|
Low-latency Queuing
Low-latency queuing (LLQ) is a network scheduling feature developed by Cisco to bring strict priority queuing (PQ) to class-based weighted fair queuing (CBWFQ). LLQ allows delay-sensitive data (such as voice) to be given preferential treatment over other traffic by letting the data to be dequeued and sent first. , Cisco IOS Software Releases 12.0 T Development Class-based weighted fair queuing (CB-WFQ) was initially released without the support of a priority queuing system, thus it could not guarantee the delay and (delay variation) requirements of real-time, interactive voice and video conversations. Since for CBWFQ, the weight for a[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Scheduling
A network scheduler, also called packet scheduler, queueing discipline (qdisc) or queueing algorithm, is an arbiter on a node in a packet switching communication network. It manages the sequence of network packets in the transmit and receive queues of the protocol stack and network interface controller. There are several network schedulers available for the different operating systems, that implement many of the existing network scheduling algorithms. The network scheduler logic decides which network packet to forward next. The network scheduler is associated with a queuing system, storing the network packets temporarily until they are transmitted. Systems may have a single or multiple queues in which case each may hold the packets of one flow, classification, or priority. In some cases it may not be possible to schedule all transmissions within the constraints of the system. In these cases the network scheduler is responsible for deciding which traffic to forward and what g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisco Systems
Cisco Systems, Inc. (using the trademark Cisco) is an American multinational corporation, multinational digital communications technology conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develops, manufactures, and sells networking hardware, software, telecommunications equipment and other high-technology services and products. Cisco specializes in specific tech markets, such as the Internet of things (IoT), internet domain, domain security, videoconferencing, and energy management with List of Cisco products, products including Webex, OpenDNS, XMPP, Jabber, Duo Security, Silicon One, and Cisco Jasper, Jasper. Cisco Systems was founded in December 1984 by Leonard Bosack and Sandy Lerner, two Stanford University computer scientists who had been instrumental in connecting computers at Stanford. They pioneered the concept of a local area network (LAN) being used to connect distant computers over a multiprotocol router (computing), route ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priority Queuing
In computer science, a priority queue is an abstract data type similar to a regular queue or stack abstract data type. In a priority queue, each element has an associated ''priority'', which determines its order of service. Priority queue serves highest priority items first. Priority values have to be instances of an ordered data type, and higher priority can be given either to the lesser or to the greater values with respect to the given order relation. For example, in Java standard library, ''PriorityQueues the least elements with respect to the order have the highest priority. This implementation detail is without much practical significance, since passing to the opposite order relation turns the least values into the greatest, and vice versa. While priority queues are often implemented using heaps, they are conceptually distinct. A priority queue can be implemented with a heap or with other methods; just as a list can be implemented with a linked list or with an array. Op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighted Fair Queuing
Weighted fair queueing (WFQ) is a network scheduling algorithm. WFQ is both a packet-based implementation of the generalized processor sharing (GPS) policy, and a natural extension of fair queuing (FQ). Whereas FQ shares the link's capacity in equal subparts, WFQ allows schedulers to specify, for each flow, which fraction of the capacity will be given. Weighted fair queuing is also known as packet-by-packet GPS (PGPS or P-GPS) since it approximates generalized processor sharing "to within one packet transmission time, regardless of the arrival patterns." Parametrization and fairness Like other GPS-like scheduling algorithms, the choice of the weights is left to the network administrator. There is no unique definition of what is "fair" (see for further discussion). By regulating the WFQ weights dynamically, WFQ can be utilized for controlling the quality of service Quality of service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jitter
In electronics and telecommunications, jitter is the deviation from true periodicity of a presumably periodic signal, often in relation to a reference clock signal. In clock recovery applications it is called timing jitter. Jitter is a significant, and usually undesired, factor in the design of almost all communications links. Jitter can be quantified in the same terms as all time-varying signals, e.g., root mean square (RMS), or peak-to-peak displacement. Also, like other time-varying signals, jitter can be expressed in terms of spectral density. Jitter period is the interval between two times of maximum effect (or minimum effect) of a signal characteristic that varies regularly with time. Jitter frequency, the more commonly quoted figure, is its inverse. ITU-T G.810 classifies deviation lower frequencies below 10 Hz as ''wander'' and higher frequencies at or above 10 Hz as ''jitter''. Jitter may be caused by electromagnetic interference and crosstalk with ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Packet
In telecommunications and computer networking, a network packet is a formatted unit of Data (computing), data carried by a packet-switched network. A packet consists of control information and user data; the latter is also known as the ''Payload (computing), payload''. Control information provides data for delivering the payload (e.g., source and destination network addresses, error detection codes, or sequencing information). Typically, control information is found in packet Header (computing), headers and Trailer (computing), trailers. In packet switching, the Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth of the transmission medium is shared between multiple communication sessions, in contrast to circuit switching, in which circuits are preallocated for the duration of one session and data is typically transmitted as a continuous bit stream. Terminology In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, ''packet'' strictly refers to a protocol data unit at layer 3, the network layer. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (computing)
In computing, bandwidth is the maximum rate of data transfer across a given path. Bandwidth may be characterized as network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth. This definition of ''bandwidth'' is in contrast to the field of signal processing, wireless communications, modem data transmission, digital communications, and electronics, in which ''bandwidth'' is used to refer to the signal bandwidth measured in hertz, meaning the frequency range between lowest and highest attainable frequency while meeting a well-defined impairment level in signal power. The actual bit rate that can be achieved depends not only on the signal bandwidth but also on the noise on the channel. Network capacity The term ''bandwidth'' sometimes defines the net bit rate ''peak bit rate'', ''information rate'', or physical layer ''useful bit rate'', channel capacity, or the maximum throughput of a logical or physical communication path in a digital communication system. For example, bandwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Service
Quality of service (QoS) is the description or measurement of the overall performance of a service, such as a telephony or computer network, or a cloud computing service, particularly the performance seen by the users of the network. To quantitatively measure quality of service, several related aspects of the network service are often considered, such as packet loss, bit rate, throughput, transmission delay, availability, jitter, etc. In the field of computer networking and other packet-switched telecommunication networks, quality of service refers to traffic prioritization and resource reservation control mechanisms rather than the achieved service quality. Quality of service is the ability to provide different priorities to different applications, users, or data Traffic flow (computer networking), flows, or to guarantee a certain level of performance to a data flow. Quality of service is particularly important for the transport of traffic with special requirements. In particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QPPB
The QoS Policy Propagation via BGP (QPPB) is a mechanism that allows propagation of quality of service (QoS) policy and classification by the sending party based on access lists, community lists, and autonomous system paths in the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), thus helping to classify based on destination instead of source address. See also * Computer network * Traffic engineering (telecommunications) Traffic engineering can mean: * Traffic engineering (transportation), a branch of civil engineering * Teletraffic engineering Teletraffic engineering, or telecommunications traffic engineering is the application of transportation traffic enginee ... External links ASR9000/XR: Implementing QOS policy propagation for BGP (QPPB)* Internet architecture {{compu-network-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
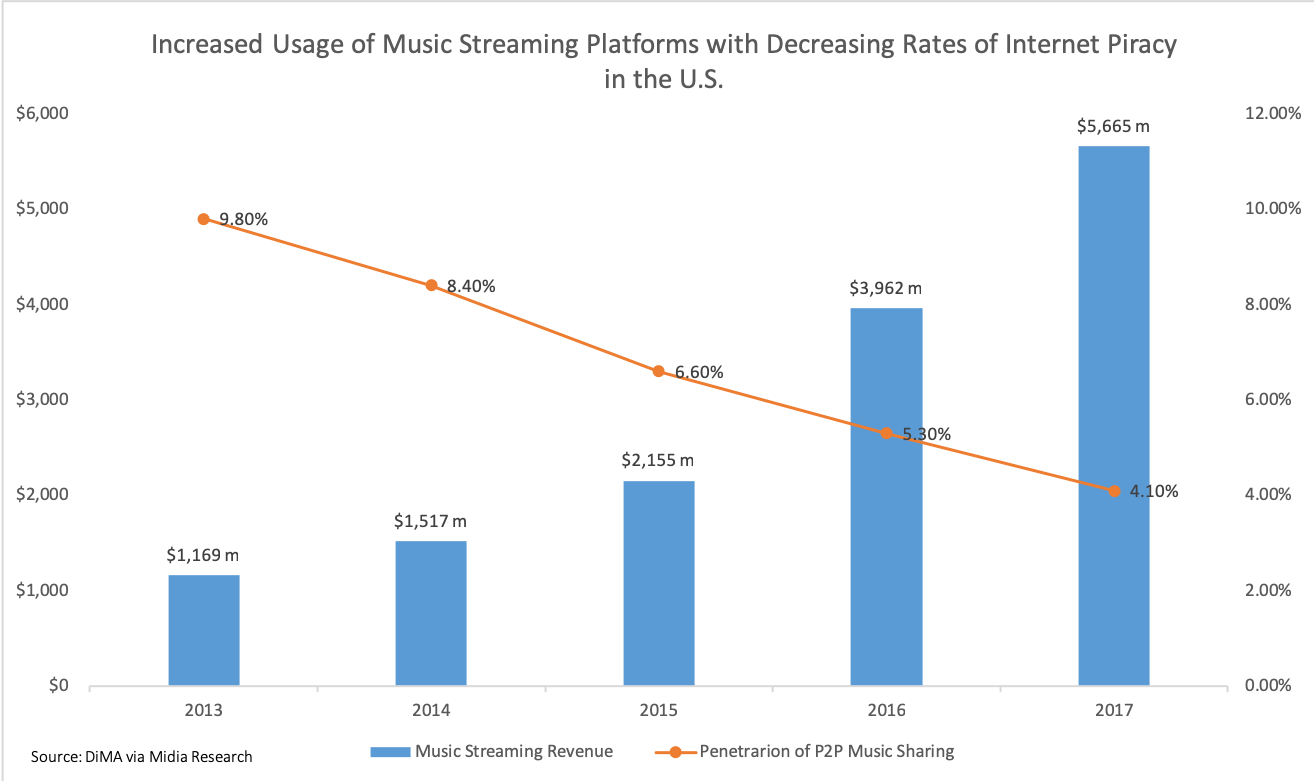
Streaming Media
Streaming media refers to multimedia delivered through a Computer network, network for playback using a Media player (other), media player. Media is transferred in a ''stream'' of Network packet, packets from a Server (computing), server to a client-server model, client and is rendered in real-time; this contrasts with file downloading, a process in which the end-user obtains an entire media file before consuming the content. Streaming is more commonly used for video on demand, streaming television, and music streaming services over the Internet. While streaming is most commonly associated with multimedia from a remote server over the Internet, it also includes offline multimedia between devices on a local area network. For example, using DLNA and a home server, or in a personal area network between two devices using Bluetooth (which uses radio waves rather than Internet Protocol, IP). Online streaming was initially popularized by RealNetworks and Microsoft in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Shaping
Traffic shaping is a bandwidth management technique used on computer networks which delays some or all datagrams to bring them into compliance with a desired ''traffic profile''. Traffic shaping is used to optimize or guarantee performance, improve latency, or increase usable bandwidth for some kinds of packets by delaying other kinds. It is often confused with traffic policing, the distinct but related practice of packet dropping and packet marking. The most common type of traffic shaping is application-based traffic shaping. In application-based traffic shaping, fingerprinting tools are first used to identify applications of interest, which are then subject to shaping policies. Some controversial cases of application-based traffic shaping include bandwidth throttling of peer-to-peer file sharing traffic. Many application protocols use encryption to circumvent application-based traffic shaping. Another type of traffic shaping is route-based traffic shaping. Route-based traf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |