|
Long Gun
A long gun is a category of firearms with long Gun barrel, barrels. In small arms, a ''long gun'' or longarm is generally designed to be held by both hands and braced against the shoulder, in contrast to a handgun, which can be fired being held with a single hand. In the context of cannons and weapon mount, mounted firearms, an artillery ''long gun'' would be contrasted with a field gun or howitzer. Small arms The actual length of the barrels of a long gun is subject to various laws in many jurisdictions, mainly concerning minimum length, sometimes as measured in a specific position or configuration. The National Firearms Act in the United States sets a minimum length of for rifle barrels and for shotgun barrels. Canada sets a minimum of for either. In addition, Canada sets a minimum fireable length for long guns with detachable or folding Stock (firearms), stocks . In the United States, the minimum length for long guns with detachable or folding stocks is with the stock in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbine
A carbine ( or ) is a long gun that has a barrel shortened from its original length. Most modern carbines are rifles that are compact versions of a longer rifle or are rifles chambered for less powerful cartridges. The smaller size and lighter weight of carbines make them easier to handle. They are typically issued to high-mobility troops such as special operations soldiers and paratroopers, as well as to mounted, artillery, logistics, or other non-infantry personnel whose roles do not require full-sized rifles, although there is a growing tendency for carbines to be issued to front-line soldiers to offset the increasing weight of other issued equipment. An example of this is the M4 carbine, the standard issue carbine of the United States Armed Forces. Etymology The name comes from its first users — cavalry troopers called " carabiniers", from the French ''carabine'', from Old French ''carabin'' (soldier armed with a musket), whose origin is unclear. One theory connects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Laying
Gun laying is the process of aiming an artillery piece or turret, such as a gun, howitzer, or mortar, on land, at sea, or in air, against surface or aerial targets. It may be laying for either direct fire, where the gun is aimed directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user, or by indirect fire, where the gun is not aimed directly at a target within the line-of-sight of the user. Indirect fire is determined from the information or data that is collected, calculated, and applied to physical coordinates to identify the location of the target by the user. The term includes automated aiming using, for example, radar-derived target data and computer-controlled guns. Description Gun laying is a set of actions to align the axis of a gun barrel so that it points in the required direction. This alignment is in the horizontal and vertical planes. A gun is "traversed" (rotated in a horizontal plane) to align it with the target, and "elevated" (moved in the vertical plane) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Of Inertia
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular/rotational mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is defined relatively to a rotational axis. It is the ratio between the torque applied and the resulting angular acceleration about that axis. It plays the same role in rotational motion as mass does in linear motion. A body's moment of inertia about a particular axis depends both on the mass and its distribution relative to the axis, increasing with mass and distance from the axis. It is an intensive and extensive properties, extensive (additive) property: for a point particle, point mass the moment of inertia is simply the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second Moment (physics), mome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particle, elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple Mass in special relativity, definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure (mathematics), measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the Force, strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is Mass versus weight, not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Dot Sight
A red dot sight is a common classification for a non- magnifying reflector (or reflex) sight that provides an illuminated red dot to the user as a point of aim. A standard design uses a red light-emitting diode (LED) at the focus of collimating optics, which generates a dot-style illuminated reticle that stays in alignment with the firearm the sight is attached to, regardless of eye position (nearly parallax free). Red dot sights are considered to be fast-acquisition and easy-to-use gun sights for firearms used in civilian target shooting, hunting, or in police and military applications. They are also used on cameras and telescopes. On cameras they are used to photograph flying aircraft, birds in flight, and other distant, rapidly moving subjects. Telescopes have a narrow field of view and therefore are often equipped with a secondary "finder scope" such as a red dot sight to orient them. Description The typical configuration for a red dot sight is a tilted spherical mir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
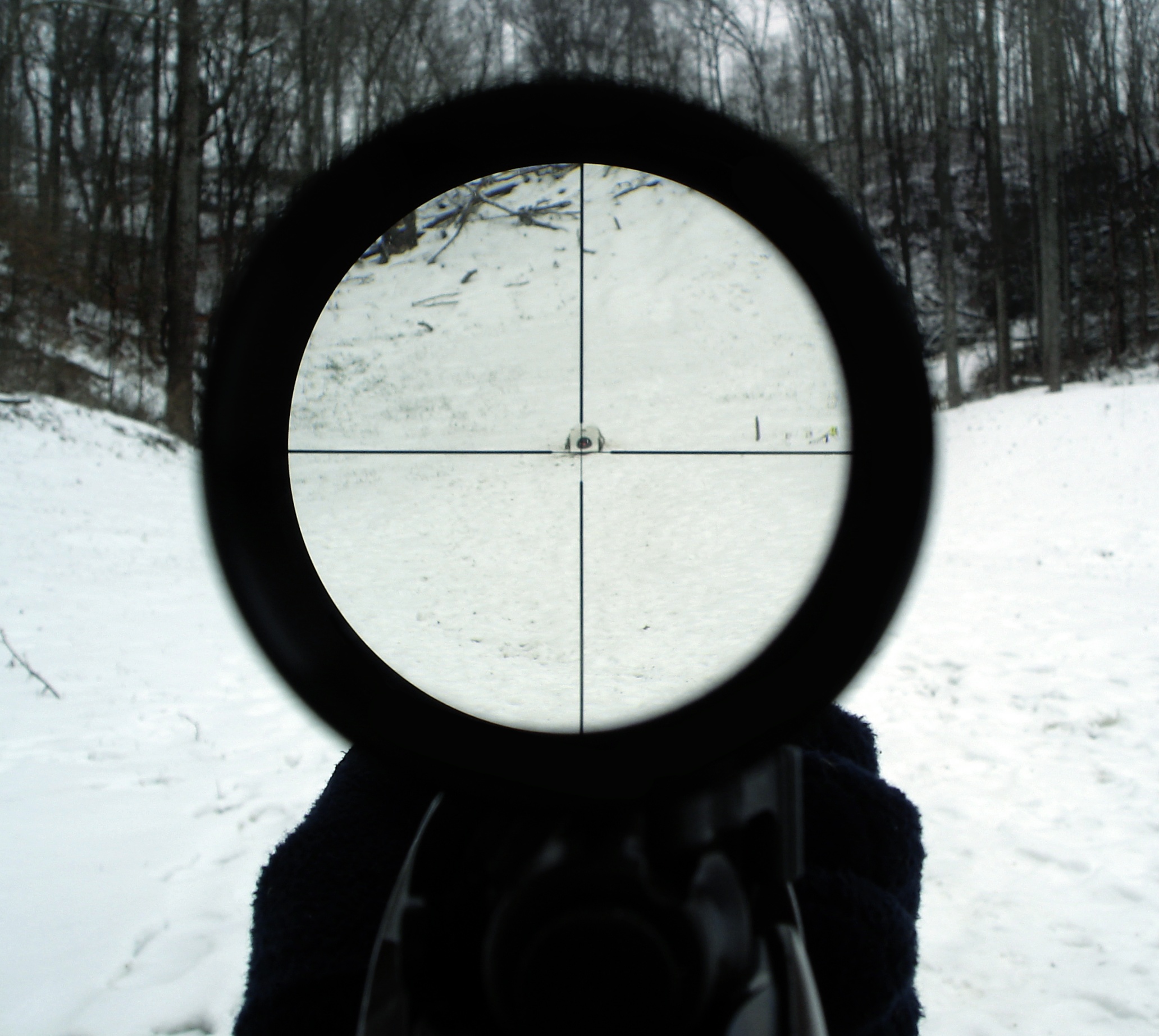
Telescopic Sight
A telescopic sight, commonly called a scope informally, is an optical sighting device based on a refracting telescope. It is equipped with some form of a referencing pattern – known as a ''reticle'' – mounted in a focally appropriate position in its optical system to provide an accurate point of aim. Telescopic sights are used with all types of systems that require magnification in addition to reliable visual aiming, as opposed to non-magnifying iron sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights or laser sights, and are most commonly found on long-barrel firearms, particularly rifles, usually via a scope mount. Similar devices are also found on other platforms such as artillery, tanks and even aircraft. The optical components may be combined with optoelectronics to add night vision or smart device features. History The first experiments directed to give shooters optical aiming aids go back to the early 17th century. For centuries, different optical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
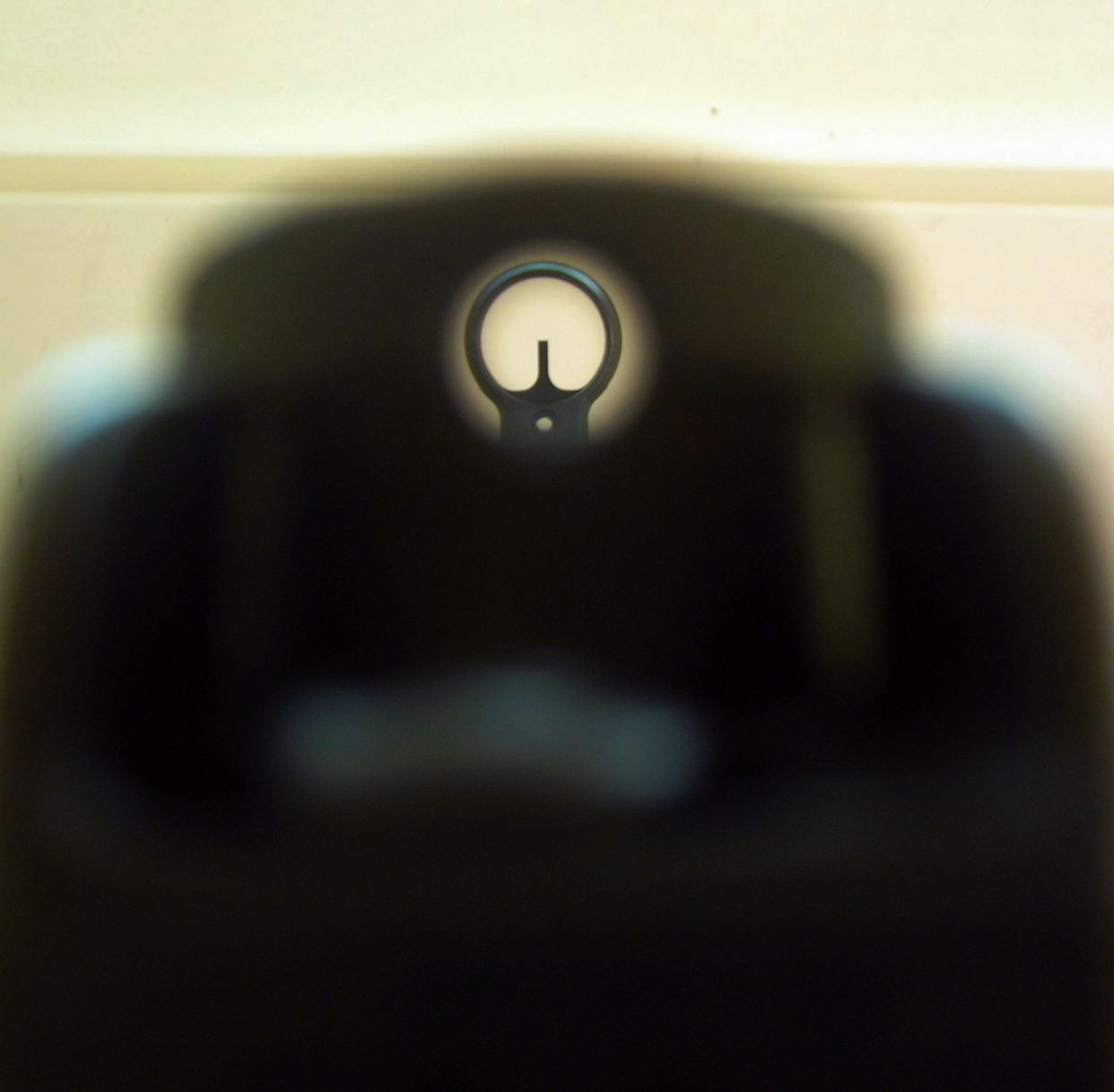
Iron Sights
Iron sights are a system of physical alignment markers used as a sighting device to assist the accurate aiming of ranged weapons such as firearms, airguns, crossbows, and bows, or less commonly as a primitive finder sight for optical telescopes. Iron sights, which are typically made of metal, are the earliest and simplest type of sighting device. Since iron sights neither magnify nor illuminate the target, they rely completely on the viewer's naked eye and the available light by which the target is visible. In this respect, iron sights are distinctly different from optical sight designs that employ optical manipulation or active illumination, such as telescopic sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights, and laser sights. Iron sights are typically composed of two components mounted perpendicularly above the weapon's bore axis: a 'rear sight' nearer (or 'proximal') to the shooter's eye, and a 'front sight' farther forward (or 'distal') near the muzzle. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
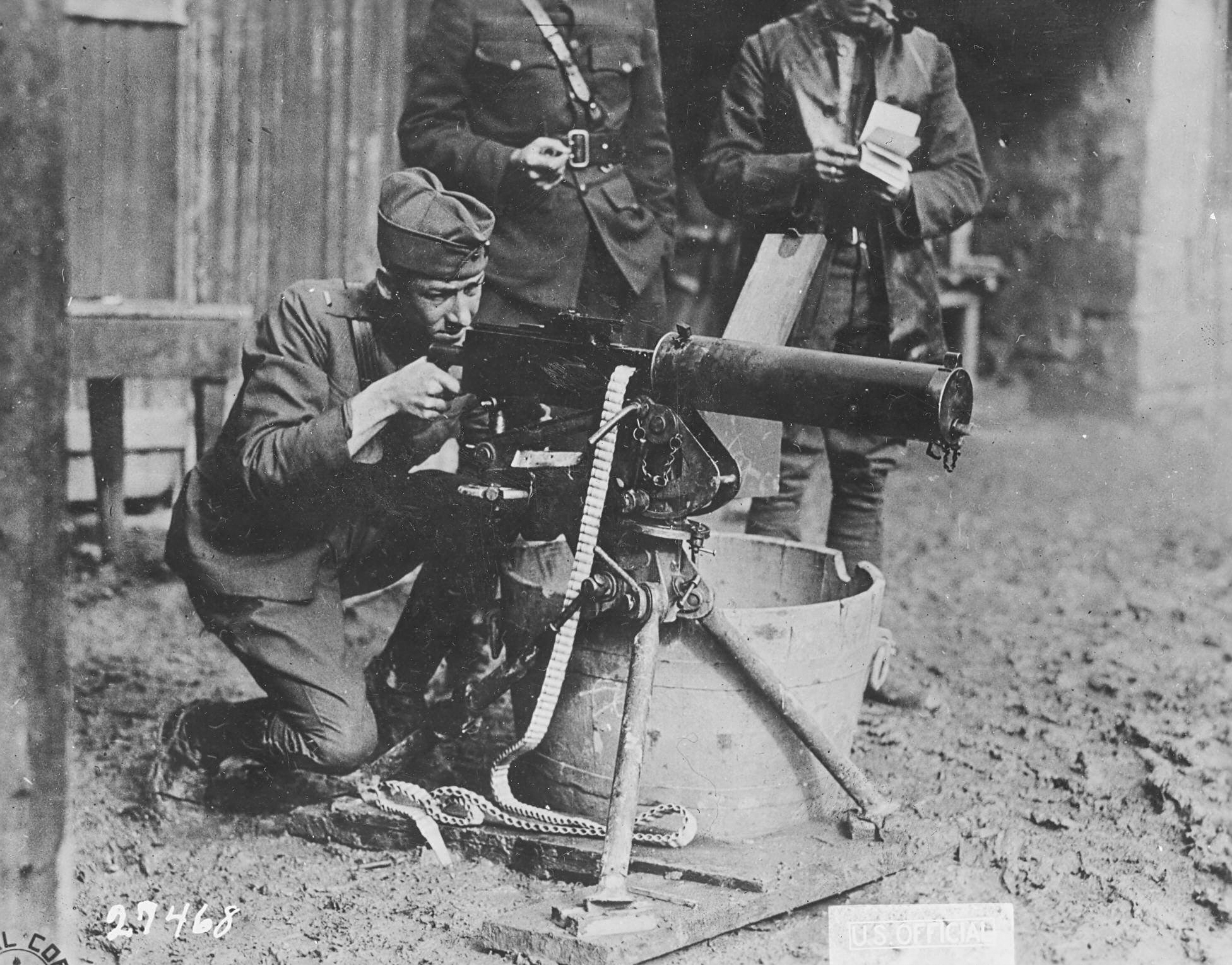
Heavy Machine Gun
A heavy machine gun (HMG) is significantly larger than light, medium or general-purpose machine guns. HMGs are typically too heavy to be man-portable (carried by one person) and require mounting onto a weapons platform to be operably stable or tactically mobile, have more formidable firepower, and generally require a team of personnel for operation and maintenance. There are two classes of weapons generally defined as HMGs: * The historical definition refers to machine guns, typically chambered in standard full-power cartridges, that are identified as being "heavy" due to their weight and cumbersomeness, which prevents infantrymen from transporting them on foot. Examples include the Maxim machine gun and M1917 Browning machine gun. * The modern definition refers to "heavy caliber" machine guns, pioneered by the German Empire's MG 18 TuF which was a Maxim derivative chambered in 13.2×92mmSR fielded near the end of World War I. They are designed to provide increased effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium Machine Gun
A medium machine gun (MMG), in modern terms, usually refers to a belt-fed machine gun firing a full-powered rifle cartridge, and is considered "medium" in weight (). Medium machine guns are light enough to be infantry-portable (as opposed to a heavy machine gun, which completely relies on mounting onto a weapons platform for operational stability and mobility), but still cumbersome enough to require a crew for optimal operational efficiency (as opposed to a light machine gun, which can be operated to full capacity by only a single gunner). History Late 19th century In the late 19th century, Gatling guns and other externally powered types, such as the Nordenfelt, were often made in different ranges of calibers, such as half-inch and one-inch. Thanks to their many barrels, overheating was not a major issue, and they were also quite heavy, being, essentially, heavy machine guns. When Hiram Maxim developed his recoil-powered machine gun that used a single barrel, the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Machine Gun
A light machine gun (LMG) is a light-weight machine gun designed to be operated by a single infantryman, with or without an assistant, as an infantry support weapon. LMGs firing cartridge (firearms), cartridges of the same caliber as the other riflemen of the same combat unit are often referred to as squad automatic weapons. Characteristics While early light machine guns fired full-powered rifle cartridges, modern light machine guns often fire smaller-caliber rifle cartridges than medium machine guns – generally the same intermediate cartridge fired by a service's standard assault rifle – and are usually lighter and more compact. Some LMGs, such as the Russian RPK, are modifications of existing designs and designed to share the same ammunition. Adaptations to the original rifle generally include a larger magazine, a heavier barrel to resist overheating, a more robust mechanism to support sustained fire and a bipod. A light machine gun is also defined by its usage as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-material Rifle
An anti-materiel rifle (AMR) is a rifle designed for use against military equipment, structures, and other hardware (materiel) targets. Anti-materiel rifles are chambered in significantly larger calibers than conventional rifles and are employed to eliminate equipment such as engines and unarmored or lightly armored targets. Although not originally designed for use against human targets, the bullet weight and velocity of anti-materiel rifles gives them exceptional long-range capability even when compared with designated sniper rifles. Anti-materiel rifles are made in both bolt-action and semi-automatic designs. The anti-materiel rifle originated in the anti-tank rifle, which itself originated during World War I. While modern tanks and most other armored vehicles are too well protected to be affected by anti-materiel rifles, the guns are still effective for attacking unarmored or lightly armored vehicles. They can also be used against stationary enemy aircraft, missile launchers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |