|
List Of Walls
See List of fortifications for a list of notable fortified structures. For city walls in particular, see List of cities with defensive walls. Pre-modern fortifications Africa * Fossatum Africae * Sungbo's Eredo, built during 800–1000 AD in Ijebu Ode in Ogun State, southwest Nigeria Americas * Great Wall of Tlaxcala, mentioned in the history of Bernal Díaz del Castillo * Walls of Old San Juan, Puerto Rico Asia * Great Wall of China, China – part of UNESCO site 438. This is mostly used to refer to the Ming Great Wall, built from 1368 to 1644, measures 8,850 km long. * Great Wall of Qi, the oldest of the Chinese Great Walls. * Great Wall of Yan (state) * Great Wall of Zhongshan (state) * Great Wall of Zhao (state) * Great Wall of Qin dynasty * Great Wall of Han dynasty (206 BC–220 AD), the longest Great Wall in history. * Great Wall of Northern Wei dynasty * Great Wall of Northern Qi dynasty * Great Wall of the Jurchen Jin Dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
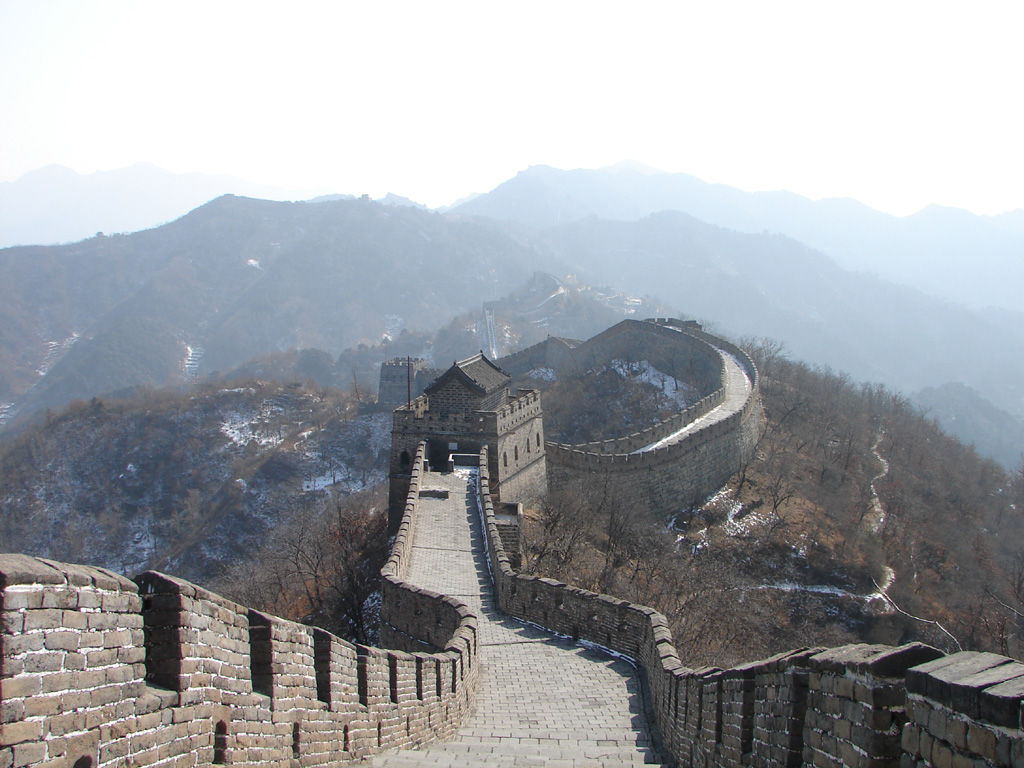
The Great Wall Of China At Jinshanling
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Great Wall
The Ming Great Wall ( zh, c=明長城, p=Míng Chángchéng), built by the Ming dynasty (1368–1644), forms the most visible parts of the Great Wall of China today. A comprehensive archaeological survey, using advanced technologies, has concluded that the Ming walls measure from Jiayu Pass in the west to the sea in Shanhai Pass, then looping over to terminate in Manchuria at the Hushan Great Wall. This is made up of sections of actual wall, of trenches and of natural defensive barriers such as hills and rivers. While the Ming walls are generally referred to as "Great Wall" (''changcheng'') in modern times, in Ming times they were called "border barriers" (邊牆; ''bianqiang'') by the Chinese, since the term ''changcheng'' was said to evoke imagery of the tyranny of Qin Shi Huang (260–210 BC) and was associated with the History of the Great Wall of China#Qin dynasty (221–206 BC), Qin Great Wall. History Early Ming walls and garrisons In 1368, the Hongwu Emperor (Zhu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheolli Jangseong
The Cheolli Jangseong or Great Wall of Korea may refer to either of two massive fortifications built between medieval Korea and the Chinese to the west and other tribes to the north. The first is a 7th-century network of military garrisons built by Goguryeo, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. These are now located in Northeast China. The second is an 11th-century wall built by Korea's Goryeo dynasty, now located in North Korea. Name The Korean name ''Cheolli Jangseong'' literally means the "Thousand Ri Wall", a reference to the Great Wall of China whose Chinese name is the "Ten-Thousand" or "Countless Li Wall". The second wall is also known in Korean as the ''Goryeo Jangseong'' ("Great Wall of Korea"). Goguryeo period After Goguryeo's victory in the Goguryeo–Sui Wars, in 631 Goguryeo began the fortification of numerous military garrisons after the Tang dynasty, the successor to the Sui in China, began incursions from the northwest.《三国史记·高句丽本记八》: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
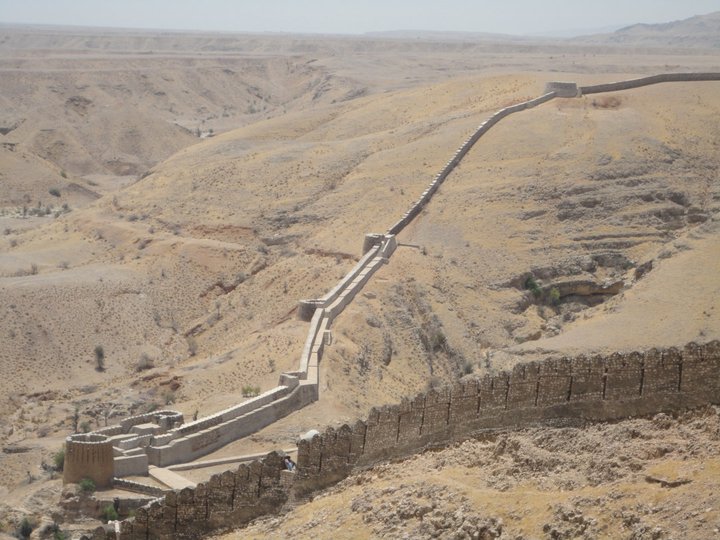
Ranikot Fort
Ranikot Fort (; also known as Rannikot), also known as the Great Wall of Sindh (), is a 19th-century (reconstructed) Talpur-era fort near Sann in Jamshoro District, Sindh, Pakistan. The fort's ramparts have been compared to the Great Wall of China. The site was nominated in 1993 by the Pakistan National Commission for UNESCO world heritage status, and has since been on the tentative list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The fort is listed as a historical site under the Antiquities Act, 1975 and its subsequent amendments, and has a protected status. Location Ranikot Fort is to the north of Hyderabad on the Indus Highway (N55). There is also an easy access of about an hour's journey from Karachi to Sann on the Indus Highway. A diversion road, starting a little distance away from Sann, the nearest town, leads to the fort along a rugged road and reaches the eastern gate of the fort, known as Sann Gate. Sann is a rail head on the Kotri-Larkana line of the Pakistan Railway. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
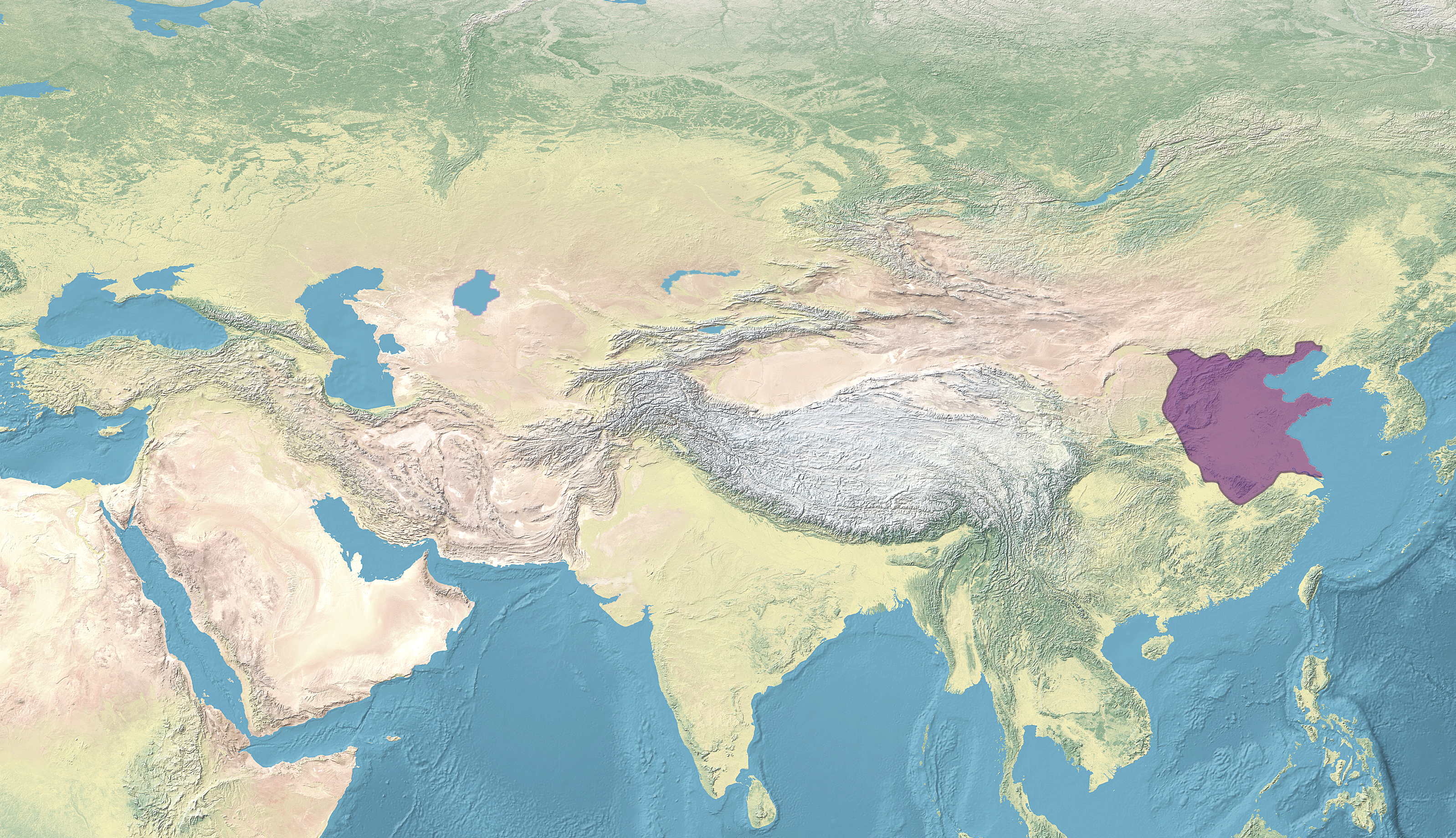
Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia ( zh, c=, w=Hsi1 Hsia4, p=Xī Xià), officially the Great Xia ( zh, c=大夏, w=Ta4 Hsia4, p=Dà Xià, labels=no), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led imperial dynasty of China that existed from 1038 to 1227. At its peak, the dynasty ruled over modern-day northwestern China, including parts of Ningxia, Gansu, eastern Qinghai, northern Shaanxi, northeastern Xinjiang, and southwest Inner Mongolia, and southernmost Outer Mongolia, measuring about . The capital of Western Xia was Xingqing (modern Yinchuan); another major Xia city and archaeological site is Khara-Khoto. Western Xia was annihilated by the Mongols in 1227. Most of its written records and architecture were destroyed, so the founders and history of the empire remained obscure until 20th-century research in China and the West. Today the Tangut language and its unique script are extinct, only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (, ), officially known as the Great Jin (), was a Jurchen people, Jurchen-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and empire ruled by the Wanyan clan that existed between 1115 and 1234. It is also often called the Jurchen dynasty or the Jurchen Jin after the ruling Jurchen people. At its peak, the empire extended from Outer Manchuria in the north to the Qinling–Huaihe Line in the south. The Jin dynasty emerged from Emperor Taizu of Jin, Wanyan Aguda's rebellion against the Liao dynasty (916–1125), which held sway over northern China until being driven by the nascent Jin to the Western Regions, where they would become known in Chinese historiography as the Qara Khitai, Western Liao. After conquering the Liao territory, the Jin launched a Jin–Song Wars, century-long campaign against the Song dynasty (960–1279) based in southern China, whose rulers were ethnically Han Chinese. Over the course of the Jin's rule, their emperors Sinicization, adap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Qi
Qi, known as the Northern Qi (), Later Qi (後齊) or Gao Qi (高齊) in historiography, was a Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese imperial dynasty and one of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties era. It ruled the eastern part of northern China from 550 to 577. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Wenxuan of Northern Qi, Gao Yang (Emperor Wenxuan), and was eventually conquered by the Xianbei-led Northern Zhou, Northern Zhou dynasty in 577. History Northern Qi was the successor state of the Chinese Xianbei state of Eastern Wei and was founded by Emperor Wenxuan of Northern Qi, Emperor Wenxuan. Emperor Wenxuan had a Han Chinese, Han father of largely Xianbei culture, Gao Huan, and a Xianbei mother, Lou Zhaojun. As Eastern Wei's powerful minister Gao Huan was succeeded by his sons Gao Cheng and Gao Yang, who took the throne from Emperor Xiaojing of Eastern Wei in 550 and established Northern Qi as Emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Northern Wei ( zh, c=北魏, p=Běi Wèi), Tuoba Wei ( zh, c=拓跋魏, p=Tuòbá Wèi), Yuan Wei ( zh, c=元魏, p=Yuán Wèi) and Later Wei ( zh, t=後魏, p=Hòu Wèi), was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Tuoba (Tabgach) clan of the Xianbei. The first of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties, it ruled northern China from 386 to 535 during the period of the Northern and Southern dynasties. Described as "part of an era of political turbulence and intense social and cultural change", the Northern Wei dynasty is particularly noted for unifying northern China in 439, bringing an end to the chaotic Sixteen Kingdoms period, and strengthening imperial control over the rural landscape via reforms in 485. This was also a period of introduced foreign ideas, such as Buddhism, which became firmly established. The Northern Wei was referred to as "Plaited Barbarians" (索虜; ''suǒlǔ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng engaged in a Qin's wars of unification, series of wars conquering each of the rival states that had previously pledged fealty to the Zhou. This culminated in 221 BC with the successful unification of China under Qin, which then assumed an imperial prerogativewith Ying Zheng declaring himself to be Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China, and bringing an end to the Warring States period (221 BC). This state of affairs lasted until 206 BC, when the dynasty collapsed in the years following Qin Shi Huang's death. The Qin dynasty's 14-year existence was the shortest of any major dynasty in Chinese history, with only two emperors. However, the succeeding Han dynasty (202 BC220 AD) largely continued the military and administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao (state)
Zhao () was one of the seven major State (Ancient China), states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It emerged from the Partition of Jin, tripartite division of Jin, along with Han (Warring States), Han and Wei (state), Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained considerable strength from the military reforms initiated during the reign of King Wuling of Zhao, King Wuling, but suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of Qin (state), Qin at the Battle of Changping. Its territory included areas in the modern provinces of Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi. It bordered the states of Qin, Wei, and Yan (state), Yan, as well as various nomadic peoples including the Donghu people, Hu and Xiongnu. Its capital was Handan, in modern Hebei province. Zhao was home to the Chinese Legalism, administrative philosopher Shen Dao, Confucian Xun Kuang, and Gongsun Long, who is affiliated to the school of names. Origins and ascendancy The Zhao (surname), Zhao clan within Jin ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |