|
Loire-Nieuport 161
The Loire-Nieuport 161 was a single-seat, single-engine, all-metal, low-wing monoplane fighter designed and built in France in 1935 to compete for a government contract. Accidents delayed its development and only three prototypes were completed. Design and development In 1934 the Ateliers et Chantiers de la Loire and the Société Nieuport-Astra merged to form the Groupement Aviation Loire-Nieuport but maintained separate design offices, leading to some confusion about nomenclature, furthered by their nationalisation in 1936 as S.N.C.A.O. One of their first products, with the definitive final name Loire-Nieuport 161, was designed to compete for a ''Service Technique'' call for a single-seat fighter. It emerged as a mostly metal, low wing monoplane powered by a supercharged upright V-12 water-cooled engine and with a retractable conventional undercarriage. The cantilever wing of the Nieuport 161, as the first prototype was titled, was built in two parts around single spars w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually air or water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or afterend. Often rudders are shaped to minimize hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may link rudders to steering wheels. In typical aircraft, the rudder is operated by pedals via mechanical linkages or hydraulics. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispano-Suiza HS
Hispano-Suiza () is a Spanish automotive company. It was founded in 1904 by Marc Birkigt and as an automobile manufacturer and eventually had several factories in Spain and France that produced luxury cars, aircraft engines, trucks and weapons. In 1923, its French luxury car arm became a semi-autonomous partnership with the Spanish parent company. In 1946, the parent company sold all of its Spanish automotive assets to Enasa, a Spanish state-owned vehicle manufacturer, and the French arm continued as an independent aviation engine and components manufacturer under the Hispano-Suiza name. In 1968, Hispano-Suiza was taken over by the aerospace company Snecma, which is now part of the French Safran Group. The relaunch of Hispano Suiza Cars has been made by the same founding family (4th generation of the Suqué Mateu Family), the company is part of the Peralada Group (owned as well by the Suqué Mateu family) in 2019 with a fully-electric 1,119 HP hypercar called Hispano-Suiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during the late 19th century. Cannons vary in gauge (firearms), gauge, effective range, mobility (military), mobility, rate of fire, elevation (ballistics), angle of fire and firepower; different forms of cannon combine and balance these attributes in varying degrees, depending on their intended use on the battlefield. A cannon is a type of heavy artillery weapon. The word ''cannon'' is derived from several languages, in which the original definition can usually be translated as ''tube'', ''cane'', or ''reed''. The earliest known depiction of cannons may have appeared in Science and technology of the Song dynasty#Gunpowder warfare, Song dynasty China as early as the 12th century; however, solid archaeological and documentary evidence of cannons do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
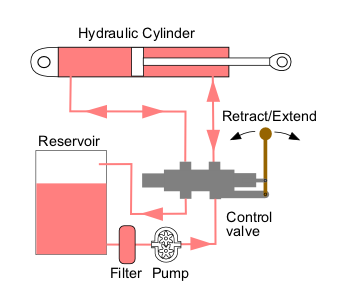
Hydraulic Machinery
Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes. Hydraulic systems, like pneumatic systems, are based on Pascal's law which states that any pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system will transmit that pressure equally everywhere and in all directions. A hydraulic system uses an incompressible liquid as its fluid, rather than a compressible gas. The popularity of hydraulic machinery is due to the large amount of power that can be transferred through small tubes and flexible hoses, the high power density and a wide array of actuators that can make use of this power, and the huge multiplication of forces t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
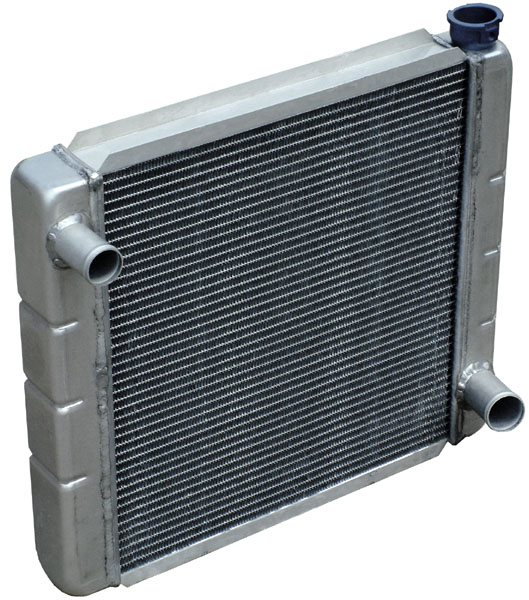
Radiator (engine Cooling)
Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in automobiles but also in piston-engined aircraft, railway locomotives, motorcycles, stationary generating plants or any similar use of such an engine. Internal combustion engines are often cooled by circulating a liquid called '' engine coolant'' through the engine block and cylinder head where it is heated, then through a radiator where it loses heat to the atmosphere, and then returned to the engine. Engine coolant is usually water-based, but may also be oil. It is common to employ a water pump to force the engine coolant to circulate, and also for an axial fan to force air through the radiator. Automobiles and motorcycles In automobiles and motorcycles with a liquid-cooled internal combustion engine, a radiator is connected to channels running through the engine and cylinder head, through which a liquid ( coolant) is pumped by a coolant pump. This liquid may be water (in climates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller (aircraft)
In aeronautics, an aircraft propeller, also called an airscrew,Beaumont, R.A.; ''Aeronautical Engineering'', Odhams, 1942, Chapter 13, "Airscrews". converts rotary motion from an engine or other power source into a swirling slipstream which pushes the propeller forwards or backwards. It comprises a rotating power-driven hub, to which are attached several radial airfoil-section blades such that the whole assembly rotates about a longitudinal axis. The blade pitch may be fixed, manually variable to a few set positions, or of the automatically variable "constant-speed" type. The propeller attaches to the power source's driveshaft either directly or through reduction gearing. Propellers can be made from wood, metal or composite materials. Propellers are most suitable for use at subsonic airspeeds generally below about , although supersonic speeds were achieved in the McDonnell XF-88B experimental propeller-equipped aircraft. Supersonic tip-speeds are used in some aircraft like the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade Pitch
Blade pitch or simply pitch refers to the angle of a blade in a fluid. The term has applications in aeronautics, shipping, and other fields. Aeronautics In aeronautics, blade pitch refers to the angle of the blades of an aircraft propeller or helicopter rotor. Blade pitch is measured relative to the aircraft body. It is usually described as "fine" or "low" for a more vertical blade angle, and "coarse" or "high" for a more horizontal blade angle. Blade pitch is normally described as a ratio of forward distance per rotation assuming no slip. Blade pitch acts much like the gearing of the final drive of a car. Low pitch yields good low speed acceleration (and climb rate in an aircraft) while high pitch optimizes high speed performance and fuel economy. It is quite common for an aircraft to be designed with a variable-pitch propeller, to give maximum thrust over a larger speed range. A fine pitch would be used during take-off and landing, whereas a coarser pitch is used for high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispano-Suiza 12X
The Hispano-Suiza 12X was an aircraft piston engine designed in France by Hispano-Suiza during the early 1930s. A 12-cylinder Vee, liquid-cooled design, the 12X was used on several aircraft types, some of them being used in limited numbers during World War II. Due to the 12X's limited power output, its derivative the more powerful Hispano-Suiza 12Y had a longer career. Variants Tabulated data from: Lage, 2004Lage, 2004, p.486-7 ;Hispano-Suiza 12Xrs Applications * Bernard 260 * Blériot-SPAD S.510 * Dewoitine D.500 * Hanriot H.110 * Hawker Spanish Fury * Hawker Spanish Osprey * Loire 102 * Loire 130 * Loire-Nieuport LN.40 * Lioré et Olivier H-246 * Mitsubishi A5M3a * Morane-Saulnier M.S. 227 * Nakajima Ki-12 * Potez 540 The Potez 540 was a French multi-role aircraft of the 1930s. Designed and built by Potez, it served with the French Air Force as a Aerial reconnaissance, reconnaissance bomber, also serving with the Spanish Republican Air Force during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispano-Suiza 12Y
The Hispano-Suiza 12Y was an aircraft engine produced by Hispano-Suiza for the French Air Force before the Second World War. The 12Y became the primary French 1,000 hp (750 kW) class engine and was used in a number of famous aircraft, including the Morane-Saulnier M.S.406 and Dewoitine D.520. Its design was based on the earlier, and somewhat smaller, 12X. The 12X did not see widespread use before the 12Y replaced it and became one of the most powerful French designs on the eve of the war. The 12Z was being designed but this was ended by the fall of France and the German occupation. The 12Y was produced under Hispano-Suiza licence in the Soviet Union as the Klimov M-100. This design led to the highly successful Klimov VK-105 series that powered the Yakovlev and Lavochkin fighters as well as the Petlyakov Pe-2 bomber. Licensed production of the early models was also undertaken in Czechoslovakia as the Avia HS 12Ydrs and in Switzerland as the HS-77. Design and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
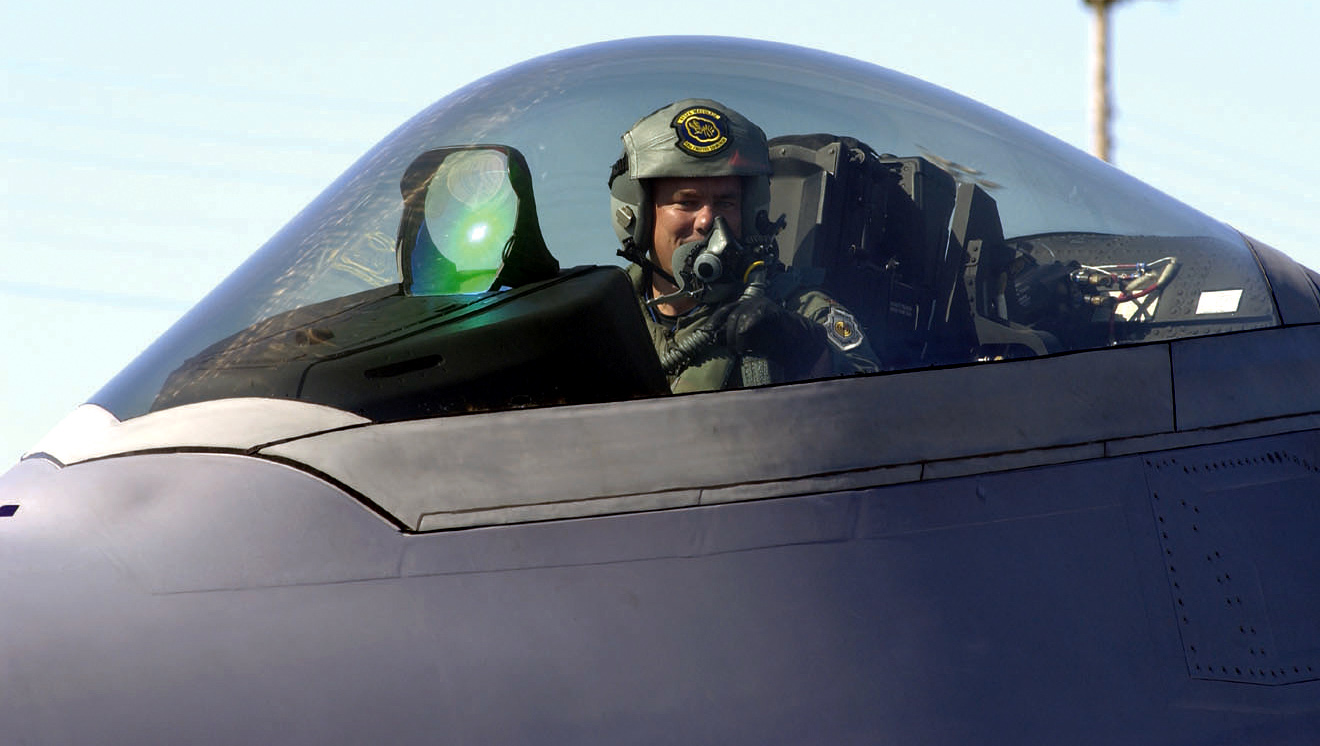
Canopy (aircraft)
An aircraft canopy is the transparent enclosure over the cockpit of some types of aircraft. An aircraft canopy provides a controlled and sometimes Cabin pressurization, pressurized environment for the aircraft's occupants, and allows for a greater field of view over a traditional flight deck. A canopy's shape is a compromise designed to minimize aerodynamic drag, while maximizing visibility for Aircraft pilot, pilots and other crewmembers. History Very early aircraft had no canopies. The pilots were exposed to the wind and weather, although most flying was done in good weather. Through World War I most aircraft had no canopy, although they often had a small windshield to deflect the prop wash and wind from hitting the pilot in the face. In the 1920s and 1930s, the increasing speed and altitude of airplanes necessitated a fully enclosed cockpit and canopies became more common. Early canopies were made of numerous pieces of flat glass held in position by a frame and muntins. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |