemically resembles a signal sequence except that it is not cleaved. They are a kind of target peptide. Function (translocation) Signal peptides function to prompt a cell to transloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for "little net". It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. There are two types of ER that share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of Cell (biology), cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |