|
Longwave Radio Mast Hellissandur
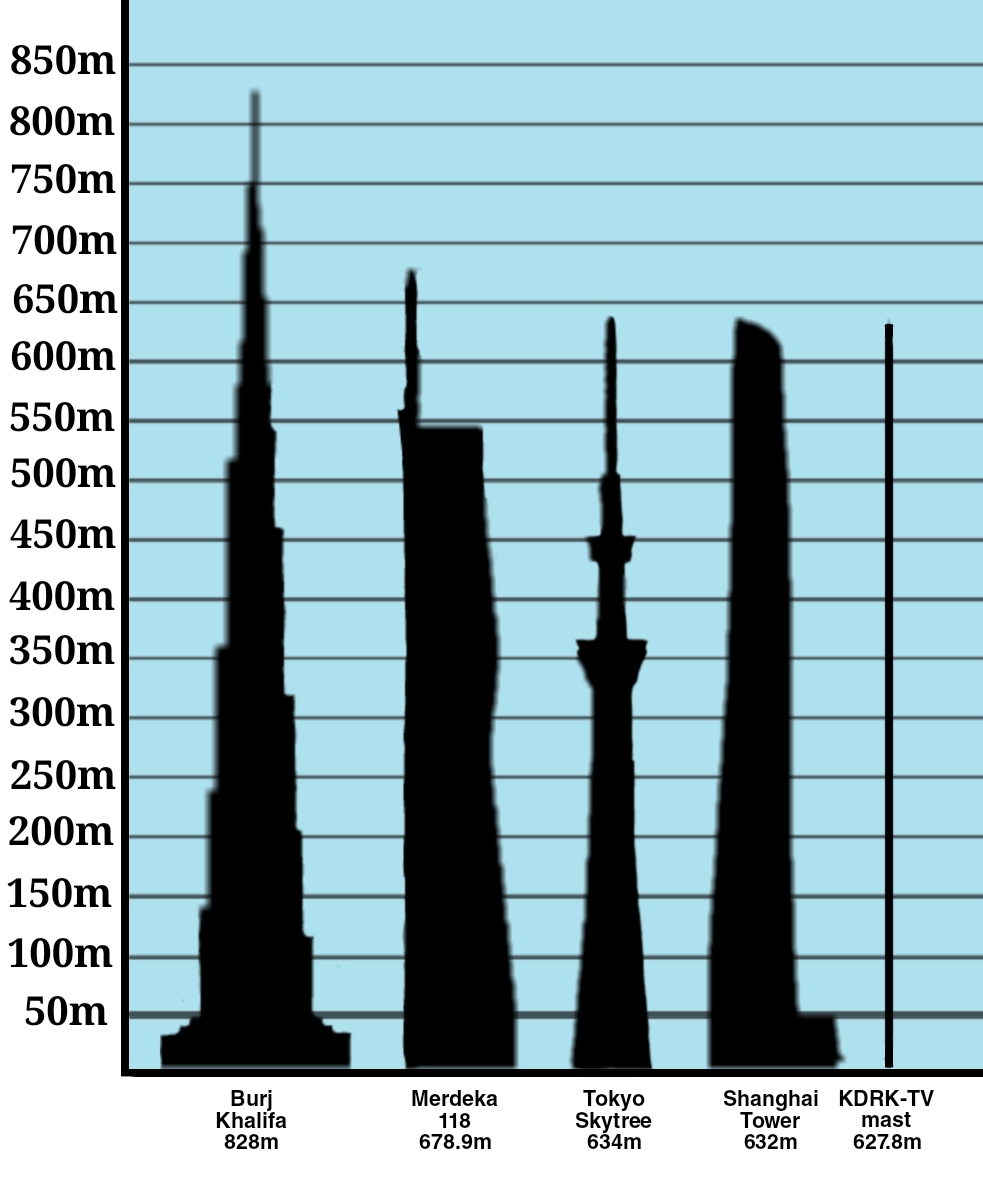
The Hellissandur longwave radio mast ( ) is a tall guyed radio mast formerly used for longwave radio transmissions of RÚV (The Icelandic National Broadcasting Service). It is situated at , near Hellissandur on the Snæfellsnes peninsula of West Iceland. It is currently the tallest longwave radio mast in the world and the tallest above ground structure in Western Europe. It formed part of RÚV's longwave service. It was intended to fill in gaps of the FM radio, serve seafarers and as a critical communications facility. It previously operated in parallel with the less powerful Eiðar longwave transmitter to form nationwide longwave coverage, but Eiðar was demolished in 2023. The mast, which is among the tallest structures in Western Europe, is insulated against the ground, and guyed at five levels by steel ropes, which are subdivided by insulators. It was built in 1963 to replace the tall LORAN-C mast, constructed in 1959 for the North Atlantic LORAN-C chain (GRD 7970 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Masts And Towers
Radio masts and towers are typically tall structures designed to support antenna (radio), antennas for telecommunications and broadcasting, including television. There are two main types: guyed and self-supporting structures. They are among the tallest human-made structures. Masts are often named after the broadcasting organizations that originally built them or currently use them. A mast radiator or radiating tower is one in which the metal mast or tower itself is energized and functions as the transmitting antenna. Terminology The terms "mast" and "tower" are often used interchangeably. However, in structural engineering terms, a tower is a self-supporting or cantilevered structure, while a Guyed mast, mast is held up by stays or guy-wires. ; A ''mast'': is a guyed mast, a thin structure without the shear strength to stand unsupported, that uses attached guy lines for stability. They may be mounted on the ground or on top of buildings. Typical ''masts'' are of steel latt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulator (electricity)
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and electrical conductor, conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are Nonmetal (chemistry), non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even the materials used as insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as electrical breakdown, and the voltage at which it occurs is called the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, Electrical insulation paper, paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Masts And Towers In Europe
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver; this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications. In radio communication, used in radio and television broadcasting, cell phones, two-way radios, wireless networking, and satellite communication, among numerous other uses, radio waves are used to carry information across space from a transmitter to a receiver, by modulating the radio signal (impressing an information signal on the radio wave by varying some aspect of the wave) in the transmitter. In radar, used to locate and track objects like ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrastructure Completed In 1963
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and private physical structures such as roads, railways, bridges, airports, public transit systems, tunnels, water supply, sewers, electrical grids, and telecommunications (including Internet connectivity and broadband access). In general, infrastructure has been defined as "the physical components of interrelated systems providing commodities and services essential to enable, sustain, or enhance societal living conditions" and maintain the surrounding environment. Especially in light of the massive societal transformations needed to mitigate and adapt to climate change, contemporary infrastructure conversations frequently focus on sustainable development and green infrastructure. Acknowledging this importance, the international community has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tallest Structures In Iceland
unt This is a list of the tallest buildings and structures in Iceland. Tallest buildings Tallest structures An incomplete list of the tallest structures in Iceland. This list contains all types of structures. Demolished This lists structures in Iceland that were at least and have since been demolished. References {{TBSW Lists of tallest buildings in Europe, Iceland Towers in Iceland Lists of buildings and structures in Iceland, Tallest buildings Lists of tallest structures by country, Iceland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Masts
The tallest structure in the world is the Burj Khalifa skyscraper at . Listed are guyed masts (such as telecommunication masts), self-supporting towers (such as the CN Tower), skyscrapers (such as the Willis Tower), oil platforms, electricity transmission towers, and bridge support towers. This list is organized by absolute height. See History of the world's tallest structures, Tallest structures by category, and List of tallest buildings for additional information about these types of structures. Terminology Terminological and listing criteria follow Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat definitions. Guyed masts are differentiated from towers – the latter not featuring any guy wires or other support structures; and buildings are differentiated from towers – the former having at least 50% of occupiable floor space although both are self-supporting structures. Lists by height This list includes structures of all types over 350 meters (1148 feet). Plus it includes fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilowatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work (physics), energy transfer. The watt is named in honor of James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish people, Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own Watt steam engine, steam engine in 1776, which became fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one meter per second against a constant opposing force of one Newton (unit), newton, the rate at which Work (physics), work is done is one watt. \mathrm. In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longwave
In radio, longwave (also spelled long wave or long-wave and commonly abbreviated LW) is the part of the radio spectrum with wavelengths longer than what was originally called the medium-wave (MW) broadcasting band. The term is historic, dating from the early 20th century, when the radio spectrum was considered to consist of LW, MW, and short-wave (SW) radio bands. Most modern radio systems and devices use wavelengths which would then have been considered 'ultra-short' (i.e. VHF, UHF, and microwave). In contemporary usage, the term ''longwave'' is not defined precisely, and its intended meaning varies. It may be used for radio wavelengths longer than 1,000 m i.e. frequencies smaller than 300 kilohertz (kHz), including the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) low frequency (LF, 30–300 kHz) and very low frequency (VLF, 3–30 kHz) bands. Sometimes the upper limit is taken to be higher than 300 kHz, but not above the start of the medium wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portugal, Spain, France, and the United Kingdom. From the 16th to 19th centuries, the Atlantic Ocean was the center of both an epo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |