|
Low-velocity Zone
In geology, the low-velocity zone (LVZ) occurs close to the boundary between the lithosphere and the asthenosphere in the upper mantle. It is characterized by unusually low seismic shear wave velocity compared to the surrounding depth intervals. This range of depths also corresponds to anomalously high electrical conductivity. It is present between about 80 and 300 km depth. This appears to be universally present for S waves, but may be absent in certain regions for P waves. A second low-velocity zone (not generally referred to as the LVZ, but as ULVZ) has been detected in a thin ≈50 km layer at the core-mantle boundary. These LVZs may have important implications for plate tectonics and the origin of the Earth's crust. The LVZ has been interpreted to indicate the presence of a significant degree of partial melting, and alternatively as a natural consequence of a thermal boundary layer and the effects of pressure and temperature on the elastic wave velocity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speeds Of Seismic Waves
In kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a non-negative scalar quantity. Introduction of the speed/velocity terminology by Prof. Tait, in 1882. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance travelled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as the duration of the time interval approaches zero. Speed is the magnitude of ''velocity'' (a vector), which indicates additionally the direction of motion. Speed has the dimensions of distance divided by time. The SI unit of speed is the metre per second (m/s), but the most common unit of speed in everyday usage is the kilometre per hour (km/h) or, in the US and the UK, miles per hour (mph). For air and marine travel, the knot is commonly used. The fastest possible speed at which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-wave Velocity
__NOTOC__ In seismology and other areas involving elastic waves, S waves, secondary waves, or shear waves (sometimes called elastic S waves) are a type of elastic wave and are one of the two main types of elastic body waves, so named because they move through the body of an object, unlike surface waves. S waves are transverse waves, meaning that the direction of particle movement of an S wave is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, and the main restoring force comes from shear stress. Therefore, S waves cannot propagate in liquids with zero (or very low) viscosity; however, they may propagate in liquids with high viscosity. Similarly, S waves cannot travel through gases. The name ''secondary wave'' comes from the fact that they are the second type of wave to be detected by an earthquake seismograph, after the compressional primary wave, or P wave, because S waves travel more slowly in solids. Unlike P waves, S waves cannot travel through the molten outer core of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Axis Theorem
The tennis racket theorem or intermediate axis theorem, is a kinetic phenomenon of classical mechanics which describes the movement of a rigid body with three distinct principal moments of inertia. It has also been dubbed the Dzhanibekov effect, after Soviet cosmonaut Vladimir Dzhanibekov, who noticed one of the theorem's logical consequences whilst in space in 1985. The effect was known for at least 150 years prior, having been described by Louis Poinsot in 1834 and included in standard physics textbooks such as ''Classical Mechanics'' by Herbert Goldstein throughout the 20th century. The theorem describes the following effect: rotation of an object around its first and third principal axes is stable, whereas rotation around its second principal axis (or intermediate axis) is not. This can be demonstrated by the following experiment: Hold a tennis racket at its handle, with its face being horizontal, and throw it in the air such that it performs a full rotation around its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Core Super-rotation
Inner core super-rotation is a hypothesized eastward rotation of the inner core of Earth relative to its mantle (geology), mantle, for a net rotation rate that is usually faster than Earth as a whole. A 1995 model of dynamo theory, Earth's dynamo proposed super-rotations of up to 3 degrees per year; the following year, a seismic study claimed that the proposal was supported by observed discrepancies in the time that p-waves take to travel through the inner and outer core. However, the hypothesis of super-rotation is disputed in the later seismic studies. The seismic support of inner core super-rotations was based on the changes of seismic waves that transversed inside the inner core and Seismic wave#Normal modes, free oscillations of Earth. The results are inconsistent between the studies. A localized temporal change of the inner core surface was discovered in 2006 and the temporal change of inner core surface also provided an explanation to the seismic evidence that was attribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzhanibekov Effect
The tennis racket theorem or intermediate axis theorem, is a kinetic phenomenon of classical mechanics which describes the movement of a rigid body with three distinct principal moments of inertia. It has also been dubbed the Dzhanibekov effect, after Soviet cosmonaut Vladimir Dzhanibekov, who noticed one of the theorem's logical consequences whilst in space in 1985. The effect was known for at least 150 years prior, having been described by Louis Poinsot in 1834 and included in standard physics textbooks such as ''Classical Mechanics'' by Herbert Goldstein throughout the 20th century. The theorem describes the following effect: rotation of an object around its first and third principal axes is stable, whereas rotation around its second principal axis (or intermediate axis) is not. This can be demonstrated by the following experiment: Hold a tennis racket at its handle, with its face being horizontal, and throw it in the air such that it performs a full rotation around its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataclysmic Pole Shift Hypothesis
The cataclysmic pole shift hypothesis is a pseudo-scientific claim that there have been recent, geologically rapid shifts in the axis of rotation of Earth, causing calamities such as floods and tectonic events or relatively rapid climate changes. There is evidence of precession and changes in axial tilt, but this change is on much longer time-scales and does not involve relative motion of the spin axis with respect to the planet. However, in what is known as true polar wander, the Earth rotates with respect to a fixed spin axis. Research shows that during the last 200 million years a total true polar wander of some 30° has occurred, but that no rapid shifts in Earth's geographic axial pole were found during this period. A characteristic rate of true polar wander is 1° or less per million years. Between approximately 790 and 810 million years ago, when the supercontinent Rodinia existed, two geologically rapid phases of true polar wander may have occurred. In each of these, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
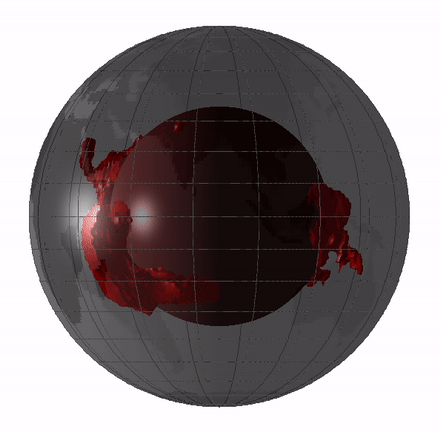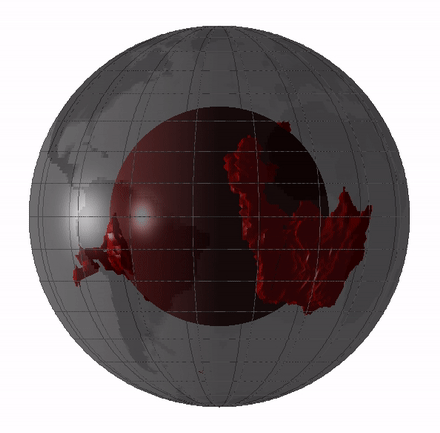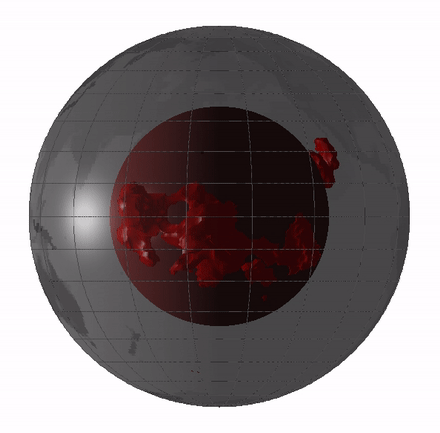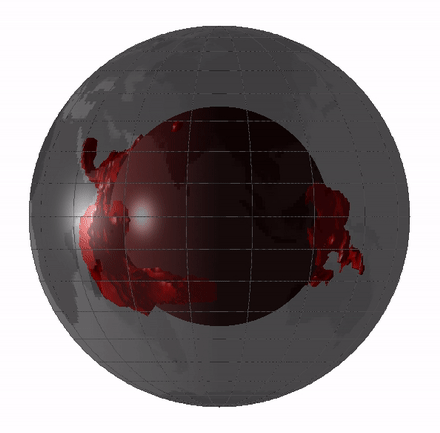
Large Low-shear-velocity Provinces
Large low-shear-velocity provinces (LLSVPs), also called large low-velocity provinces (LLVPs) or superplumes, are characteristic structures of parts of the lowermost mantle, the region surrounding the outer core deep inside the Earth. These provinces are characterized by slow shear wave velocities and were discovered by seismic tomography of deep Earth. There are two main provinces: the African LLSVP and the Pacific LLSVP, both extending laterally for thousands of kilometers and possibly up to 1,000 kilometres vertically from the core–mantle boundary. These have been named Tuzo and Jason respectively, after Tuzo Wilson and W. Jason Morgan, two geologists acclaimed in the field of plate tectonics. The Pacific LLSVP is across and underlies four hotspots on Earth's crust that suggest multiple mantle plumes underneath. These zones represent around 8% of the volume of the mantle, or 6% of the entire Earth. Other names for LLSVPs and their superstructures include superswells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle Plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspots, such as Hawaii or Iceland, and large igneous provinces such as the Deccan and Siberian Traps. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries. Concepts Mantle plumes were first proposed by J. Tuzo Wilson in 1963 and further developed by W. Jason Morgan in 1971 and 1972. A mantle plume is posited to exist where super-heated material forms ( nucleates) at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle. Rather than a continuous stream, plumes should be viewed as a series of hot bubbles of material. Reaching the brittle upper Earth's crust they form diapirs. These diapirs are "hotspots" in the crust. In particular, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterworth-Heinemann
Butterworth–Heinemann is a British publishing company specialised in professional information and learning materials for higher education and professional training, in printed and electronic forms. It was formed in 1990 by the merger of Heinemann Professional Publishing and Butterworths Scientific, both subsidiaries of Reed International. With its earlier constituent companies, the founding dates back to 1923. It has publishing units in Oxford (UK) and Waltham, Massachusetts (United States). As of 2006, it is an imprint of Elsevier. See also *LexisNexis Butterworths LexisNexis is an American data analytics company headquartered in New York, New York. Its products are various databases that are accessed through online portals, including portals for computer-assisted legal research (CALR), newspaper search, ... References External links * Book publishing companies of the United Kingdom Elsevier imprints {{publish-corp-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows electric current. Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek letter (rho). The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-metre (Ω⋅m). For example, if a solid cube of material has sheet contacts on two opposite faces, and the resistance between these contacts is , then the resistivity of the material is . Electrical conductivity (or specific conductance) is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. It represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly signified by the Greek letter (sigma), but (kappa) (especially in electrical engineering) and (gamma) are sometimes used. The SI unit of electrical conductivity is siemens per metre (S/m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows electric current. Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek alphabet, Greek letter (Rho (letter), rho). The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-metre (Ω⋅m). For example, if a solid cube of material has sheet contacts on two opposite faces, and the Electrical resistance, resistance between these contacts is , then the resistivity of the material is . Electrical conductivity (or specific conductance) is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. It represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly signified by the Greek letter (Sigma (letter), sigma), but (kappa) (especially in electrical engineering) and (gamma) are sometimes used. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lehmann Discontinuity
__NOTOC__ The Lehmann discontinuity is an abrupt increase of ''P''-wave and ''S''-wave velocities at the depth of in Earth's mantle, discovered by seismologist Inge Lehmann. It appears beneath continents, but not usually beneath oceans, and does not readily appear in globally averaged studies. Several explanations have been proposed: a lower limit to the pliable asthenosphere, a phase transition, and most plausibly, depth variation in the shear wave anisotropy. Notes General references * – some historic background. Further reading External linksInge Lehmann UCLA The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the C ...Career highlights of Inge Lehmann from UCLA Structure of the Earth {{geophysics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |