|
List Of Stars In Canis Minor ...
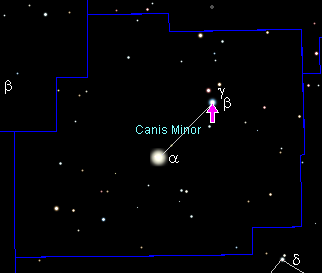
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Canis Minor, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also *Lists of stars by constellation Notes References * Wagman, M., ''Lost Stars: Lost, Missing, and Troublesome Stars from the Catalogues of Johannes Bayer, Nichoilas-Louis de Lacaille, John Flamsteed, and Sundry Others'', The McDonald & Woodward Publishing Company, Blaksburg, 2003, p. 460. * Flamsteed, J., (ed.) "Stellarum Inerrantium Catalogus Britannicus", ''Historia Coelestis Britannca'', vol.3, H. Meere, London, 1725, p. 32. * * * * * * * {{Stars of Canis Minor *List Canis Minor Canis Minor is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its total mass is the main factor determining its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Brightest Stars
This is a list of stars arranged by their apparent magnitude – their brightness as observed from Earth. It includes all stars brighter than magnitude +2.50 in visible light, measured using a ''V''-band filter in the UBV photometric system. Stars in binary systems (or other multiples) are listed by their ''total'' or ''combined'' brightness if they appear as a single star to the naked eye, or listed separately if they do not. As with all magnitude systems in astronomy, the scale is logarithmic and inverted i.e. lower/more negative numbers are brighter. Most stars on this list appear bright from Earth because they are nearby, not because they are intrinsically luminous. For a list which compensates for the distances, converting the ''apparent'' magnitude to the ''absolute'' magnitude, see the list of most luminous stars. Measurement The Sun is the brightest star as viewed from Earth, at −26.74 mag. The second brightest is Sirius at −1.46 mag. For compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6 Canis Minoris
6 Canis Minoris is a star in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor, located around 570 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.55. This object is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −16.3 km/s. Kinematically, it is a member of an outlying group belonging to the Ursa Major flow of the Sirius supercluster. This is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of K1 III. It has a mild barium anomaly, which may indicate this is a binary star system with a white dwarf companion. The interferometry-measured angular diameter of the visible component is about , which, at its estimated distance, equates to a physical radius of about 44 times the radius of the Sun. This star has four times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 761 times the Sun's luminosity The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux (power emitted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Flamsteed
John Flamsteed (19 August 1646 – 31 December 1719) was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, ''Catalogus Britannicus'', and a star atlas called '' Atlas Coelestis'', both published posthumously. He also made the first recorded observations of Uranus, although he mistakenly catalogued it as a star, and he laid the foundation stone for the Royal Greenwich Observatory. Life Flamsteed was born in Denby, Derbyshire, England, the only son of Stephen Flamsteed and his first wife, Mary Spadman. He was educated at the free school of Derby and at Derby School, in St Peter's Churchyard, Derby, near where his father carried on a malting business. At that time, most masters of the school were Puritans. Flamsteed had a solid knowledge of Latin, essential for reading the scientific literature of the day, and a love of history, leaving the school in May 1662.Birks, John L. (1999) ''John Flamsteed, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argo Navis
Argo Navis (the Ship Argo), or simply Argo, is one of the 48 Ptolemy's constellations, now a grouping of three IAU constellations. It is formerly a single large constellation in the southern sky. The genitive is "Argus Navis", abbreviated "Arg". Flamsteed and other early modern astronomers called it Navis (the Ship), genitive "Navis", abbreviated "Nav". The constellation proved to be of unwieldy size, as it was 28% larger than the next largest constellation and had more than 160 easily visible stars. The 1755 catalogue of Nicolas Louis de Lacaille divided it into the three modern constellations that occupy much of the same area: Carina (the keel), Puppis (the poop deck) and Vela (the sails). Argo derived from the ship '' Argo'' in Greek mythology, sailed by Jason and the Argonauts to Colchis in search of the Golden Fleece. Some stars of Puppis and Vela can be seen from Mediterranean latitudes in winter and spring, the ship appearing to skim along the "river of the Milky Way. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Elert Bode
Johann Elert Bode (; 19 January 1747 – 23 November 1826) was a German astronomer known for his reformulation and popularisation of the Titius–Bode law. Bode determined the orbit of Uranus and suggested the planet's name. Life and career Bode was born in Hamburg. As a youth, he suffered from a serious eye disease that particularly damaged his right eye; he continued to have trouble with his eyes throughout his life. His early promise in mathematics brought him to the attention of Johann Georg Büsch, who allowed Bode to use his own library for study. He began his career with the publication of a short work on the solar eclipse of 5 August 1766. This was followed by an elementary treatise on astronomy entitled ''Anleitung zur Kenntniss des gestirnten Himmels'' (1768, 10th ed. 1844), the success of which led to his being invited to Berlin by Johann Heinrich Lambert in 1772 for the purpose of computing ephemerides on an improved plan. There he founded, in 1774, the well-kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 66141
HD 66141 is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor. It has the Bayer designation G Canis Minoris, the Gould designation 50 G. Canis Minoris, and has the HR 3145 identifier from the ''Bright Star Catalogue''. When first catalogued it was in the Puppis constellation and was designated "13 Puppis", but it subsequently migrated to Canis Minor. Bode gave it the Bayer designation of Lambda Canis Minoris. Properties This star has an orange hue and is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye on a dark night, having an apparent visual magnitude of +4.39. It is located at a distance of approximately 254 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +71.6 km/s. The star is considered a member of the thin disk population. It has one known exoplanet companion. The stellar classification of HD 66141 is K2IIIbFe-0.5:, which indicates an evolved K-type giant star with a mild underabundan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiregular Variable
In astronomy, a semiregular variable star, a type of variable star, is a giant or supergiant of intermediate and late (cooler) spectral type showing considerable periodicity in its light changes, accompanied or sometimes interrupted by various irregularities. Periods lie in the range from 20 to more than 2000 days, while the shapes of the light curves may be rather different and variable with each cycle. The amplitudes may be from several hundredths to several magnitudes (usually 1-2 magnitudes in the V filter). Classification The semiregular variable stars have been sub-divided into four categories for many decades, with a fifth related group defined more recently. The original definitions of the four main groups were formalised in 1958 at the tenth general assembly of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) has updated the definitions with some additional information and provided newer reference stars where old examples such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Canis Minoris
Gamma Canis Minoris (γ Canis Minoris) is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation Canis Minor. Its orange colour is obvious when seen through binoculars. The system is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.33. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.25 mas as seen from Earth, this system is located about 320 light years from the Sun. This spectroscopic binary star system has an orbital period of 389.31 days, a semimajor axis of 1.48 AU, and an eccentricity of 0.2586. Their variable radial velocity was discovered by H. M. Reese in 1902 at Lick Observatory. Both components are evolved, K-type giant stars, most likely on their first ascent along the red giant branch. The primary, component A, has a stellar classification In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Cassiopeiae Variable
A Gamma Cassiopeiae variable (γ Cassiopeiae variable) is a type of variable star, named for its prototype γ Cassiopeiae. Variability γ Cassiopeiae variables show irregular changes in brightness on a timescale of decades. These typically have amplitudes of the order of a magnitude. For example, γ Cassiopeiae is usually about magnitude 2.5 and has varied between magnitudes 1.6 and 3.0. The variations are associated with changes in the spectrum between normal absorption spectra and Be star spectra, often also including shell star characteristics. Pleione and γ Cassiopeiae itself are both variable stars that have intermittent shell episodes where strong shell features appear in the spectrum and the brightness increases or decreases significantly. At other times the shell is not detectable in the spectrum, and even the emission lines may disappear. The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) categorises γ Cassiopeiae stars as eruptive variables and describes them as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Canis Minoris
Beta Canis Minoris (β Canis Minoris, abbreviated Beta CMi, β CMi), also named Gomeisa , is a star in the constellation of Canis Minor. In the night sky it is notable for its proximity to the prominent star Procyon. Nomenclature ''β Canis Minoris'' ( Latinised to ''Beta Canis Minoris'') is the star's Bayer designation. The traditional name ''Gomeisa'' comes from the Arabic ''al-ghumaisa''' ("the bleary-eyed (woman)"), short for مرزم الغميصاء ''mirzam al-ghumaisa''' ("girdle of the bleary-eyed one"). In Arabic, the short form would be identical with the name of Procyon. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Gomeisa'' for this star. In Chinese, (), meaning '' South River'', refers to an asterism consisting of β Canis Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |