|
List Of Uncrewed Spaceflights To Mir ...
This is a list of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir. Components of the space station are indicated in green. *A. - Time from docking until debris impact in the Pacific Ocean at approximately 05:59 GMT on 23 March 2001. *B. - From time of launch *C. - Remained attached during deorbit of space station on 23 March 2001. *D. - Decayed naturally See also *Mir * List of Progress flights * List of human spaceflights to Mir * List of human spaceflights to the International Space Station *Uncrewed spaceflights to the International Space Station * List of Mir spacewalks References {{Space exploration lists and timelines * Mir, uncrewed spaceflights Uncrewed spacecraft Mir ''Mir'' (, ; ) was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, first by the Soviet Union and later by the Russia, Russian Federation. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Station
A space station (or orbital station) is a spacecraft which remains orbital spaceflight, in orbit and human spaceflight, hosts humans for extended periods of time. It therefore is an artificial satellite featuring space habitat (facility), habitation facilities. The purpose of maintaining a space station varies depending on the program. Most often space stations have been research stations, but they have also served militarization of space, military or commercialization of space, commercial uses, such as hosting space tourism, space tourists. Space stations have been hosting the only continuous human presence in space, presence of humans in space. The first space station was Salyut 1 (1971), hosting the first crew, of the ill-fated Soyuz 11. Consecutively space stations have been operated since Skylab (1973) and occupied since 1987 with the Salyut program, Salyut successor Mir. Uninterrupted human presence in orbital space through space stations have been sustained since the operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress 34
Progress 34 () was a Soviet uncrewed Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in January 1988 to resupply the Mir space station. Launch Progress 34 launched on 20 January 1988 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Kazakh SSR. It used a Soyuz-U2 rocket. Docking Progress 34 docked with the aft port of the Kvant-1 module of Mir on 23 January 1988 at 00:09:09 UTC, and was undocked on 4 March 1988 at 03:40:09 UTC. Decay It remained in orbit until 4 March 1988, when it was deorbited. The deorbit burn occurred at 06:45:00 UTC and the mission ended at 07:29:30 UTC. See also * 1988 in spaceflight * List of Progress missions * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir This is a list of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir. Components of the space station are indicated in green. *A. - Time from docking until debris impact in the Pacific Ocean at approximately 05:59 GMT on 23 March 2001. *B. - From time of launch *C. ... References Progress (spacecraft) missions 1988 in the Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
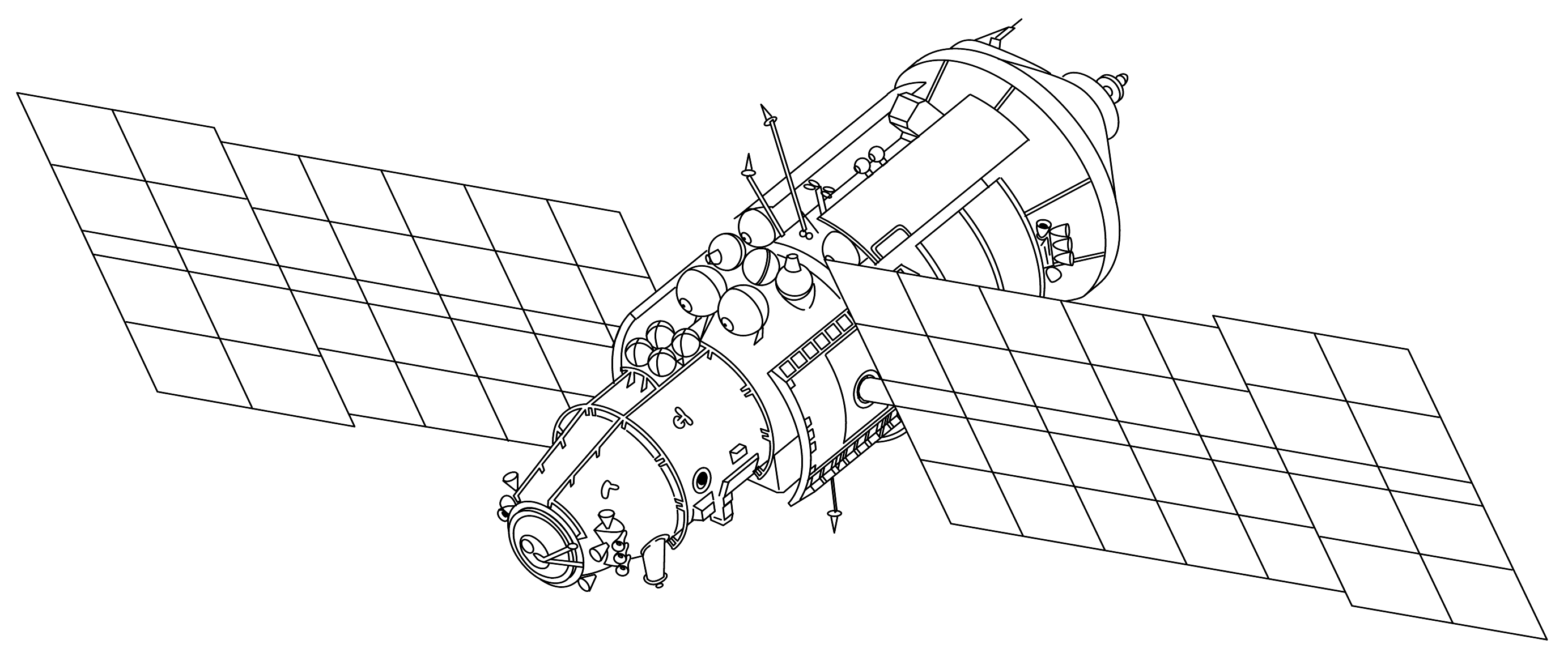
Kristall
The Kristall () (77KST, TsM-T, 11F77T) module was the fourth module and the third major addition to ''Mir''. As with previous modules, its configuration was based on the 77K (TKS) module, and was originally named "Kvant 3". It was launched on May 31, 1990 on Proton-K. It docked to Mir autonomously on June 10, 1990. Description Kristall had several materials processing furnaces. They were called Krater 5, Optizon 1, Zona 2, and Zona 3. It also had a biotechnology experiment called the Aniur electrophoresis unit. These experiments were capable of generating 100 kg of raw materials for use on Earth. Located in the docking node was the Priroda 5 camera which was used for Earth resources experiments. Kristall also had several astronomy and astrophysics experiments which were designed to augment experiments that were already located in Kvant-1. Kristall's solar panels were also different from others on Mir. They were designed to be "collapsible" which means that they could be de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress 42
Progress 42 () was a Soviet unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in May 1990 to resupply the Mir space station. Launch Progress 42 launched on 5 May 1990 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Kazakh SSR. It used a Soyuz-U2 rocket. Docking Progress 42 docked with the aft port of the Kvant-1 module of Mir on 7 May 1990 at 22:45:03 UTC, and was undocked on 27 May 1990 at 07:08:58 UTC. Decay It remained in orbit until 27 May 1990, when it was deorbited. The deorbit burn occurred at 11:40:00 UTC and the mission ended at 12:27:30 UTC. See also * 1990 in spaceflight * List of Progress missions * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir This is a list of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir. Components of the space station are indicated in green. *A. - Time from docking until debris impact in the Pacific Ocean at approximately 05:59 GMT on 23 March 2001. *B. - From time of launch *C. ... References Progress (spacecraft) missions 1990 in the Soviet Union Spacecra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-3
Progress M-3 () was a Soviet uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1990 to resupply the Mir space station. The twentieth of sixty four Progress flights to visit Mir, it was a Progress-M 11F615A55 spacecraft, and had the serial number A serial number (SN) is a unique identifier used to ''uniquely'' identify an item, and is usually assigned incrementally or sequentially. Despite being called serial "numbers", they do not need to be strictly numerical and may contain letters ... 203. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-6 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. Progress M-3 was launched at 23:10:57 GMT on 28 February 1990, atop a Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It docked with the aft port of the ''Kvant-1'' module at 01:04:32 GMT on 3 March. During the 56 days for which it was docked with Mir, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-2
Progress M-2 (), was a Soviet uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1989 to resupply the Mir space station. The nineteenth of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it used the Progress-M 11F615A55 configuration, and had the serial number 202. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the EO-5 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. Progress M-2 was launched at 03:30:50 GMT on 20 December 1989, atop a Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It docked with the aft port of the ''Kvant-1'' module of Mir at 05:41:21 GMT on 22 December. During the time it was docked, Mir was in an orbit of around . Progress M-2 remained docked with Mir for forty eight days before undocking at 02:33:07 GMT on 9 February 1990 to make way for the Soyuz TM-9 spacecraft, carrying the EO-6 crew to the station. Progress M-2 was deorbited at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant-2
Kvant-2 (; English: Quantum-II/2) (77KSD, TsM-D, 11F77D) was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket. It docked to Mir on December 6. Its control system was designed by the NPO "Electropribor" (Kharkiv, Ukraine). Description Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft (77k module). Kvant-2 was divided into three compartments. They were the EVA airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment. The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock. Before Kvant-2 docked to the station, EVAs had to be carried by depressurizing the docking node on the Core Module. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit for the Orlan space suit. It delivered the Salyut 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-1
Progress M-1 (), was a Soviet uncrewed cargo spacecraft which was launched in 1989 to resupply the Mir space station. The eighteenth of sixty four Progress spacecraft to visit Mir, it was the first Progress-M spacecraft to be launched, and had the serial number 201. It carried supplies including food, water and oxygen for the Mir EO-5 crew aboard Mir, as well as equipment for conducting scientific research, and fuel for adjusting the station's orbit and performing manoeuvres. At the time of docking, Mir was uncrewed, and remained so until the arrival of the Mir EO-5 crew two weeks later. Launch Progress M-1 was launched at 03:09:32 UTC on 23 August 1989, atop a Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket flying from Site 1/5 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It docked with the forward port of Mir Core Module at 05:19:02 UTC on 25 August 1989. During the time it was docked, Mir was in an orbit of around . Progress M-1 remained docked with Mir for three months before undocking at 09:02:23 UTC on 1 Decemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress 41
Progress 41 () was a Soviet unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in March 1989 to resupply the Mir EO-4 expedition aboard the Mir space station. Launch Progress 41 launched on 16 March 1999 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Kazakh SSR. It used a Soyuz-U2 rocket. Docking Progress 41 docked with the aft port of the Kvant-1 module of Mir on 18 March 1989 at 20:50:46 UTC, and was undocked on 21 April 1989 at 01:46:15 UTC. Decay It remained in orbit until 25 April 1989. Progress 41 deorbited in an uncontrolled decay, after it had run out of fuel from boosting Mir into a higher orbit. The mission ended at 12:02 UTC. See also * 1989 in spaceflight * List of Progress missions * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir This is a list of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir. Components of the space station are indicated in green. *A. - Time from docking until debris impact in the Pacific Ocean at approximately 05:59 GMT on 23 March 2001. *B. - From time of launch *C. .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress 40
Progress 40 () was a Soviet unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in February 1989 to resupply the Mir EO-4 expedition aboard the Mir space station. Launch Progress 40 launched on 10 February 1989 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Kazakh SSR. It used a Soyuz-U2 rocket. Docking Progress 40 docked with the aft port of the Kvant-1 module of Mir on 12 February 1989 at 10:29:38 UTC, and was undocked on 3 March 1989 at 01:45:52 UTC. Decay It remained in orbit until 5 March 1989, when it was deorbited. The deorbit burn occurred at 01:08 UTC and the mission ended at 01:59 UTC. See also * 1989 in spaceflight * List of Progress missions * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir This is a list of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir. Components of the space station are indicated in green. *A. - Time from docking until debris impact in the Pacific Ocean at approximately 05:59 GMT on 23 March 2001. *B. - From time of launch *C. ... References Progress (spacecraft) m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress 39
Progress 39 () was a Soviet unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in December 1988 to resupply the Mir EO-4 expedition aboard the Mir space station. Launch Progress 39 launched on 25 December 1988 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Kazakh SSR. It used a Soyuz-U2 rocket. Docking Progress 39 docked with the aft port of the Kvant-1 module of Mir on 27 December 1988 at 05:35:10 UTC, and was undocked on 7 February 1989 at 06:45:34 UTC. Decay It remained in orbit until 7 February 1989, when it was deorbited. The deorbit burn occurred at around 12:49 UTC and the mission ended at 13:49 UTC. See also * 1988 in spaceflight * List of Progress missions * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir This is a list of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir. Components of the space station are indicated in green. *A. - Time from docking until debris impact in the Pacific Ocean at approximately 05:59 GMT on 23 March 2001. *B. - From time of launch *C. ... References Progress ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress 38
Progress 38 () was a Soviet uncrewed Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in September 1988 to resupply the Mir space station. Launch Progress 38 launched on 9 September 1988 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Kazakh SSR. It used a Soyuz-U2 rocket. Docking Progress 38 docked with the aft port of the Kvant-1 module of Mir on 12 September 1988 at 01:22:28 UTC, and was undocked on 23 November 1988 at 12:12:46 UTC. Decay It remained in orbit until 23 November 1988, when it was deorbited. The deorbit burn occurred at 18:26:00 UTC and the mission ended at 19:06:58 UTC. See also * 1988 in spaceflight * List of Progress missions * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir This is a list of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir. Components of the space station are indicated in green. *A. - Time from docking until debris impact in the Pacific Ocean at approximately 05:59 GMT on 23 March 2001. *B. - From time of launch *C. ... References Progress (spacecraft) missions 1988 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |