|
List Of Largest Power Stations
This article lists the largest power stations in the world, the ten overall and the five of each type, in terms of installed electrical capacity. Non-renewable power stations are those that run on coal, fuel oils, nuclear fuel, natural gas, oil shale and peat, while renewable power stations run on fuel sources such as biomass, geothermal, hydroelectric, solar, and wind. Only the most significant fuel source is listed for power stations that run on multiple sources. , the largest power generating facility ever built is the Three Gorges Dam in China, completed in 2012. The facility generates power by utilizing 32 Francis turbines for a total capacity of . The eight largest power stations are also hydroelectric dams, beginning with Baihetan Dam, at , also in China. The largest natural gas plant is Jebel Ali, UAE () and the largest coal plant is Tuoketuo, China (). The largest nuclear plant is Kori, South Korea () following the 2011 suspension of Kashiwazaki-Kariwa, Japan ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
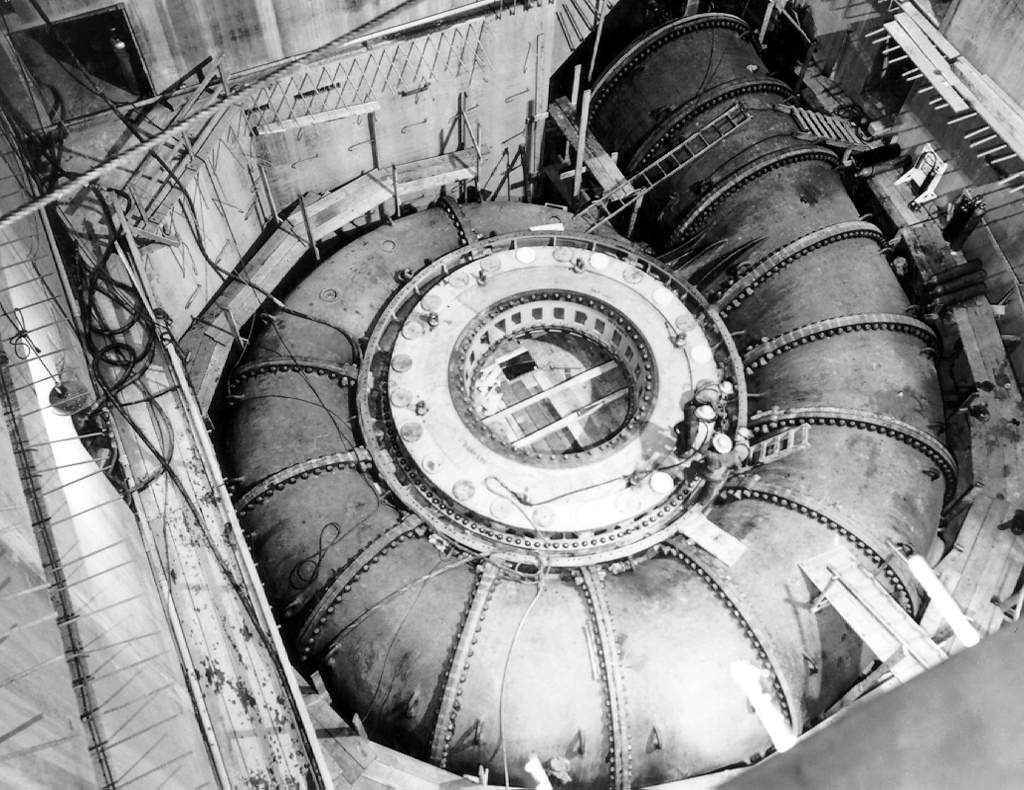
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terawatt Hour
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a non-SI unit of energy equal to 3.6 megajoules (MJ) in SI units, which is the energy delivered by one kilowatt of power for one hour. Kilowatt-hours are a common billing unit for electrical energy supplied by electric utilities. Metric prefixes are used for multiples and submultiples of the basic unit, the watt-hour (3.6 kJ). Definition The kilowatt-hour is a composite unit of energy equal to one kilowatt (kW) multiplied by (i.e., sustained for) one hour. The International System of Units (SI) unit of energy meanwhile is the joule (symbol J). Because a watt is by definition one joule per second, and because there are 3,600 seconds in an hour, one kWh equals 3,600 kilojoules or 3.6 MJ."Half-high dots or spaces are used to express a derived unit formed from two or more other units by multiplication.", Barry N. Taylor. (2001 ed.''The International System of Units.'' (Special publication 33 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work (physics), energy transfer. The watt is named in honor of James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish people, Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own Watt steam engine, steam engine in 1776, which became fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one meter per second against a constant opposing force of one Newton (unit), newton, the rate at which Work (physics), work is done is one watt. \mathrm. In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Coordinate System
A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical coordinate system, spherical or geodetic coordinates, geodetic coordinate system for measuring and communicating position (geometry), positions directly on Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest, and most widely used type of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface. A full GCS specification, such as those listed in the EPSG Geodetic Parameter Dataset, EPSG and ISO 19111 standards, also includes a choice of geodetic datum (including an Earth ellipsoid), as different datums will yield different latitude and longitude values for the same location. History The invention of a geographic coordinate system is generally credited to Eratosthenes of Cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is the List of African countries by area, second-largest country in Africa and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 112 million, the DR Congo is the most populous nominally List of countries and territories where French is an official language, Francophone country in the world. Belgian French, French is the official and most widely spoken language, though there are Languages of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, over 200 indigenous languages. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, the Cabinda Province, Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean to the west; the Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Inga Dam
The Grand Inga Dam (French: ''Barrage du Grand Inga'') is a series of seven proposed hydroelectric power stations at the site of the Inga Falls, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. If built as planned, the 40–70 GW project would be the largest power station in the world. Location The project would be located across the Congo River, approximately , upstream of where the river empties into the Atlantic Ocean. This is approximately , southwest of Kinshasa, the capital and largest city of the DR Congo. This is the site of the Inga Falls and is the location of the 351 MW Inga 1 Hydropower Station and the 1,424 MW Inga 2 Hydropower Station, approximately upstream of Matadi, the country's largest port. Overview The project would involve building a dam across the south of the Bundi River valley where it meets the Congo, then diverting the Congo from above the waterfalls into the north of the valley to create a huge reservoir. It is anticipated that the vertical drop, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gansu Wind Farm
The Gansu Wind Farm Project or Jiuquan Wind Power Base is a group of large wind farms under construction in western Gansu province in China. The Gansu Wind Farm Project is located in desert areas near the city of Jiuquan in two localities of Guazhou County and also near Yumen City, in the northwest province of Gansu, which has an abundance of wind. In 2015 the complex was operating at below 40% utilization of the current 8 GW with a planned capacity of 20 GW. In 2017 the 2,383 km long Jiuquan - Hunan HVDC transmission line entered service connecting the remote complex to the Hunan regional grid allowing full utilization of its generation capacity. After 4 years of delays, the latest phase of construction was completed, bringing total generation capacity up to 10GW. Overview The project is one of six national wind power megaprojects approved by the Chinese government. It is expected to grow to 20 gigawatts by 2020, at an estimated cost of 120 billion Chinese yuan ($17.5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonghe Talatan Solar Park
Gonghe may refer to: * Gonghe Regency, a regency that ruled the Chinese Zhou dynasty from 841 to 828 BC * Gonghe County (共和县), of Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai Province, China *Abbreviation of ( zh, hp=Gōngyè Hézuòshè, link=no), meaning Chinese Industrial Cooperatives {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant
The is a large, modern (housing the world's first advanced boiling water reactor or ABWR) nuclear power plant on a site.TEPCO Official Press Release (Japanese)First in Japan – Use of the Full Area for Power Plant Buildings, Reinforced Concrete R&D, and Waste Incinerator Building. 25 July 2002. The campus spans the towns of Kashiwazaki and Kariwa in Niigata Prefecture, Japan, on the coast of the Sea of Japan, where it gets cooling water. The plant is owned and operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), and it is the largest nuclear generating station in the world by net electrical power rating. On 16 July 2007, the Chūetsu offshore earthquake took place, with its epicenter located only from the plant. The earthquake registered Mw 6.6, ranking it among the strongest earthquakes to occur in the immediate range of a nuclear power plant. This shook the plant beyond design basis and initiated an extended shutdown for inspection, which indicated that greater earthqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kori Nuclear Power Plant
The Kori Nuclear Power Plant ( Korean: 고리원자력발전소, Hanja: 古里原子力發電所) is a South Korean nuclear power plant located in Kori, a suburban village in Busan. It is the world's second largest fully operational nuclear generating station by total reactor count and the number of currently operational reactors since 2016, after it exceeded in nameplate capacity Canada's Bruce Nuclear Generating Station. It is owned and operated by Korea Hydro & Nuclear Power, a subsidiary of KEPCO. The first reactor began commercial operation in 1978 and operated until 2017 when it was decommissioned. Units 2, 3, and 4 started commercial operations in the 1980s. All reactors on site are pressurized water reactors. Reactors An expansion of the plant begun in 2006 added four new Korean-sourced reactors, the so-called Shin Kori reactors (Korean: 신고리; ''shin'' 신 meaning "new"). The first pair of Shin Kori reactors are of the OPR-1000 design, while the second two are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |