|
Loss And Damage (climate Change)
Loss and damage (in the context of climate change) is a concept to describe results from the adverse effects of climate change and how to deal with them (beyond climate change adaptation). There has been slow progress on implementing mitigation and adaptation. Some losses and damages are already occurring, and further loss and damage is unavoidable. There is a distinction between economic losses and non-economic losses. The main difference between the two is that non-economic losses involve things that are not commonly traded in markets. The appropriate response by governments to loss and damage has been disputed since the UNFCCC's adoption of the term and concept. Establishing liability and compensation for loss and damage has been a long-standing goal for vulnerable and developing countries in the Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS) and the Least Developed Countries Group in negotiations. However, developed countries have resisted this. The present UNFCCC mechanism to address ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices increase greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Due to climate change, deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Increased warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Impact On The Environment
Human impact on the environment (or anthropogenic impact) refers to changes to biophysical environments and to ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources caused directly or indirectly by humans. Modifying the environment to fit the needs of built environment, society is causing severe effects including global warming, environmental degradation (such as ocean acidification), Holocene extinction, mass extinction and biodiversity loss, ecological crisis, and ecological collapse. Some human activities that cause damage (either directly or indirectly) to the environment on a global scale include population growth, overconsumption, overexploitation, pollution, and deforestation. Some of the problems, including global warming and biodiversity loss, have been proposed as representing Global catastrophic risk, catastrophic risks to the survival of the human species. The term ''anthropogenic'' designates an effect or object resulting from human activity. The term was first used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Assessment Report
The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess scientific, technical, and socio-economic information concerning climate change. Three Working Groups (WGI, II, and III) have been working on the following topics: The Physical Science Basis (WGI); Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (WGII); Mitigation of Climate Change (WGIII). Of these, the first study was published in 2021, the second report February 2022, and the third in April 2022. The final synthesis report is due to be finished by early 2023. The first of the three working groups published its report on 9 August 2021, ''Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis''. A total of 234 scientists from 66 countries contributed to this first working group (WGI) report. The authors built on more than 14,000 scientific papers to produce a 3,949-page report, which was then approved by 195 governments. The Summary for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This type of research typically involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, or observations in order to collect data that is rich in detail and context. Qualitative research is often used to explore complex phenomena or to gain insight into people's experiences and perspectives on a particular topic. It is particularly useful when researchers want to understand the meaning that people attach to their experiences or when they want to uncover the underlying reasons for people's behavior. Qualitative methods include ethnography, grounded theory, discourse analysis, and interpretative phenomenological analysis. Qualitative research methods have been used in sociology, anthropology, political science, psychology, social work, folklore, educational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to advance scientific knowledge about climate change caused by human activities. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) established the IPCC in 1988. The United Nations endorsed the creation of the IPCC later that year. It has a secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, hosted by the WMO. It has 195 member states who govern the IPCC. The member states elect a bureau of scientists to serve through an assessment cycle. A cycle is usually six to seven years. The bureau selects experts to prepare IPCC reports. It draws the experts from nominations by governments and observer organisations. The IPCC has three working groups and a task force, which carry out its scientific work. The IPCC informs governments about the state of knowledge of climate change. It does this by examining all the relevant scientific literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
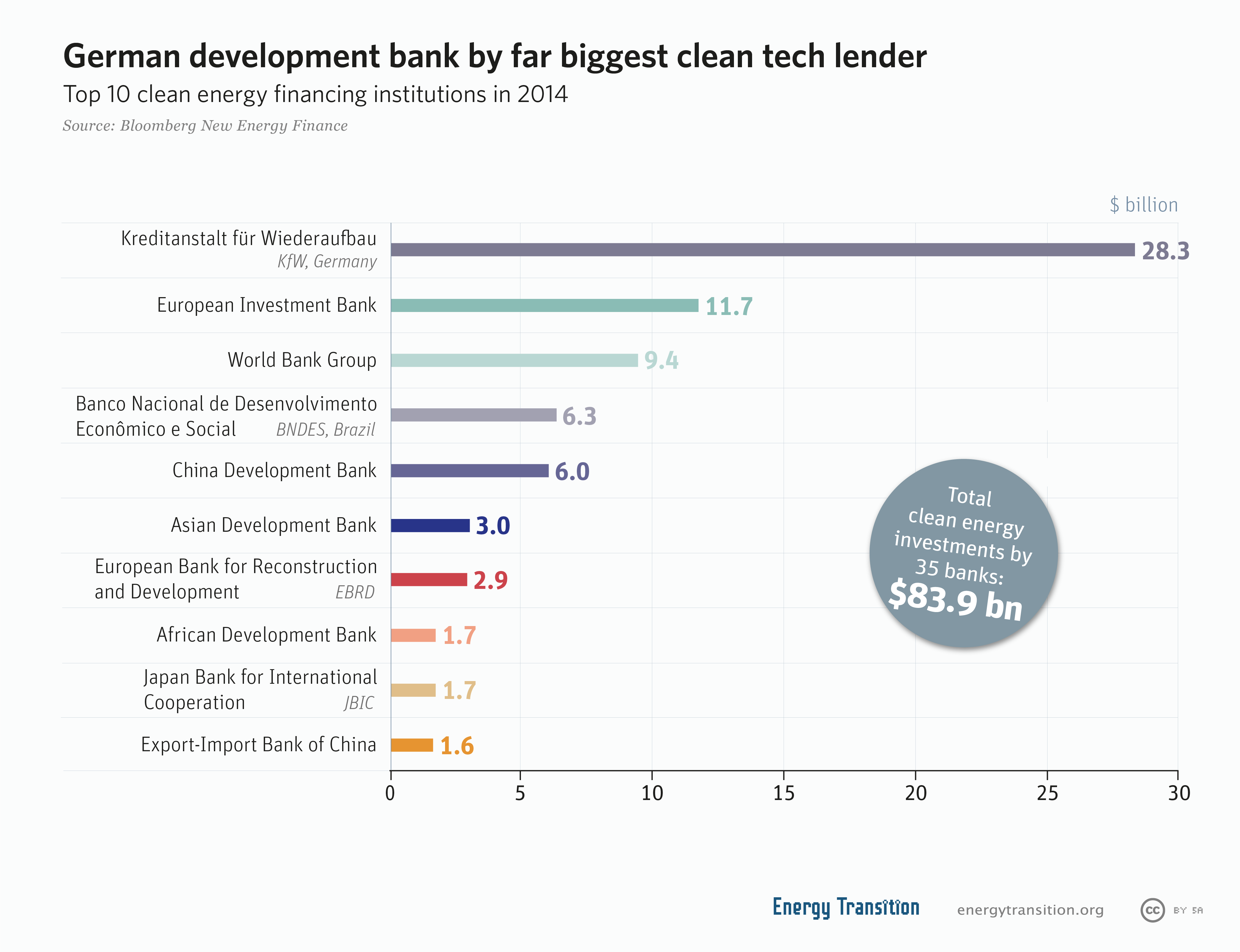
Climate Finance
Climate finance is "finance that aims at reducing emissions, and enhancing sinks of greenhouse gases and aims at reducing vulnerability of, and maintaining and increasing the resilience of, human and ecological systems to negative climate change impacts", as defined by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Standing Committee on Finance. The term has been used in a narrow sense to refer to transfers of public resources from developed to developing countries, in light of their UN Climate Convention obligations to provide "new and additional financial resources", and in a wider sense to refer to all financial flows relating to climate change mitigation and adaptation. The 21st session of the Conference of Parties (COP) to the UNFCCC (Paris 2015) introduced a new era for climate finance, policies, and markets. The Paris Agreement adopted there defined a global action plan to put the world on track to avoid dangerous climate change by limiting global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was negotiated by 196 parties at the 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference near Paris, France. As of September 2022, 194 members of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are parties to the agreement. Of the four UNFCCC member states which have not ratified the agreement, the only major emitter is Iran. The United States withdrew from the Agreement in 2020, but rejoined in 2021. The Paris Agreement was opened for signature on 22 April 2016 ( Earth Day) at a ceremony in New York. After the European Union ratified the agreement, sufficient countries had ratified the Agreement responsible for enough of the world's greenhouse gases for the Agreement to enter into force o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bali Action Plan
After the 2007 United Nations Climate Change Conference held on the island of Bali in Indonesia in December 2007, the participating nations adopted the Bali Road Map as a two-year process working towards finalizing a binding agreement at the 2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference in Copenhagen, Denmark. The conference encompassed meetings of several bodies, including the 13th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP 13) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and the third session of the Conference of the Parties serving as the meeting of the Parties to the Kyoto Protocol (CMP 3). The Bali Road Map includes the Bali Action Plan (BAP), which was adopted by Decision 1/CP.13 of COP-13. It also includes the Ad Hoc Working Group on Further Commitments for Annex I Parties under the Kyoto Protocol (AWG-KP) negotiations and their 2009 deadline, the launch of the Adaptation Fund, the scope and content of the Article 9 review of the Kyoto Protocol, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flat Coast
At a flat coast or flat shoreline, the land descends gradually into the sea. Flat coasts can be formed either as a result of the sea advancing into gently-sloping terrain or through the abrasion of loose rock. They may be basically divided into two parallel strips: the shoreface and the beach. Flat coasts consist of loose material such as sand and gravel. Wind transports finer grains of sand inland over the dunes. The sea washes pebbles and sand away from the coast and dumps it at other locations. Flat coast littoral series The typical sequence of landforms created by the sea is described as a "littoral series". Sandbars, runnels and creeks The littoral series of a flat coast starts in the permanently flooded shallow water region, or shoreface, with a sand or gravel reef (also called a bar). The longshore bar is an elongated ridge of sand found parallel to the shore in the surf zone on many flat coasts. It consists mainly of sand or gravel, depending on the material avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Compensation
Financial compensation refers to the act of providing a person with money or other things of economic value in exchange for their goods, labor, or to provide for the costs of injuries that they have incurred. Kinds of financial compensation include: * Damages, legal term for the financial compensation recoverable by reason of another's breach of duty * Nationalization compensation, compensation paid in the event of nationalization of property * Payment * Remuneration ** Deferred compensation ** Executive compensation ** Royalties ** Salary ** Wage ** Employee benefits * Workers' compensation, to protect employees who have incurred work-related injuries See also * Income * Faithless servant The faithless servant doctrine is a doctrine under the laws of a number of states in the United States, and most notably New York State law, pursuant to which employees who act unfaithfully towards their employers must forfeit to their employers a ... Monetary economics {{financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Liability
In law, liable means "responsible or answerable in law; legally obligated". Legal liability concerns both civil law and criminal law and can arise from various areas of law, such as contracts, torts, taxes, or fines given by government agencies. The claimant is the one who seeks to establish, or prove, liability. Theories of liability Claimants can prove liability through a myriad of different theories, known as theories of liability. Which theories of liability are available in a given case depends on nature of the law in question. For example, in case involving a contractual dispute, one available theory of liability is breach of contract; or in the tort context, negligence, negligence per se, respondeat superior, vicarious liability, strict liability, or intentional conduct are all valid theories of liability. Each theory of liability has certain conditions, or elements, that must be proven by the claimant before liability will be established. For example, the theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference
The 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference, more commonly referred to as COP26, was the 26th United Nations Climate Change conference, held at the SEC Centre in Glasgow, Scotland, United Kingdom, from 31 October to 13 November 2021. The president of the conference was UK cabinet minister Alok Sharma. Delayed for a year due to the COVID-19 pandemic, it was the 26th Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the third meeting of the parties to the 2015 Paris Agreement (designated CMA1, CMA2, CMA3), and the 16th meeting of the parties to the Kyoto Protocol (CMP16). The conference was the first since the Paris Agreement of COP21 that expected parties to make enhanced commitments towards mitigating climate change; the Paris Agreement requires parties to carry out a process colloquially known as the ' ratchet mechanism' every five years to provide improved national pledges. The result of COP26 was the Glasgow C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
