|
Lowell Mill Girls
The Lowell mill girls were young female workers who came to work in textile mills in Lowell, Massachusetts during the Industrial Revolution in the United States. The workers initially recruited by the corporations were daughters of New England farmers, typically between the ages of 15 and 35. By 1840, at the height of the Textile Revolution, the Lowell textile mills had recruited over 8,000 workers, with women making up nearly three-quarters of the mill workforce. During the early period, women came to the mills for various reasons: to help a brother pay for college, for the educational opportunities offered in Lowell, or to earn supplemental income for the family. Francis Cabot Lowell emphasized the importance of providing housing and a form of education to mirror the boarding schools that were emerging in the 19th century. He also wanted to provide an environment that sharply contrasted the poor conditions of the British Mills notoriously portrayed by Dickens. Their wages were o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloth
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, and different types of fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: consumer textiles for domestic purposes and technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, while in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. The durability of textiles is an important property, with common cotton or blend garments (such as t-shirts) able to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
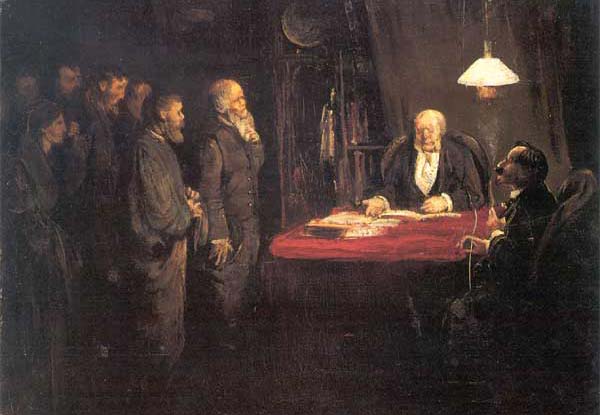
Strike Action
Strike action, also called labor strike, labour strike in British English, or simply strike, is a work stoppage caused by the mass refusal of employees to Working class, work. A strike usually takes place in response to employee grievances. Strikes became common during the Industrial Revolution, when Labour economics, mass labor became important in factories and mines. As striking became a more common practice, governments were often pushed to act (either by private business or by union workers). When government intervention occurred, it was rarely neutral or amicable. Early strikes were often deemed unlawful conspiracies or anti-competitive cartel action and many were subject to massive legal repression by state police, federal military power, and federal courts. Many Western nations legalized striking under certain conditions in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Strikes are sometimes used to pressure governments to change policies. Occasionally, strikes destabilize the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowell Offering 1
Lowell may refer to: Places United States * Lowell, Arkansas * Lowell, Florida * Lowell, Idaho * Lowell, Indiana * Lowell, Maine * Lowell, Massachusetts ** Lowell National Historical Park ** Lowell (MBTA station) ** Lowell Ordnance Plant * Lowell, Michigan * Lowell, Missouri * Lowell, Holt County, Missouri, an extinct trading post in Lincoln Township, Holt County, Missouri * Lowell, North Carolina * Lowell, Washington County, Ohio * Lowell, Seneca County, Ohio * Lowell, Oregon * Lowell, Vermont, a New England town ** Lowell (CDP), Vermont, the main village in the town * Lowell, West Virginia * Lowell (town), Wisconsin ** Lowell, Wisconsin, a village within the town of Lowell * Lowell Hill, California * Lowell Point, Alaska *Lowell Township (other) Other countries * Lowell glacier, near the Alsek River, Canada Elsewhere * Lowell (lunar crater) * Lowell (Martian crater) Institutions in the United States Arizona * Lowell Observatory, astronomical non-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For History And New Media
Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media (RRCHNM), formerly the Center for History and New Media (CHNM), is a research center specializing in digital history and information technology at George Mason University (GMU) in Fairfax County, Virginia. It was one of the first digital history centers in the world, established by Roy Rosenzweig in 1994 to use digital media and information technology to democratize history: to incorporate multiple voices, reach diverse audiences, and encourage popular participation in presenting and preserving the past. Its current director is Lincoln Mullen. History Under Roy Rosenzweig CHNM was founded in the fall of 1994 by Roy Rosenzweig as a research center within the GMU Department of History and Art History. Its origins lay in Rosenzweig's work with Steve Brier and Josh Brown on a CD-ROM version of the American Social History Project's American history textbook, ''Who Built America?'' but as Rosenzweig was initially the only person at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
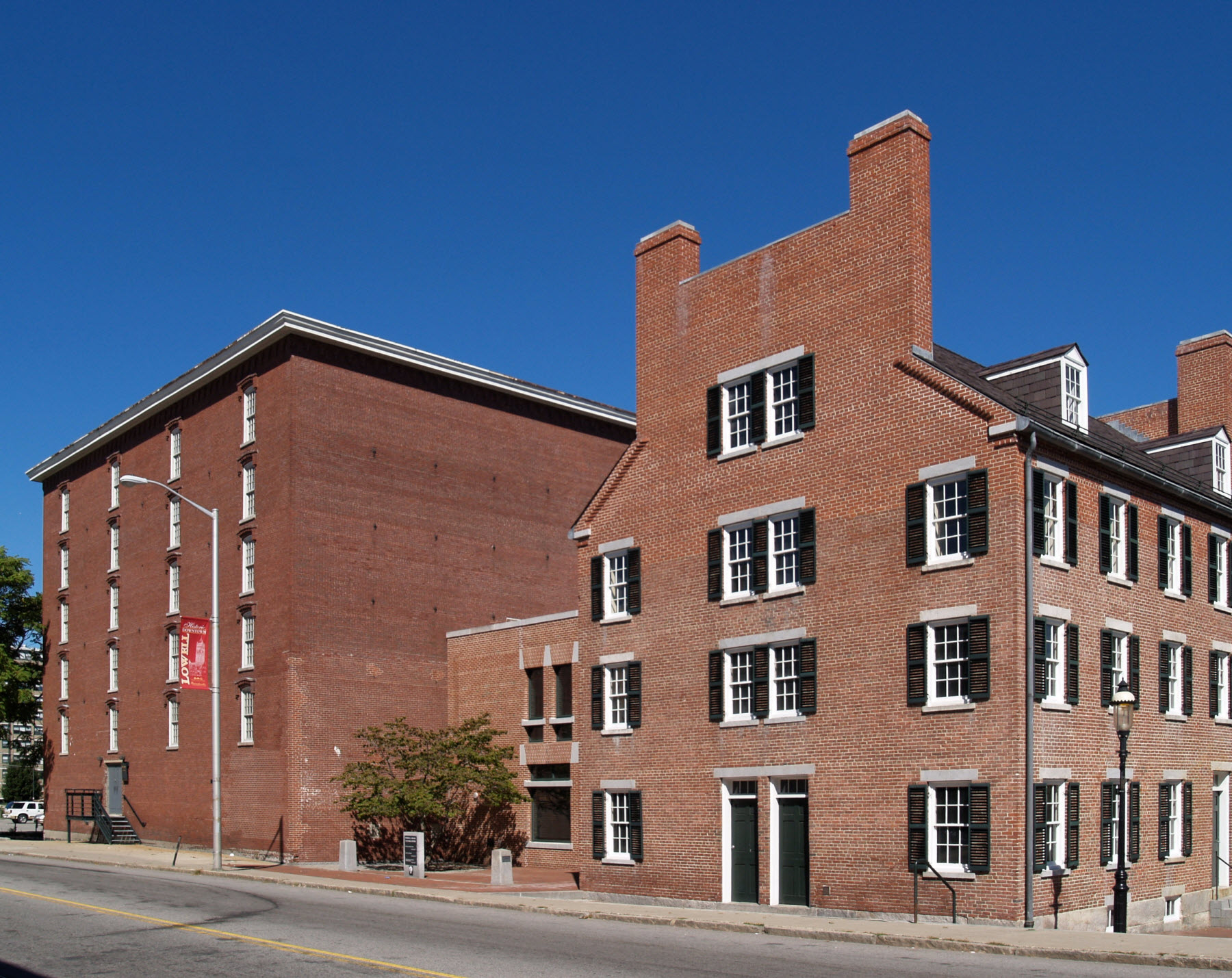
Boarding Houses
A boarding house is a house (frequently a family home) in which lodgers rent one or more rooms on a nightly basis and sometimes for extended periods of weeks, months, or years. The common parts of the house are maintained, and some services, such as laundry and cleaning, may be supplied. It normally provides "room and board," with some meals as well as accommodation. Lodgers legally obtain a licence, not exclusive possession, to use their rooms and so the landlord retains the right of access. Arrangements Formerly boarders would typically share washing, breakfast, and dining facilities; in recent years, it has become common for each room to have its own washing and toilet facilities. Such boarding houses were often found in English seaside towns (for tourists) and college towns (for students). It was common for there to be one or two elderly long-term residents. "The phrase "boardinghouse reach" eferring to a diner reaching far across a dining tablecomes from an important va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, minister, abolitionism, abolitionist, and poet who led the Transcendentalism, Transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champion of individualism and critical thinking, as well as a prescient critic of the countervailing pressures of society and conformity. Friedrich Nietzsche thought he was "the most gifted of the Americans," and Walt Whitman called Emerson his "master". Emerson gradually moved away from the religious and social beliefs of his contemporaries, formulating and expressing the philosophy of Transcendentalism in his 1836 essay, "Nature (Emerson), Nature". His speech "The American Scholar," given in 1837, was called America's "intellectual Declaration of Independence" by Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr.Richardson, p. 263. Emerson wrote most of Essays (Emerson), his important essays as lectures and then revised them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harriet Martineau
Harriet Martineau (12 June 1802 – 27 June 1876) was an English social theorist.Hill, Michael R. (2002''Harriet Martineau: Theoretical and Methodological Perspectives'' Routledge. She wrote from a sociological, holism, holistic, religious and feminine angle, translated works by Auguste Comte, and, rare for a woman writer at the time, earned enough to support herself. Martineau advised a focus on all aspects of society, including the role of the home in domestic life as well as key political, religious, and social institutions. The young Queen Victoria, Princess Victoria enjoyed her work and invited her to Coronation of Queen Victoria, her coronation in 1838. The novelist Margaret Oliphant called her "a born lecturer and politician... less distinctively affected by her sex than perhaps any other, male or female, of her generation." Her commitment to abolitionism has seen Martineau's achievements studied world-wide, particularly at American institutions of higher education. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English novelist, journalist, short story writer and Social criticism, social critic. He created some of literature's best-known fictional characters, and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian era.. His works enjoyed unprecedented popularity during his lifetime and, by the 20th century, critics and scholars had recognised him as a literary genius. His novels and short stories are widely read today. Born in Portsmouth, Dickens left school at age 12 to work in a boot-blacking factory when his father John Dickens, John was incarcerated in a debtors' prison. After three years, he returned to school before beginning his literary career as a journalist. Dickens edited a weekly journal for 20 years; wrote 15 novels, five novellas, hundreds of short stories and nonfiction articles; lectured and performed Penny reading, readings extensively; was a tireless letter writer; and campaigned vigor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
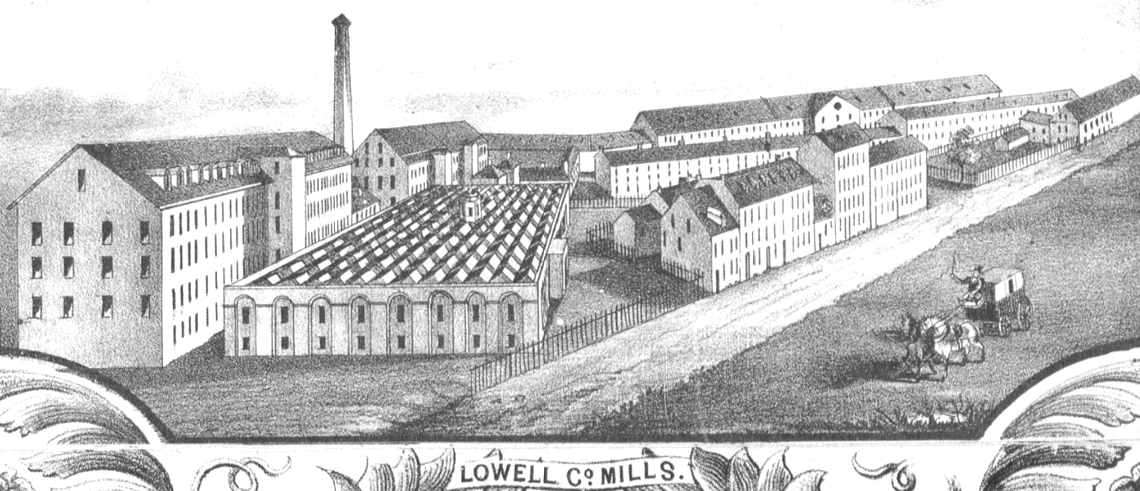
Lowell Mills
The Lowell Mills were 19th-century textile mills that operated in the city of Lowell, Massachusetts, which was named after Francis Cabot Lowell; he introduced a new manufacturing system called the "Lowell system", also known as the " Waltham-Lowell system". Philosophical context Francis Cabot Lowell sought to create an efficient manufacturing process in the United States that was different than what he saw in Great Britain. His vision relied on his "great faith in the people of New England" and employees "would be housed and fed by the company and remain employed only a few years rather than form a permanently downtrodden underclass". After a trip to London in 1811 during which he memorized the design of power looms, Lowell founded the Boston Manufacturing Company in 1813 along with Nathan Appleton, Patrick Tracy Jackson, and the other so-called " Boston Associates". This group of Boston-area merchants were "committed to the ideals of the original Protestant ethic and Repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowell System
The Waltham-Lowell system was a labor and production model employed during the rise of the textile industry in the United States, particularly in New England, during the rapid expansion of the Industrial Revolution in the early 19th century. The textile industry was one of the earliest to become mechanized, made possible by inventions such as the spinning jenny, spinning mule, and water frame around the time of the American Revolution. Models of production and labor sources were first explored in textile manufacturing. The system used domestic labor, often referred to as mill girls, young women who came to the new textile centers from rural towns to earn more money than they could at home, and to live a cultured life in the city. Their life was very regimented: they lived in boarding houses and were held to strict hours and a moral code. Competition grew in the domestic textile industry and wages declined, so workers began to go on strike. Resistance was led by the mill girls. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harriet Hanson Robinson
Harriet Jane Hanson Robinson (February 8, 1825 – December 22, 1911) worked as a bobbin doffer in a Massachusetts cotton mill and was involved in a turnout, became a poet and author, and played an important role in the women's suffrage movement in the United States. Early life Harriet was the daughter of Harriet Browne Hanson and the carpenter William Hanson. Both parents were descended from early English settlers but without distinguished ancestors. Her elder brother was John Wesley Hanson (1823–1901), and she had two surviving younger brothers: Benjamin and William. Harriet's father died when she was five, which left his widow to support four young children. Harriet's mother was determined to keep her family together, despite the difficulty in doing so. Harriet later recalled in her autobiography ''Loom and Spindle'' her mother's response after a neighbour had offered to adopt Harriet so that her mother had one less mouth to feed: "No; while I have one meal of victuals a da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |