|
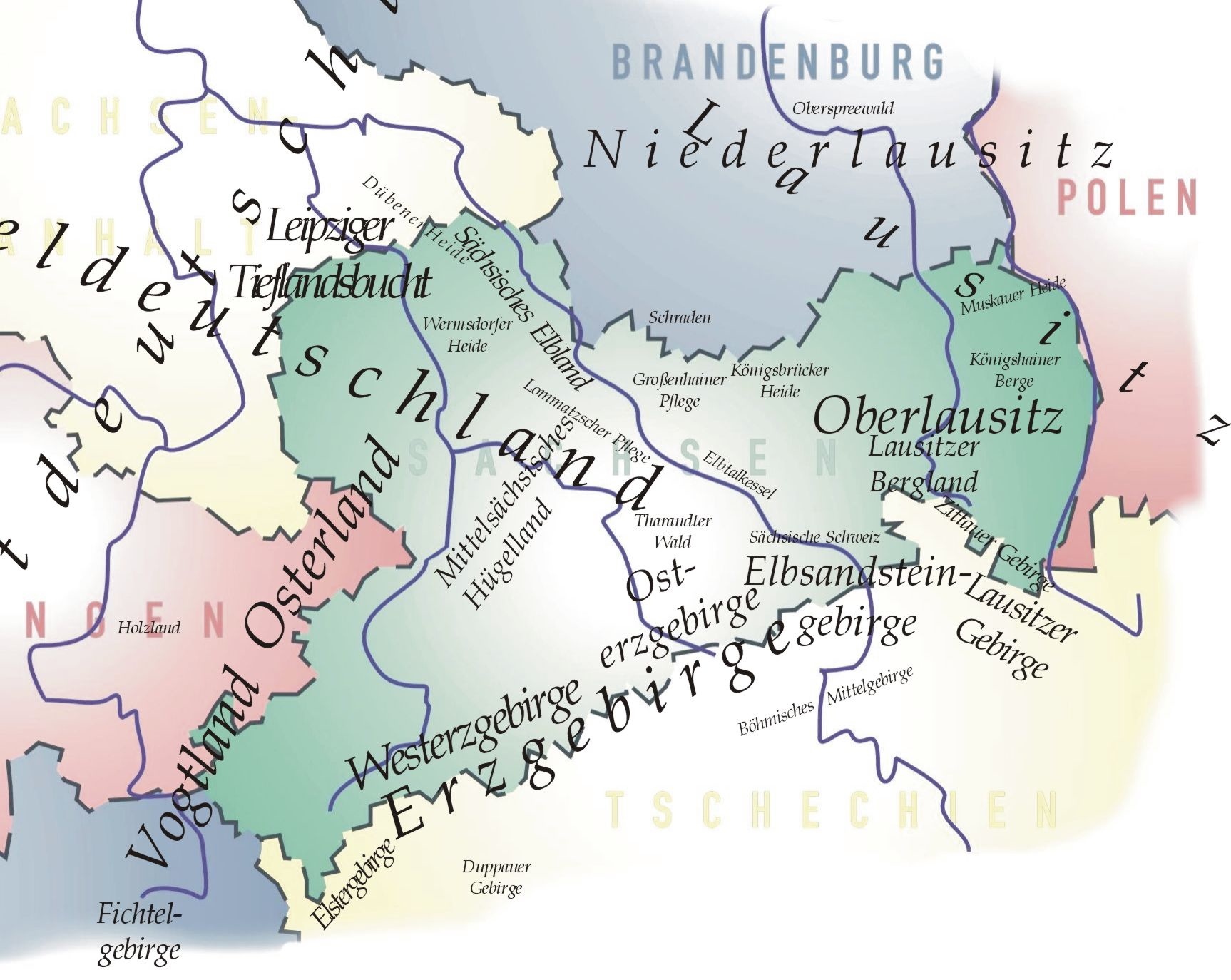
List Of Regions Of Saxony
A classification of the various regions of Saxony cannot be achieved in any uniform or standard way, as the commonly used names usually represent a mixture of historical regions and geographical features. Many well-known names of regions, such as Lusatia, comprise a mixture of natural habitats and geological zones, while other, scientifically assigned, names are only known in university departments. The following list contains, in alphabetical order, both those names that are commonly used, as well as those only known regionally or used in the scientific field. They are listed by their English names with their German names in brackets. Names of settlements or other geographic features are omitted here. Overall, across much of the area, Saxony belongs both to Eastern Germany and Central Germany (geography), Central Germany. However, on a smaller scale there are many regions and landscapes that overlap the boundaries of the Free State and extend beyond it: * Bahra (river), Bahra V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lusatia
Lusatia (; ; ; ; ; ), otherwise known as Sorbia, is a region in Central Europe, formerly entirely in Germany and today territorially split between Germany and modern-day Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers in the east to the Pulsnitz and Black Elster rivers in the west, and is located within the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg as well as in the Polish voivodeships of Lower Silesia and Lubusz. Major rivers of Lusatia are the Spree and the Lusatian Neisse, which defines the border between Germany and Poland. The Lusatian Mountains of the Western Sudetes separate Lusatia from Bohemia (Czech Republic) in the south. Lusatia is traditionally divided into Upper Lusatia, the hilly southern part, and Lower Lusatia, the flat northern part. The areas east and west along the Spree in the German part of Lusatia are home to the Slavic Sorbs, one of Germany’s four officially recognized indigenous ethnic minorities. The Upper Sorbs inhabit Saxon U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gimmlitz Valley
The Gimmlitz is a river of Saxony Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ..., Germany. It is a right tributary of the Freiberger Mulde, which it joins in Lichtenberg, Mittelsachsen, Lichtenberg. See also *List of rivers of Saxony Rivers of Saxony Rivers of Germany {{Saxony-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Saxon Hills
The Central Saxon Hills ({{langx, de, Mittelsächsische Hügelland, also called the ''Sächsisches Burgen- und Heideland''), is a region of '' Hügelland'' with indistinct boundaries in the centre of the German state of Saxony. Geographic location To the north the region extends roughly as far as the confluence of the Freiberg and Zwickau Mulde rivers and along the Freiberg Mulde to Nossen and on in the valley of the Triebisch to just before Meissen. Its short eastern boundary runs from Meissen along the Triebisch in a southerly direction to the Tharandt Forest, continuing through it. In the south, the hill country is bounded by an artificial line from the Tharandt Forest and running north of the cities and towns of Freiberg, Chemnitz, Glauchau and Werdau. In the west the region is bounded by the Thuringian state border, the River Pleiße and a line from Frohburg to the confluence of the two Muldes. According to other sources, the ''Lommatzscher Pflege'' and the so-called O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meissen Upland
Meissen ( ), is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden and 75 km (46 mi) west of Bautzen on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, the Albrechtsburg castle, the Gothic Meissen Cathedral and the Meissen Frauenkirche. The ''Große Kreisstadt'' is the capital of the Meissen district. History It grew out of the early West Slavic settlement of ''Miśni'' inhabited by Glomatians and was founded as a German town by King Henry the Fowler in 929. In 968, the Diocese of Meissen was founded, and Meissen became the episcopal see of a bishop. The Catholic bishopric was suppressed in 1581 after the diocese accepted the Protestant Reformation (1559), but re-created in 1921 with its seat first at Bautzen and now at the Katholische Hofkirche in Dresden. In 965, the Margraviate of Meissen, a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, was founded, with Meissen as its capital. A market ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the Germany, German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the south, Lower Lusatia is a settlement area of the West Slavic Sorbs whose endangered Lower Sorbian language is related to Upper Sorbian language, Upper Sorbian and Polish language, Polish. Geography This sparsely inhabited area within the North European Plain (North German Plain, Northern Lowland) is characterised by extended Scots pine, pine forests, heathlands and meadows. In the north it is confined by the middle Spree (river), Spree River with Lake Schwielochsee (lake), Schwielochsee and its eastern continuation across the Oder at Eisenhüttenstadt, Fürstenberg to Chlebowo, Lubusz Voivodeship, Chlebowo. In the glacial valley between Lübben (Spreewald), Lübben and Cottbus, the Spree River branches out into the Spreewald ("Spree Woods") riparian fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lößnitz (landscape)
Bergstadt Lößnitz (“Mining Town of Lößnitz”, also spelt Lössnitz), sometimes also called ''Muhme'' (“Aunt”) for its age, is a town in the district of Erzgebirgskreis, Saxony, Germany, and belongs to the Town League of Silberberg (''Städtebund Silberberg''). Its name comes from the Slavic languages, Slavic ''lesnice'', meaning “forest place”. Geography Lößnitz is a small town in the western part of the Ore Mountains lying nestled among wooded mountain ranges in a glen, roughly 432 m above sea level. It lies 4 km northeast of Aue, Saxony, Aue and 27 km southwest of Chemnitz. Constituent communities Lößnitz has six ''Ortsteile'' (constituent communities), namely Affalter (since 1999), Dittersdorf (since 1973), Grüna (from 1974 a constituent community of Affalter), Dreihansen (said to have been a self-standing community in 1791), Niederlößnitz (since 1898) and Streitwald (from 1939 a constituent community of Affalter). History Lößnitz w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig Bay
The Leipzig BayDickinson (1964), p. 29.''Utrata Fachwörterbuch: Geographie - Englisch-Deutsch/Deutsch-Englisch'' by Jürgen Utrata (2014). Retrieved 10 Apr 2014.() or Leipzig Basin or Saxon LowlandDickinson (1964), p. 37. or Saxon Bay is a very flat, originally lakeless and highly fertile in Central , in northwestern |
Lusatian Mountains
The Lusatian Mountains (; ; ) are a mountain range of the Western Sudetes on the southeastern border of Germany with the Czech Republic. They are a continuation of the Ore Mountains range west of the Elbe valley. The mountains of the northern, German, part are called the Zittau Mountains. Geography The range is among the westernmost extensions of the Sudetes, which stretch along the border between the historic region of Silesia in the north, and Bohemia and Moravia in the south up to the Moravian Gate in the east, where they join the Carpathian Mountains. The northwestern foothills of the Lusatian Mountains are called the Lusatian Highlands; in the southwest the range borders on the České Středohoří mountains. The range is largely made up of sandstone sedimentary rocks leaning on a Precambrian crystalline Basement (geology), basement. The northern ridge is marked by the Lusatian Fault, a geological disturbance zone separating the Bohemian sandstones from the Lusatian gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lusatian Highlands
The Lusatian Highlands at www.silvaportal.info. Accessed on 10 July 2011. or Lusatian Hills AA, 1994. Retrieved 23 Jan 2015 (, ; (for the Czech part only); Upper Sorbian: ''Łužiske hory'') form a y region in and the . A western extension of the |
Königshain Hills
The Königshain Hills (, Upper Sorbian: ''Limas'') lie in Eastern Upper Lusatia west of the town of Görlitz in the Landkreis Görlitz, county of the same name. They are located north and south of the village of Königshain after which they are named, and are an extensive, mainly wooded granite region. Their highest points are the Kämpferberge (415m above sea level) and the well-known Hochstein (Königshain Hills), Hochstein, 406m above sea level. The entire hill range has been a protected area since 1974. In a part ''(Elysium)'' of the former Firsten Quarry there is a bird reserve. External links Königshain Hills {{DEFAULTSORT:Konigshain Hills Natural regions of Saxony Hill ranges of Germany Climbing areas of Germany Protected areas of Saxony Quarries in Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |