|
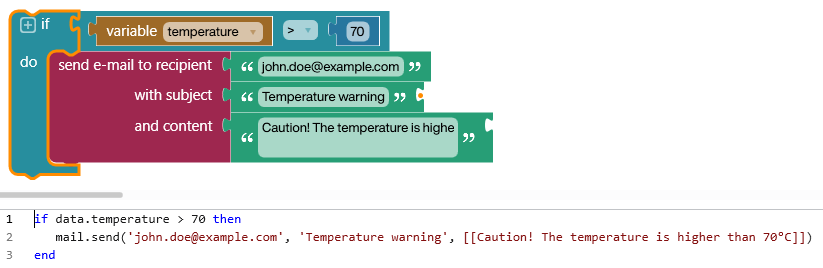
Low-code Development Platforms
A low-code development platform (LCDP) provides a development environment used to create application software, generally through a graphical user interface (as opposed to only writing code, though some coding is possible and may be required). A low-coded platform may produce entirely operational applications, or require additional coding for specific situations. Low-code development platforms are typically on a High-level programming language, high abstraction level, and can reduce the amount of traditional time spent, enabling accelerated delivery of business applications. A common benefit is that a wider range of people can contribute to the application's development, not only those with coding skills, but good governance is needed to be able to adhere to common rules and regulations. LCDPs can also lower the initial cost of setup, training, deployment, and maintenance. Low-code development platforms trace their roots back to fourth-generation programming language and the rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backend As A Service
Backend as a service (BaaS), sometimes also referred to as mobile backend as a service (MBaaS), is a service for providing web app and mobile app developers with a way to easily build a backend to their frontend applications. Features available include user management, push notifications, and integration with social networking services. These services are provided via the use of custom software development kits (SDKs) and application programming interfaces (APIs). BaaS is a relatively recent development in cloud computing, with most BaaS startups dating from 2011 or later. Some of the most popular service providers are AWS Amplify and Firebase. Purpose Web and mobile apps require a similar set of features on the backend, including notification service, integration with social networks, and cloud storage. Each of these services has its own API that must be individually incorporated into an app, a process that can be time-consuming and complicated for app developers. BaaS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Low-code Development Platforms
Below is a list of notable low-code development platforms. Implementations * AppSheet is a no-code application from Google that offers users the ability to create applications for mobile and web. * Acceleo is an open-source code generator for Eclipse used to generate any textual language (Java, PHP, Python, etc.) from EMF models defined from any many ( UML, SysML, etc.). * Actifsource is a plugin for Eclipse that allows graphical modelling and model-based code generation using custom templates. * Appian is an enterprise low-code automation platform for mobile application development. The platform includes a visual interface and pre-built development modules. * Betty Blocks is a low-code platform for building custom applications, such as branded web portals, feature-rich business solutions, and modern digital experiences. * Caspio is a low-code application development platform for creating online databases and web applications. * DMS Software Reengineering Toolkit is a syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Online Database Creator Apps
This list of online database creator apps lists notable web apps where end users with minimal database administration expertise can create online databases to share with team members. Users need not have the coding skills to manage the solution stack themselves, because the web app already provides this predefined functionality. Such online database creator apps serve the gap between IT professionals (who can manage such a stack themselves) and people who would not create databases at all anyway. In other words, they provide a low-code way of doing database administration. As the concept of low-code development in general continues to evolve, some of the brands that began as online database creator apps are evolving into low-code development platforms A low-code development platform (LCDP) provides a development environment used to create application software, generally through a graphical user interface (as opposed to only writing code, though some coding is possible and may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow-based Programming
In computer programming, flow-based programming (FBP) is a programming paradigm that defines application software, applications as networks of black box process (computer science), processes, which exchange data across predefined connections by message passing, where the connections are specified ''externally'' to the processes. These black box processes can be reconnected endlessly to form different applications without having to be changed internally. FBP is thus naturally Software componentry, component-oriented. FBP is a particular form of dataflow programming based on bounded buffers, information packets with defined lifetimes, named ports, and separate definition of connections. Introduction Flow-based programming defines applications using the metaphor of a "data factory". It views an application not as a single, sequential process, which starts at a point in time, and then does one thing at a time until it is finished, but as a network of asynchronous processes communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End-user Development
End-user development (EUD) or end-user programming (EUP) refers to activities and tools that allow end-users – people who are not professional software developers – to program computers. People who are not professional developers can use EUD tools to create or modify ''software artifacts'' (descriptions of automated behavior) and complex data objects without significant knowledge of a programming language. In 2005 it was estimated (using statistics from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics) that by 2012 there would be more than 55 million end-user developers in the United States, compared with fewer than 3 million professional programmers. Various EUD approaches exist, and it is an active research topic within the field of computer science and human-computer interaction. Examples include natural language programming, spreadsheets, scripting languages (particularly in an office suite or art application), visual programming, trigger-action programming and programming by examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End-user Computing
End-user computing (EUC) refers to systems in which non-programmers can create working applications. EUC is a group of approaches to computing that aim to better integrate end users into the computing environment. These approaches attempt to realize the potential for high-end computing to perform problem-solving in a trustworthy manner. End-user computing can range in complexity from users simply clicking a series of buttons, to citizen developers writing scripts in a controlled scripting language, to being able to modify and execute code directly. Examples of end-user computing are systems built using fourth-generation programming languages, such as MAPPER or SQL, or one of the fifth-generation programming languages, such as ICAD. Factors Factors contributing to the need for further EUC research include knowledge processing, pervasive computing, issues of ontology, interactive visualization, and the like. Some of the issues related to end-user computing concern software arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRAKON
DRAKON () is a Free and open-source software, free and open source algorithmic visual programming language, visual programming and modeling language developed as part of the defunct Soviet Union Buran program, Buran space program in 1986 following the need in increase of software development productivity. The visual language provides a uniform way to represent processes in flowcharts. There are various implementation of the language specification that may be used to draw and export actual flowcharts. Notable examples include free and open source DRAKON Editor (September 2011). History The development of DRAKON started in 1986 to address the emerging risk of misunderstandings - and subsequent errors - between users of different programming languages in the Russian space program. Its development was directed by Vladimir Parondzhanov with the participation of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Academician Pilyugin Center, Moscow) and Russian Academy of Sciences (Keldysh Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shadow IT
In organizations, shadow IT refers to information technology (IT) systems deployed by departments other than the central IT department, to bypass limitations and restrictions that have been imposed by central information systems. While it can promote innovation and productivity, shadow IT introduces security risks and compliance concerns, especially when such systems are not aligned with corporate governance. Origins Information systems in large organizations can be a source of frustration for their users. In order to bypass limitations of solutions provided by a centralized IT department, as well as restrictions that are deemed detrimental to individual productivity, non-IT departments might develop independent IT resources and for the specific or urgent need or requirements. In some cases, IT specialists could be recruited or software solutions procured outside of the centralized IT department, sometimes without the knowledge, or approval of corporate governance channels. Ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governance, Risk Management, And Compliance
Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) is the term covering an organization's approach across these three practices: governance, risk management, and compliance amongst other disciplines. The first scholarly research on GRC was published in 2007 by OCEG's founder, Scott Mitchell, where GRC was formally defined as "the integrated collection of capabilities that enable an organization to reliably achieve objectives, address uncertainty and act with integrity" aka ''Principled Performance®''. The research referred to common "keep the company on track" activities conducted in departments such as internal audit, compliance, risk, legal, finance, IT, HR as well as the lines of business, executive suite and the board itself. Overview Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) are three related facets that aim to assure an organization reliably achieves objectives, addresses uncertainty and acts with integrity. Governance is the combination of processes established and executed by the dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |