|
Low German (other)
Low German is a Germanic language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and in Northeastern Netherlands. * East Low German, a group of dialects spoken in north-eastern Germany and northern Poland * Mennonite Low German, a language or group of dialects spoken by Mennonites * Middle Low German, a language spoken from about 1100 to 1600 * Old Low German, a language documented from the 8th until the 12th century * West Low German, a group of dialects spoken in northwest Germany, The Netherlands, and Denmark * Low Germanic, term used by the German linguist Theo Vennemann in his controversial classification of the Germanic languages Other uses *Low German house, a type of German timber-framed farmhouse *Sometimes used to refer to parts of Northern Germany Northern Germany (german: link=no, Norddeutschland) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low German
: : : : : (70,000) (30,000) (8,000) , familycolor = Indo-European , fam2 = Germanic , fam3 = West Germanic , fam4 = North Sea Germanic , ancestor = Old Saxon , ancestor2 = Middle Low German , dia1 = West Low German , dia2 = East Low German , iso2 = nds , iso3 = nds , iso3comment = (Dutch varieties and Westphalian have separate codes) , lingua = 52-ACB , map = Nds Spraakrebeet na1945.svg , mapcaption = Present day Low German language area in Europe. , glotto = lowg1239 , glottoname = Low German , notice = IPA Low German or Low Saxon (in the language itself: , and other names; german: Plattdeutsch, ) is a West Germanic language variety spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern part of the Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
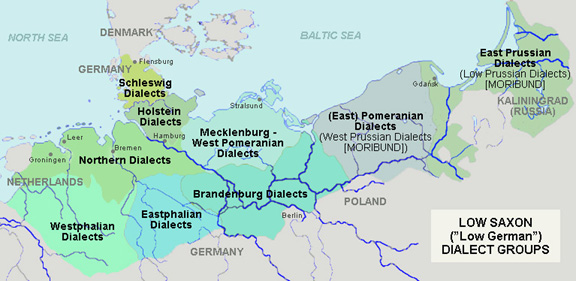
East Low German
East Low German (german: ostniederdeutsche Dialekte, ostniederdeutsche Mundarten, Ostniederdeutsch; nds, Oostplattdütsch) is a group of Low German dialects spoken in north-eastern Germany as well as by minorities in northern Poland. Together with West Low German dialects, it forms a dialect continuum of the Low German language. Before 1945, the dialect was spoken along the entire then-German-settled Baltic Coast from Mecklenburg, through Pomerania, West Prussia into certain villages of the East Prussian Klaipėda Region. East Pomeranian, Central Pomeranian and West Pomeranian should not be confused with the West Slavic Pomeranian language (german: Pomoranisch). Related languages East Low German belongs to the dialect continuum of the continental West Germanic languages. It developed from the older Middle Low German. In the West it fades into West Low German. The distinction is usually made referring to the plural endings of the verbs: East Low German endings are based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mennonite Low German
Plautdietsch () or Mennonite Low German is a Low Prussian dialect of East Low German with Dutch influence that developed in the 16th and 17th centuries in the Vistula delta area of Royal Prussia. The word ''Plautdietsch'' translates to "flat (or low) German" (referring to the plains of northern Germany or the simplicity of the language). In other Low German dialects, the word for Low German is usually realised as ''Plattdütsch/Plattdüütsch'' or ''Plattdüütsk'' , but the spelling ''Plautdietsch'' is used to refer specifically to the Vistula variant of the language. Plautdietsch was a German dialect like others until it was taken by Mennonite settlers to the southwest of the Russian Empire starting in 1789. From there it evolved and subsequent waves of migration brought it to North America, starting in 1873. In Latin America the first settlement occurred in Argentina in 1877 coming from Russia. Plautdietsch is spoken by about 400,000 Russian Mennonites, most notably in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. "Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented in writing since about 1225/34 ('' Sachsenspiegel''). During the Hanseatic period (from about 1300 to about 1600), Middle Low German was the leading written language in the north of Central Europe and served as a lingua franca in the northern half of Europe. It was used parallel to medieval Latin also for purposes of diplomacy and for deeds. Terminology While ''Middle Low German'' (MLG) is a scholarly term developed in hindsight, speakers in their time referred to the language mainly as (Saxon) or (the Saxon language). This terminology was also still known in Luther's time in the adjacent Central German-speaking areas. Its Latin equivalent was also used as meaning 'Low German' (among other meanings). Some languages whose first contacts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Low German
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). It is a West Germanic language, closely related to the Anglo-Frisian languages. It is documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it gradually evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken throughout modern northwestern Germany, primarily in the coastal regions and in the eastern Netherlands by Saxons, a Germanic tribe that inhabited the region of Saxony. It partially shares Anglo-Frisian's (Old Frisian, Old English) Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law which sets it apart from Low Franconian and Irminonic languages, such as Dutch, Luxembourgish and German. The grammar of Old Saxon was fully inflected with five grammatical cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, and instrumental), three grammatical numbers (singular, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
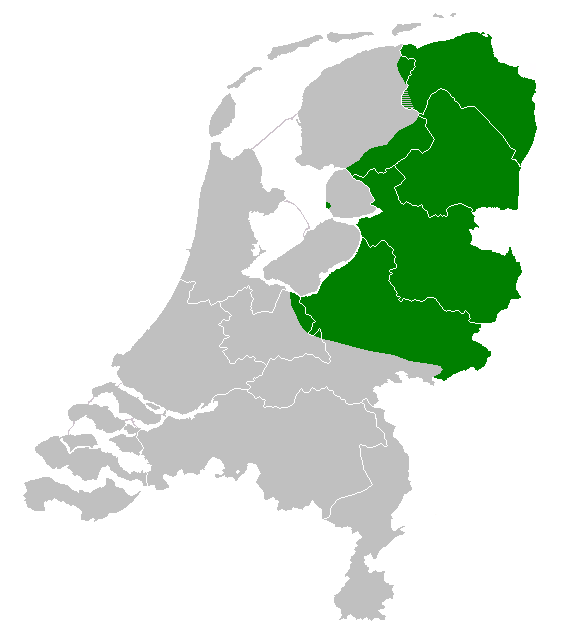
West Low German
Low Saxon, also known as West Low German ( nds, Nedersassisch, Nedersaksies; nl, Nedersaksisch) are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark (in North Schleswig by parts of the German-speaking minority). It is one of two groups of mutually intelligible dialects, the other being East Low German dialects. A 2005 study found that there were approximately 1.8 million "daily speakers" of Low Saxon in the Netherlands. 53% spoke Low Saxon or Low Saxon and Dutch at home and 71% could speak it. loemhoff, H. (2005). Taaltelling Nedersaksisch. Een enquête naar het gebruik en de beheersing van het Nedersaksisch in Nederland. Groningen: Sasland./ref> According to another study the percentage of speakers among parents dropped from 34% in 1995 to 15% in 2011. The percentage of speakers among their children dropped from 8% to 2% in the same period. Extent The language area comprises the North German states of Lower Saxony, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Germanic
: : : : : (70,000) (30,000) (8,000) , familycolor = Indo-European , fam2 = Germanic , fam3 = West Germanic , fam4 = North Sea Germanic , ancestor = Old Saxon , ancestor2 = Middle Low German , dia1 = West Low German , dia2 = East Low German , iso2 = nds , iso3 = nds , iso3comment = (Dutch varieties and Westphalian have separate codes) , lingua = 52-ACB , map = Nds Spraakrebeet na1945.svg , mapcaption = Present day Low German language area in Europe. , glotto = lowg1239 , glottoname = Low German , notice = IPA Low German or Low Saxon (in the language itself: , and other names; german: Plattdeutsch, ) is a West Germanic language variety spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern part of the Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theo Vennemann
Theo Vennemann genannt Nierfeld (; born 27 May 1937 in Oberhausen-Sterkrade) is a German historical linguist known for his controversial theories of a "Vasconic" and an "Atlantic" stratum in European languages, published since the 1990s. He was professor of Germanic and theoretical linguistics at Ludwig Maximilian University, Munich from 1974 (retired 2005). Theories Vennemann's book ''Europa Vasconica – Europa Semitica'' (2003) was reviewed in '' Lingua'' by linguists Philip Baldi and B. Richard Page, who made reasoned dismissals of a number of his proposals. The reviewers still applauded Vennemann's "efforts to reassess the role and extent of language contact in the development of Indo-European languages in Europe". Vennemann's controversial claims about the prehistory of European languages include the following: * Vasconic substratum theory: A "Vasconic" language family ancestral to Basque is a substratum of European languages, especially Germanic, Celtic, and It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
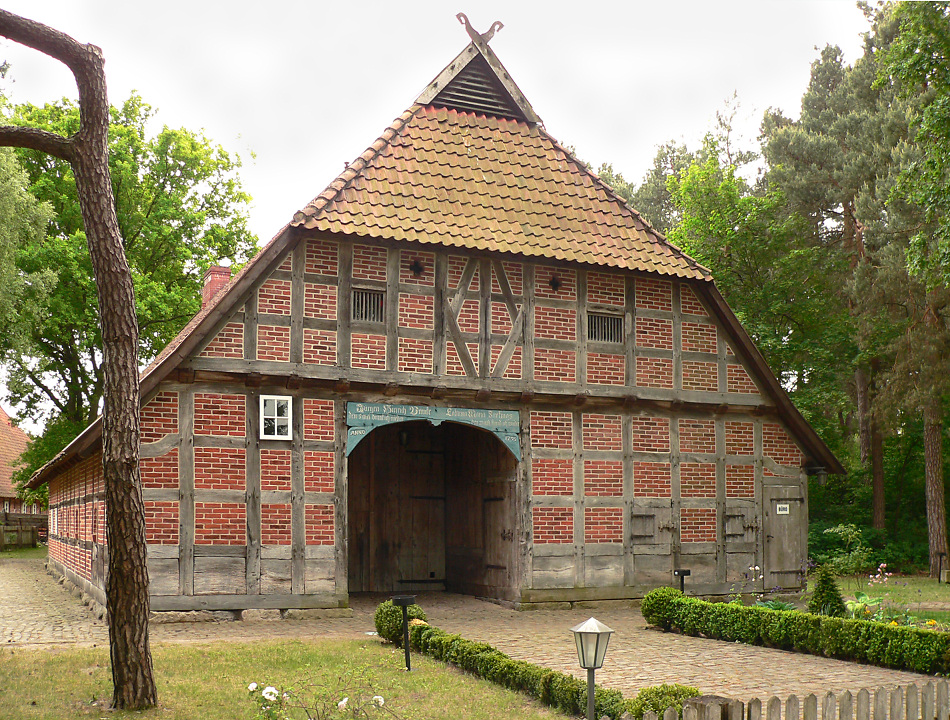
Low German House
The Low German house or ''Fachhallenhaus'' is a type of timber-framed farmhouse found in northern Germany and the easternmost Netherlands, which combines living quarters, byre and barn under one roof. It is built as a large hall with bays on the sides for livestock and storage and with the living accommodation at one end. The Low German house appeared during the 13th to 15th centuries and was referred to as the Low Saxon house (''Niedersachsenhaus'') in early research works. Until its decline in the 19th century, this rural, agricultural farmhouse style was widely distributed through the North German Plain, all the way from the Lower Rhine to Mecklenburg. Even today, the ''Fachhallenhaus'' still characterises the appearance of many north German villages. Name The German name, ''Fachhallenhaus'', is a regional variation of the term ''Hallenhaus'' ("hall house", sometimes qualified as the "Low Saxon hall house"). In the academic definition of this type of house the word ''Fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |