|
List Of Stars In Fornax
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Fornax, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also *Lists of stars by constellation *List of UDF objects (1–500) References * * * * * * * {{Fornax Fornax, *List Lists of stars by constellation, Fornax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellations in the far southern sky were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta3 Fornacis
Eta3 Fornacis (η3 Fornacis) is an orange giant in the constellation of Fornax Fornax () is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere, partly ringed by the celestial river Eridanus. Its name is Latin for furnace. It was named by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1756. Fornax is one of the 88 mod .... The star has a spectral type of K2III and an apparent magnitude of 5.47. The star is visually close to, but unrelated with the similar stars η2 Fornacis and η1 Fornacis. The star is located at approximately 489 light years away with a luminosity of about , and is a suspected binary system with the primary being the orange giant. References Fornax Fornacis, Eta2 K-type giants 017829 0851 013265 {{giant-star-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma2 Fornacis
Gamma2 Fornacis, a name Latinized from γ2 Fornacis, is a single star in the southern constellation Fornax. It has a white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye at night with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.4. The distance to Gamma2 Fornacis is approximately 520 light years based on parallax. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of 24 km/s. Gamma1 Fornacis is a 6th magnitude star about four degrees to the north. The stellar classification of Gamma2 Fornacis is A1 V, which is notation for an A-type main-sequence star that, like the Sun, is generating energy through core hydrogen fusion. Comparison of its properties to theoretical models suggest an age of about 400 million years old. It has a high rate of spin, showing a projected rotational velocity of 149 km/s. The star has 2.4 times the mass of the Sun and 4.5 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 117 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi Fornacis
π Fornacis (Latinised as Pi Fornacis) is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Fornax. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.360, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye on a dark night. With an annual parallax shift of 11.27 mas, it is estimated to lie around 289 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an interstellar absorption factor of 0.10 due to dust. This system is a member of the thin disk population of the Milky Way galaxy. The primary, component A, is an evolved G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G8 III. It has an estimated mass slightly higher than the Sun, but has expanded to more than nine times the Sun's radius. The star is roughly three billion years old and is spinning slowly with a projected rotational velocity of 0.9 km/s. Pi Fornacis A radiates 59 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 5,048 K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Fornacis
μ Fornacis (Latinised as Mu Fornacis) is the Bayer designation for a star in the southern constellation of Fornax. With an apparent visual magnitude of 5.27, it is visible to the naked eye. The distance to this star, as determined by its annual parallax shift of 10.18 mas, is around 320 light years. This is an A-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of A0 V. It is a Be star that displays "central quasi emission" (CQE) bumps in its spectrum due to a surrounding shell of material. The star has an estimated 3.1 times the mass of the Sun and 2.5 times the Sun's radius. Mu Fornacis is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 320 km/s and is around 188 million years old. It radiates 68.7 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 11,745 K. Mu Fornacis appears to be emitting an infrared excess at a wavelength of 22 μm, which could be due to an orbiting debris disk. Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kappa Fornacis
Kappa (uppercase Κ, lowercase κ or cursive ; el, κάππα, ''káppa'') is the 10th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless velar plosive sound in Ancient and Modern Greek. In the system of Greek numerals, has a value of 20. It was derived from the Phoenician letter kaph . Letters that arose from kappa include the Roman K and Cyrillic К. The uppercase form is identical to the Latin K. Greek proper names and placenames containing kappa are often written in English with "c" due to the Romans' transliterations into the Latin alphabet: Constantinople, Corinth, Crete. All formal modern romanizations of Greek now use the letter "k", however. The cursive form is generally a simple font variant of lower-case kappa, but it is encoded separately in Unicode for occasions where it is used as a separate symbol in math and science. In mathematics, the kappa curve is named after this letter; the tangents of this curve were first calculated by Isaac Barrow in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phi Fornacis
Phi Fornacis is a single star in the southern constellation of Fornax. It has a white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.13. The distance to this object is approximately 154 light-years based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +19 km/s. This is an A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A2.5V. Phi Fornacis is 238 million years old and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 117 km/s. It has 2.1 times the mass of the Sun and 1.7 times the Sun's radius. The star is radiating 17 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 9,449 km/s. It displays an infrared excess, suggesting a circumstellar disk A circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Fornacis
Delta Fornacis, Latinized from δ Fornacis, is a solitary, blue-white hued star near the middle of the southern constellation of Fornax. With an apparent visual magnitude of 5.00, it is faintly visible to the naked eye at night. The star has an annual parallax shift of , indicating it lies at a distance of approximately 790 light years from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +26 km/s. The stellar classification of Delta Fornacis is B5 III, matching an evolved B-type giant star. It has an angular diameter of , which, at the estimated distance of the star, yields a physical size of around 6 times the radius of the Sun. Around 63 million years old, the star is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 185 km/s. It has an estimated 5.9 times the Sun's mass and radiates 1,291 times the solar luminosity from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 16,230 K. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Delta For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega Fornacis
Omega Fornacis, which is Latinized from ω Fornacis, is a wide binary star system in the southern constellation of Fornax. It has a blue-white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye as a fifth-magnitude star. The system lies at a distance of approximately 470 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +10 km/s. The dual nature of this system was discovered in 1836 by John Herschel. As of 2013, the two components had an angular separation of along a position angle of 246°. This corresponds to a projected separation of . The magnitude 4.95 primary, designated component A, is a chemically peculiar B-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of B9V It has 3.4 times the Sun's mass and is radiating around 268 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 10,910 K. Component B, the magnitude 7.71 secondary, is an A-type main-sequence star An A-type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
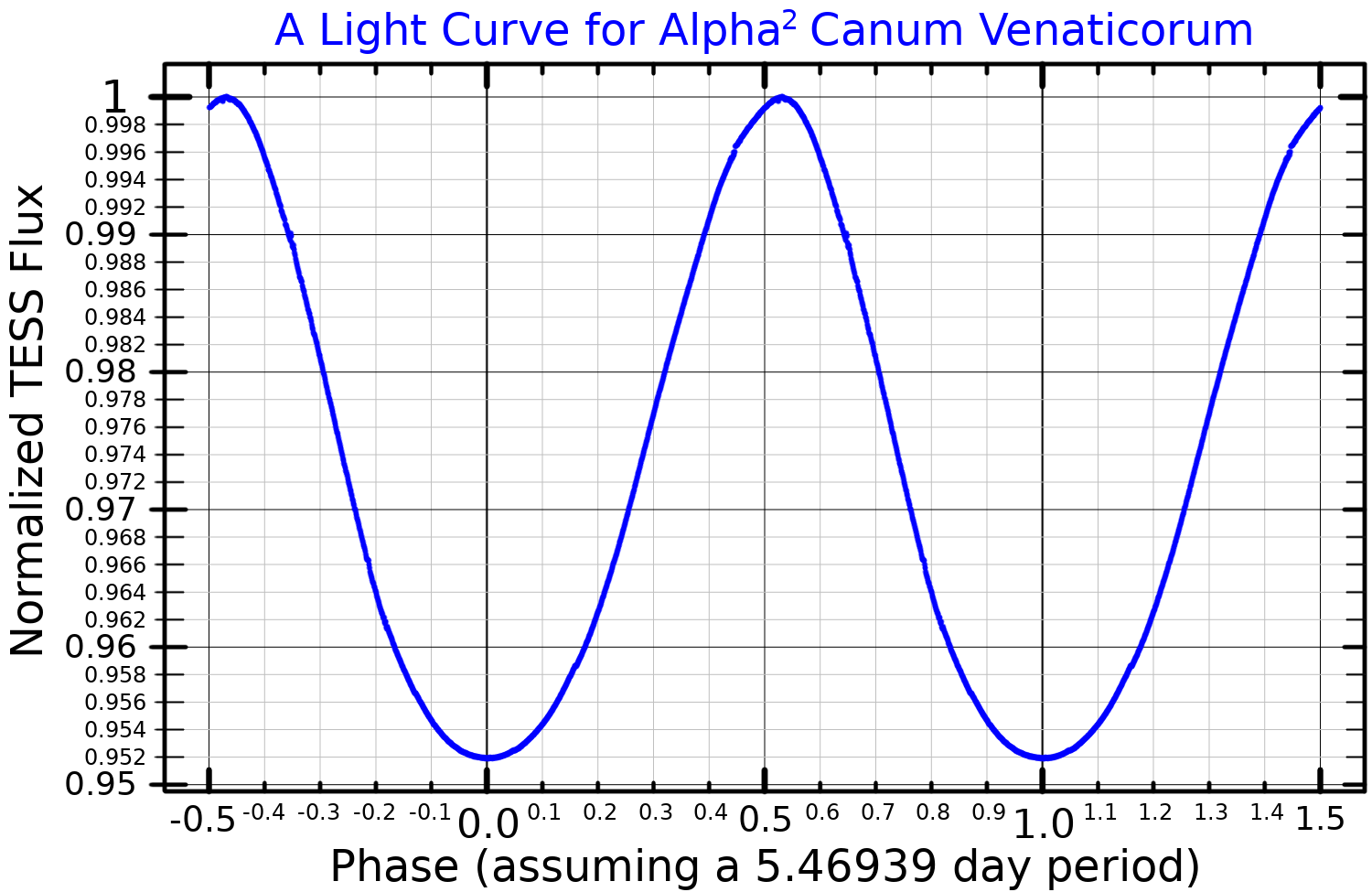
Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum Variable
An Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable (or α2 CVn variable) is a type of variable star. These stars are chemically peculiar main sequence stars of spectral class B8p to A7p. They have strong magnetic fields and strong silicon, strontium, or chromium spectral lines. Their brightness typically varies by 0.01 to 0.1 magnitudes over the course of 0.5 to 160 days. In addition to their intensities, the intensities and profiles of the spectral lines of α2 CVn variables also vary, as do their magnetic fields. The periods of these variations are all equal and are believed to equal the period of rotation of the star. It is thought that they are caused by an inhomogeneous distribution of metals in the atmospheres of these stars, so that the surface of the star varies in brightness from point to point. The type-star which this class is named after is α² Canum Venaticorum, a star in the binary system of Cor Caroli, which is in the northern constellation of Canes Venatici Canes Ven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |