|
List Of Proposed Etymologies Of OK
Several etymologies have been proposed for the word ''OK'' or ''okay''. The majority can be easily classified as false etymologies, or possibly folk etymologies. H. L. Mencken, in ''The American Language'', lists serious candidates and "a few of the more picturesque or preposterous". Allen Walker Read surveyed a variety of explanations in a 1964 article titled "The Folklore of 'O. K. Eric Partridge Eric Honeywood Partridge (6 February 1894 – 1 June 1979) was a New Zealand–United Kingdom, British lexicography, lexicographer of the English language, particularly of its slang. His writing career was interrupted only by his service in the ... described O.K. as "an evergreen of the correspondence column." References Sources * * Citations {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Proposed Etymologies Of Ok OK OK Pseudolinguistics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etymologies
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. Most directly tied to historical linguistics, philology, and semiotics, it additionally draws upon comparative semantics, morphology, pragmatics, and phonetics in order to attempt a comprehensive and chronological catalogue of all meanings and changes that a word (and its related parts) carries throughout its history. The origin of any particular word is also known as its ''etymology''. For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts, particularly texts about the language itself, to gather knowledge about how words were used during earlier periods, how they developed in meaning and form, or when and how they entered the language. Etymologists also apply the methods of comparative linguistics to reconstruct in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses of the U.S. Congress. Jacksonian democracy, His political philosophy became the basis for the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party. Jackson's legacy is controversial: he has been praised as an advocate for working Americans and Nullification crisis, preserving the union of states, and criticized for his racist policies, particularly towards Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans. Jackson was born in the colonial Carolinas before the American Revolutionary War. He became a American frontier, frontier lawyer and married Rachel Donelson Jackson, Rachel Donelson Robards. He briefly served in the U.S. House of Representatives and the U.S. Senate, representing Tennessee. After resigning, he served a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
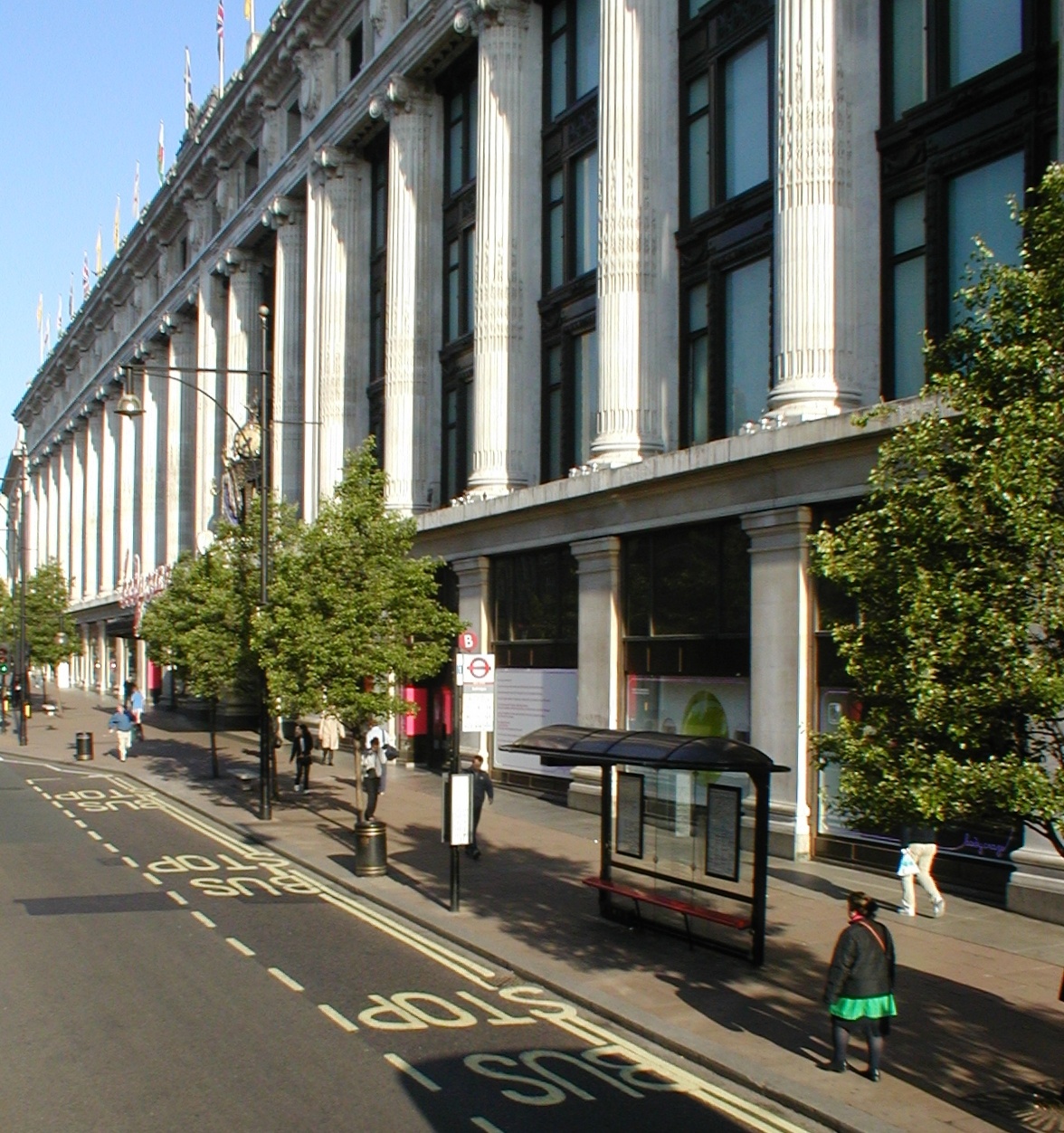
Harry Gordon Selfridge
Harry Gordon Selfridge, Sr. (11 January 1858 – 8 May 1947) was an American retail magnate who founded the London-based department store Selfridges. The early years of his leadership led to his becoming one of the most respected and wealthy retail magnates in the United Kingdom. He was known as the 'Earl of Oxford Street'. Born in Ripon, Wisconsin, and raised in Jackson, Michigan, Selfridge delivered newspapers and left school at 14 when he found work at a local bank. Selfridge eventually obtained a stock boy position at Marshall Field's department store in Chicago, where over the next 25 years, he rose to become a partner. In 1890 he married Rose Selfridge, Rose Buckingham who was from a prominent Chicago family. In 1906 following a trip to London, Selfridge invested £400,000 to build a new department store in what was then the unfashionable western end of Oxford Street. Selfridges, Oxford Street, Selfridges opened to the public on 15 March 1909, and Selfridge remained chai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selfridges
Selfridges, also known as Selfridges & Co., is a chain of upmarket department stores in the United Kingdom that is operated by Selfridges Retail Limited. It was founded by Harry Gordon Selfridge in 1908. The historic Daniel Burnham-designed Selfridges, Oxford Street, Selfridges flagship store at 400 Oxford Street in London opened on 15 March 1909 and is the second-largest shop in the UK (after Harrods). Other Selfridges stores opened in the Manchester area at the Trafford Centre (1998) and at Exchange Square (Manchester), Exchange Square (2002), and in Birmingham at the Selfridges Building, Birmingham, Bullring (2003). During the 1940s, smaller provincial Selfridges stores were sold to the John Lewis Partnership, and in 1951, the original Oxford Street store was acquired by the Liverpool-based Lewis's chain of department stores. Lewis's and Selfridges were then taken over in 1965 by the Sears plc, Sears Group, owned by Charles Clore.subscription required Expanded under the Sears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821), are published by Times Media, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'' were founded independently and have had common ownership only since 1966. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. ''The Times'' was the first newspaper to bear that name, inspiring numerous other papers around the world. In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as or , although the newspaper is of national scope and distribution. ''The Times'' had an average daily circulation of 365,880 in March 2020; in the same period, ''The Sunday Times'' had an average weekly circulation of 647,622. The two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josh Billings
Henry Wheeler Shaw (April 21, 1818October 14, 1885), better known by the pen name Josh Billings, was a 19th-century American humorist and lecturer. Biography Shaw was born in Lanesborough, Massachusetts on April 21, 1818. His father was Henry Shaw, who served in the United States House of Representatives from 1817 to 1821,Biographical Introduction to The complete works of Josh Billings (Henry W. Shaw) p. xiv (1876)Encyclopædia Britannica Vol. 24, p. 813 (11th ed. 1911) and his grandfather [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabo Language
The Jabo language is a Kru language spoken by the Jabo people of Liberia. They have also been known in the past as the Gweabo. Classification Jabo is part of the Grebo language continuum, encoded by ''Ethnologue'' more specifically as a dialect of the Southern Grebo language.In a working-group draft of ISO-639-3 written in 2001 (URL accessed 2006-4-2, the code GRJ was assigned to the "Jabo language", while the code GEU was applied to the coordinate taxon "Glebo". However, Jabo satisfies the ISO 639-3 criteria for an individual language: *The shared core-vocabulary score for Jabo and Seaside Grebo is reported as being as low as 75%. *The Jabo and Grebo political territories have been distinct at least since the time of the founding of "Maryland in Africa." The two peoples are currently in different counties (Grand Kru County and Maryland County), and the Jabo claim a greater affinity for the Kru (Krao) than for the Grebo.Ethnologue. *The physical separation of the Jabo and Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Liberia border, its east, and the Atlantic Ocean to its south and southwest. It has a population of around 5.5million and covers an area of . The official language is English. Languages of Liberia, Over 20 indigenous languages are spoken, reflecting the country's ethnic and cultural diversity. The capital and largest List of cities in Liberia, city is Monrovia. Liberia began in the early 19th century as a project of the American Colonization Society (ACS), which believed that black people would face better chances for freedom and prosperity in Africa than in the United States. Between 1822 and the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, more than 15,000 freed and free-born African Americans, along with 3,198 Afro-Caribbeans, relocated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka Language
The Mandinka language (; Ajami: ), or Mandingo, is a Mande language spoken by the Mandinka people of northern Guinea-Bissau, the Casamance region of Senegal, and The Gambia where it is one of the principal languages. Mandinka belongs to the Manding branch of Mande and is similar to Bambara and Maninka/Malinké but with only 5 instead of 7 vowels, due to lacking the ATR distinction. The varieties spoken in Urban Gambia and Senegal borders on a pitch accent due to its proximity with non-tonal neighboring languages like Wolof. Phonology Mandinka is here represented by the variety spoken in Casamance. There is little dialectical diversity. Tone Mandinka has two tones, high and low. Unmodified nouns are either high tone on all syllables or low tone on all syllables. The definite suffix ''-o'' takes a low tone on high-tone nouns and a falling tone on low-tone nouns. It also assimilates any preceding short vowel, resulting in a long /oo/ with either low or falling tone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In The United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of List of ethnic groups of Africa, Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the Southern United States, South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during the early Slavery in the colonial history of the United States, colonial period, it was practiced in what became British America, Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, abolition in 1865, and issues concerning slavery seeped into every aspect of national politics, economics, and social custom. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction era, Recons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolof Language
Wolof ( ; , ) is a Niger–Congo language spoken by the Wolof people in much of the West African subregion of Senegambia that is split between the countries of Senegal, The Gambia and Mauritania. Like the neighbouring languages Serer and Fula, it belongs to the Senegambian branch of the Niger–Congo language family. Unlike most other languages of its family, Wolof is not a tonal language. Wolof is the most widely spoken language in Senegal, spoken natively by the Wolof people (40% of the population) but also by most other Senegalese as a second language. Wolof dialects vary geographically and between rural and urban areas. The principal dialect of Dakar, for instance, is an urban mixture of Wolof, French, and Arabic. ''Wolof'' is the standard spelling and may also refer to the Wolof ethnicity or culture. Variants include the older French , , or , which now typically refers either to the Jolof Empire or to jollof rice, a common West African rice dish. Now-archaic forms incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Horseshoe Bend (1814)
The Battle of Horseshoe Bend (also known as ''Tohopeka'', ''Cholocco Litabixbee'', or ''The Horseshoe''), was fought during the War of 1812 in the Mississippi Territory, now central Alabama. On March 27, 1814, United States forces and Native Americans in the United States, Indian allies under Major General Andrew Jackson defeated the Red Sticks, a part of the Creek people, Creek Indian tribe who opposed American expansion, effectively ending the Creek War. Background The Creek people, Creek Indians of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and the eastern part of the Mississippi Territory had become divided into two factions: the Upper Creek (or Red Sticks), a majority who opposed American expansion and sided with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British and the colonial authorities of Spanish Florida during the War of 1812; and the Lower Creek, who were more assimilated into the Anglo-Americans, Anglo culture, had a stronger relationship with the U.S. Indian Agent Benj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |