|
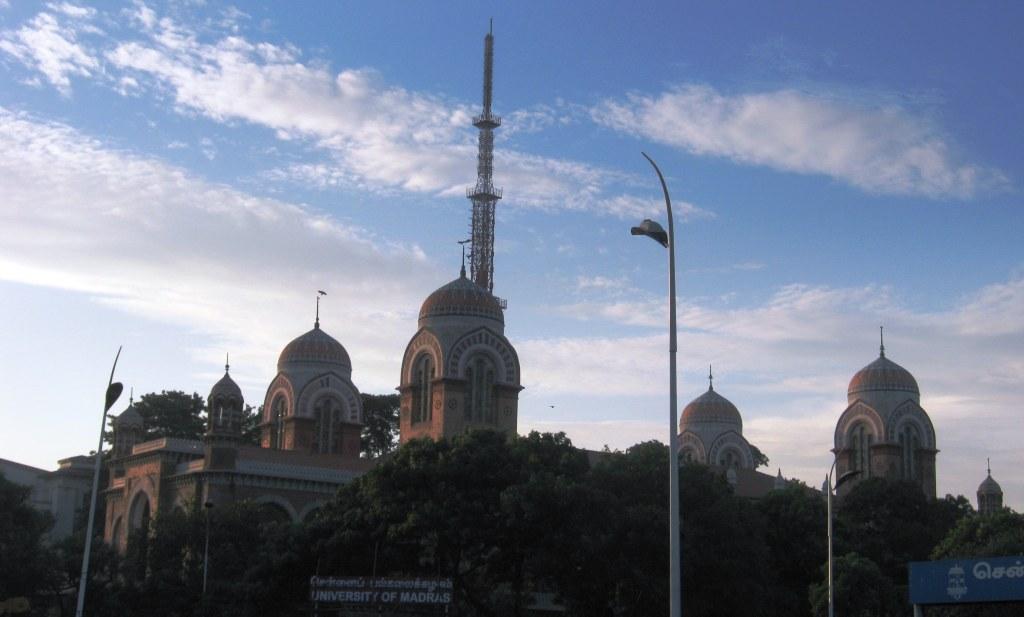
List Of Universities In India
The higher education system in India includes both private and public universities. Public universities are supported by the Government of India and the state governments, while private universities are mostly supported by various bodies and societies. Universities in India are recognised by the University Grants Commission (UGC), which draws its power from the '' University Grants Commission Act, 1956''. In addition, 15 Professional Councils are established, controlling different aspects of accreditation and co-ordination. The types of universities include: * Central universities, or Union universities, are established by an Act of Parliament and are under the purview of the Department of Higher Education in the Ministry of Education. the list of central universities published by the UGC includes 56 central universities. * State universities are run by the state government of each of the states and territories of India and are usually established by a local legislative as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
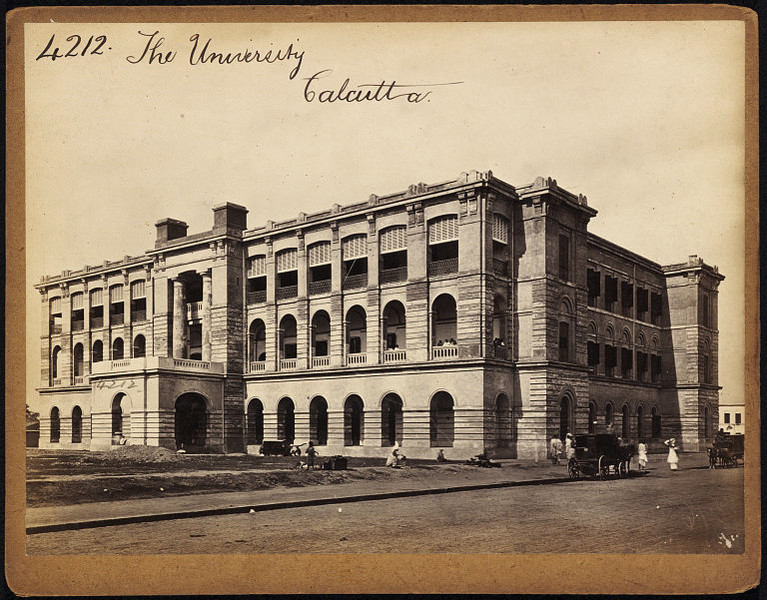
University Of Calcutta
The University of Calcutta, informally known as Calcutta University (), is a Public university, public State university (India), state university located in Kolkata, Calcutta (Kolkata), West Bengal, India. It has 151 affiliated undergraduate colleges and 16 institutes in Kolkata and nearby areas. It was established on 24 January 1857 and is the oldest multidisciplinary university of Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asian Region. Today, the university's jurisdiction is limited to a few districts of West Bengal, but at the time of its establishment it had a catchment area ranging from Kabul to Myanmar. It is accredited as an "A" grade university by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC). The university has a total of fourteen campuses spread over the city of Kolkata and its suburbs. As of 2020, 151 colleges and 21 institutes and centres are affiliated with CU. The university was fourth in the Indian University Ranking 2021 list, released by the National Institu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a city and union territory in northern India, serving as the shared capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana. Situated near the foothills of the Shivalik range of Himalayas, it borders Haryana to the east and Punjab in the remaining directions. Chandigarh constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which also includes the adjacent satellite cities of Panchkula in Haryana and Mohali in Punjab. It is located 260 km (162 miles) northwest of New Delhi and 229 km (143 miles) southeast of Amritsar and 104 km (64 miles) southwest of Shimla. Chandigarh is one of the earliest planned cities in post independence India and is internationally known for its architecture and urban design. The master plan of the city was prepared by Swiss-French architect Le Corbusier, which built upon earlier plans created by the Polish architect Maciej Nowicki and the American planner Albert Mayer. Narinder Singh Lamba, in the capacity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Territory
Among the states and union territories of India, a Union Territory (UT) is a region that is directly governed by the Government of India, central government of India, as opposed to the states, which have their own State governments of India, state government systems. Unlike states, Union Territories do not have their own full-fledged government but are administered by a Lieutenant governor or Administrator appointed by the President of India. Union Territories are created for various reasons, including geographical importance, strategic necessity, or historical factors. These areas are under the control of the central government to ensure uniformity in governance across the country. Some Union Territories, such as Delhi (National Capital Territory) and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry, have been granted special status and are allowed to have their own legislative assemblies, which can pass laws on certain matters, though the central government still retains significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Legislative Assemblies Of India
The State Legislative Assembly, also known as the Vidhan Sabha or the Saasana Sabha, is a legislative body in each of the states and certain union territories of India. Members of the legislative assembly are often directly elected to serve five year terms from single-member constituencies. A legislative assembly may be dissolved in a state of emergency, by the governor on request of the chief minister of the respective state or union territory, or if a motion of no confidence is passed against the ruling majority party or coalition. Definition and powers As per the Constitution of India, where there is a unicameral legislature, the legislative body is termed as the legislative assembly. In bicameral jurisdictions, there exists a State Legislative Council. The legislative assembly has the power to create or abolish the legislative council of the respective state or union territory by passing a resolution to that effect by a majority of not less than two-thirds of the members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of State Private Universities In India
State private universities in India are regulated under the UGC (Establishment and Maintenance of Standards in Private University) Regulations, 2003. Per these regulations, state private universities are established by an Act of a State Legislative Assembly and listed by the UGC in the Gazette upon receiving the Act. The UGC sends committees to inspect the state private universities and publishes their inspection report. The UGC publishes and regularly updates the lists of state private universities. The earliest date of notification is that of Sikkim Manipal University, 11 October 1995. State private universities were established in 26 of the 28 states of India and in none of the 8 union territories. Section 12 (B) of the UGC Act of 1956 also grants the UGC the right to "allocate and disburse, out of the Fund of the Commission, grants to Universities..." As such, the UGC may declare a state private university as "Included under 12(B) of the UGC Act, 1956". Updates to these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indira Gandhi Centre For Atomic Research
Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR) is one of India's premier nuclear research centres. It is the second largest establishment of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), next to Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), located at Kalpakkam, 80 km south of Chennai, India. It was established in 1971 as an exclusive centre dedicated to the pursuit of fast reactor science and technology, due to the vision of Vikram Sarabhai. Originally, it was called Reactor Research Centre (RRC). It was renamed to Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR) by the then Prime Minister of India Rajiv Gandhi in December 1985. The centre is engaged in broad-based multidisciplinary programme of scientific research and advanced engineering directed towards the development of fast breeder reactor technology in India. History The fast reactor related research in India, originated at BARC, Mumbai. Later, RRC was established at Kalpakkam with the same mandate. The Central Workshop, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai
The Institute of Mathematical Sciences (IMSc) (sometimes also referred to as ''Matscience'') is a research centre located in Chennai, India.R. Jagannathan, ''The Institute of Mathematical Sciences'', Resonance (January 1999) vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 89-92Complete Article It is a constituent institute of the Homi Bhabha National Institute. IMSc is a national institute for fundamental research in frontier disciplines of the mathematical and physical sciences: theoretical computer science, mathematics, theoretical physics, and computational biology. It is funded mainly by the Department of Atomic Energy. The institute operates the Kabru (supercomputer), Kabru supercomputer. History The institute was founded by Alladi Ramakrishnan in 1962 in Chennai. It is modelled after the Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, New Jersey, United States. It went through a phase of expansion when E. C. G. Sudarshan in the 1980s and R. Ramachandran in 1990s were the directors. The current director of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homi Bhabha National Institute
The Homi Bhabha National Institute (HBNI) is an Indian deemed university established by the Department of Atomic Energy, which unifies academic programmes of several of its constituent institutions. Deemed universities in India have been divided in three categories by the Ministry of Human Resource Development ( MHRD) and HBNI has been placed in category 'A', highest of the three categories. Homi Bhabha National Institute, Mumbai and its Constituent Units are the institutions of excellence as per section 4(b) of "The Central Education Institutions (Reservation in Admission) Act, 2006". National Assessment and Accreditation Council has accredited HBNI with a CGPA of 3.40 on a four-point scale at A+ grade valid up to 25 March 2026. History The Indian Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) was set up in 1954 and its mandate includes research including fundamental research in matters connected with atomic energy and the development of its uses in power generation, research, agricultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Institute Of Science
The Indian Institute of Science (IISc) is a Public university, public, Deemed university, deemed, research university for higher education and research in science, engineering, design, and management. It is located in Bengaluru, Karnataka. The institute was established in 1909 with active support from Jamsetji Tata and thus is also locally known as the Tata Institute. It was granted a deemed university status in 1958 and recognized as an Institute of Eminence in 2018. History Foundations and early history After an accidental meeting between Jamsetji Tata and Swami Vivekananda, on a ship in 1893 where they discussed Tata's plan of bringing the steel industry to India, Tata wrote to Vivekananda five years later: "I trust, you remember me as a fellow-traveller on your voyage from Japan to Chicago. I very much recall at this moment your views on the growth of the ascetic spirit in India... I recall these ideas in connection with my scheme of Research Institute of Science for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deemed University
In India, a deemed university or deemed-to-be-university is an accreditation granted to higher educational institutions by the Ministry of Education. According to the ministry's definition, the accreditation indicates, "an Institution of higher education, other than universities, working at a very high standard in specific area of study" and the accreditation grants "the academic status and privileges of a university". Deemed university status The higher education system in India includes both private and public universities. Public universities are supported by the Government of India and the state governments, while private universities are mostly supported by various bodies and societies. Universities in India are recognized by the University Grants Commission, which draws its power from the '' University Grants Commission Act, 1956''. In addition to this, 15 Professional Councils are established, controlling different aspects of accreditation and coordination. The status o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affiliated College
An affiliated school (also affiliated college, federated school, federated college or federated university) is an educational institution that operates independently, but also has a formal collaborative agreement with another, usually larger institution that may have some level of control or influence over its academic policies, standards or programs. While a university may have one or several affiliated colleges, it is not necessarily a collegiate university, which is a union or federation of semi-autonomous colleges. For the most part, this model is restricted to colleges and university, universities. On rarer occasions, however, elementary schools or high schools may also enter into affiliating agreements. Examples of affiliated schools by area Canada In Canada several universities have federated or affiliated colleges, some of which predate the parent institution. University of Alberta St. Joseph's College, Edmonton, St. Joseph's College is the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |