|
List Of Instruments Used In Endocrinology
Endocrinology is a branch of internal medicine dealing with hormones, the chemical messengers released internally to regulate the body's physiology, physiologic functions. Endocrinologists diagnose and manage diseases of endocrine glands, including hypothalamus, Pituitary gland, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreatic islets, adrenals, testes, and ovaries. Some of the most common conditions treated are diabetes mellitus, Thyroid disease, diseases of the thyroid gland, metabolic bone disease, metabolic bone disorders, Pituitary disease, pituitary disorders, and Reproductive system disease#Endocrine, disorders of the reproductive system and infertility; in Pediatric endocrinology, children, typical conditions are growth deficiency, Delayed puberty, delay of puberty, and a variety of genetic disorders. In endocrinology, diagnosis is heavily relied on Medical test, laboratory tests, as it is important to find out diseases before they actually become Signs and symptoms, clinically evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrinology
Endocrinology (from ''endocrine system, endocrine'' + ''wikt:-logy#Suffix, -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, human development (biology), growth and development, tissue (biology), tissue function, sleep, digestion, Respiration (physiology), respiration, excretion, mood (psychology), mood, Stress (physiology), stress, lactation, Motor coordination, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology. The endocrine system consists of several glands, all in different parts of the body, that secrete hormones directly into the blood rather than into a Duct (anatomy), duct system. Therefore, endocrine glands are regarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive System Disease
A reproductive system disease is any disease of the human reproductive system. Types Infections Reproductive tract infection (RTI) are infections that affect the reproductive tract, which is part of the reproductive system. For females, reproductive tract infections can affect the upper reproductive tract (fallopian tubes, ovary and uterus) and the lower reproductive tract (vagina, cervix and vulva); for males these infections affect the penis, testicles, urethra or the vas deferens. The three types of reproductive tract infections are endogenous infections, iatrogenic infections and the more commonly known sexually transmitted infections. Each has its own specific causes and symptoms, caused by a bacterium, virus, fungus or other organism. Some infections are easily treatable and can be cured, some are more difficult, and some are non curable such as AIDS and herpes. Congenital abnormalities Examples of congenital abnormalities of the reproductive system include: * Kallmann syndr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
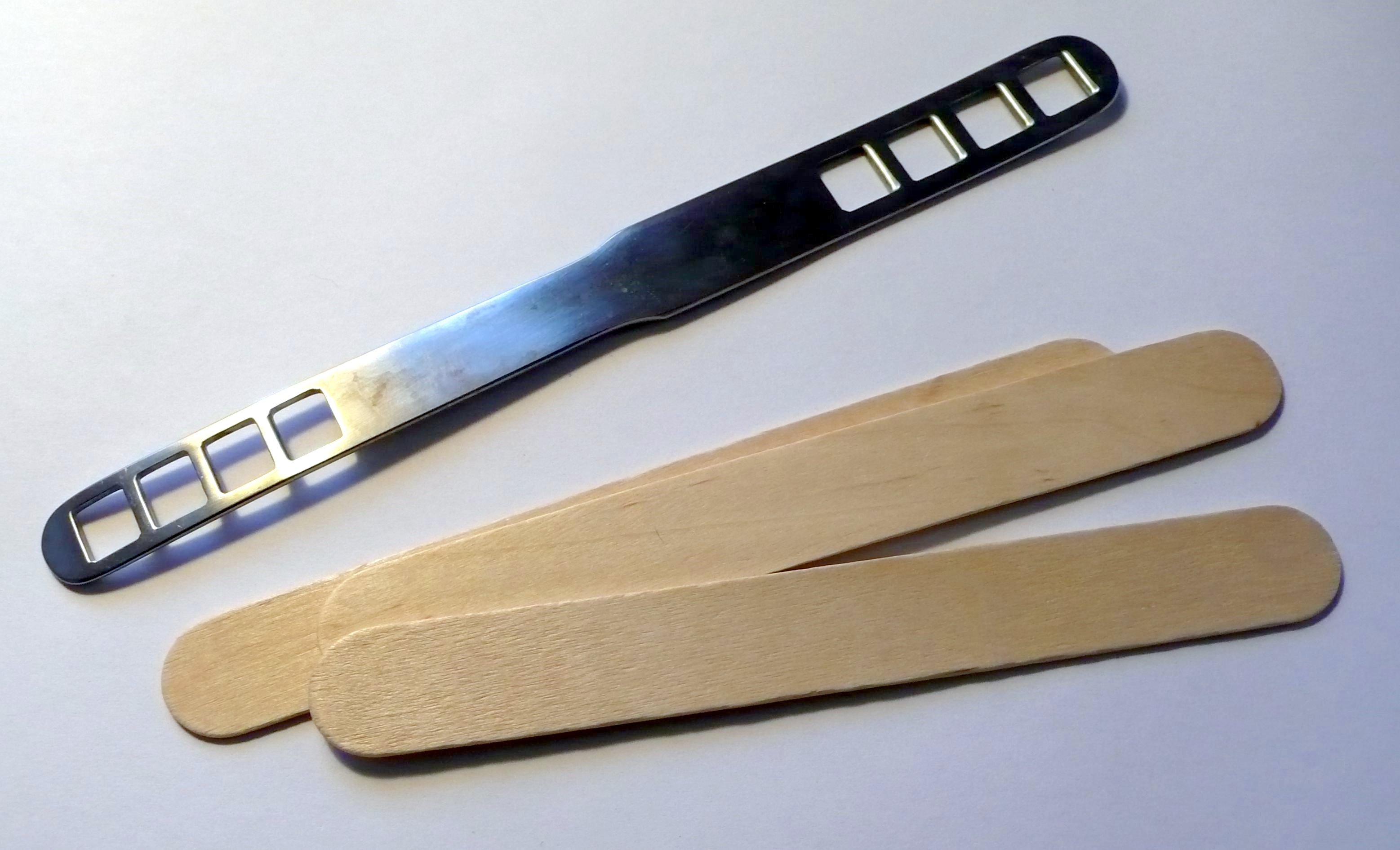
Sphygmomanometer
A sphygmomanometer ( ), also known as a blood pressure monitor, blood pressure machine, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury or aneroid manometer to measure the pressure. Manual sphygmomanometers are used with a stethoscope when using the auscultatory technique. A sphygmomanometer consists of an inflatable cuff, a measuring unit (the mercury manometer, or aneroid gauge), and a mechanism for inflation which may be a manually operated bulb and valve or a pump operated electrically. Etymology The word ''sphygmomanometer'' uses the combining form of '' sphygmo-'' + '' manometer''. The roots involved are as follows: Greek ''sphygmos'' "pulse", plus the scientific term '' manometer'' (from French ''manomètre''), i.e. "pressure meter", itself coined from ''manos'' "thin, sparse", and ''metron'' "measure". Most sphygmom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
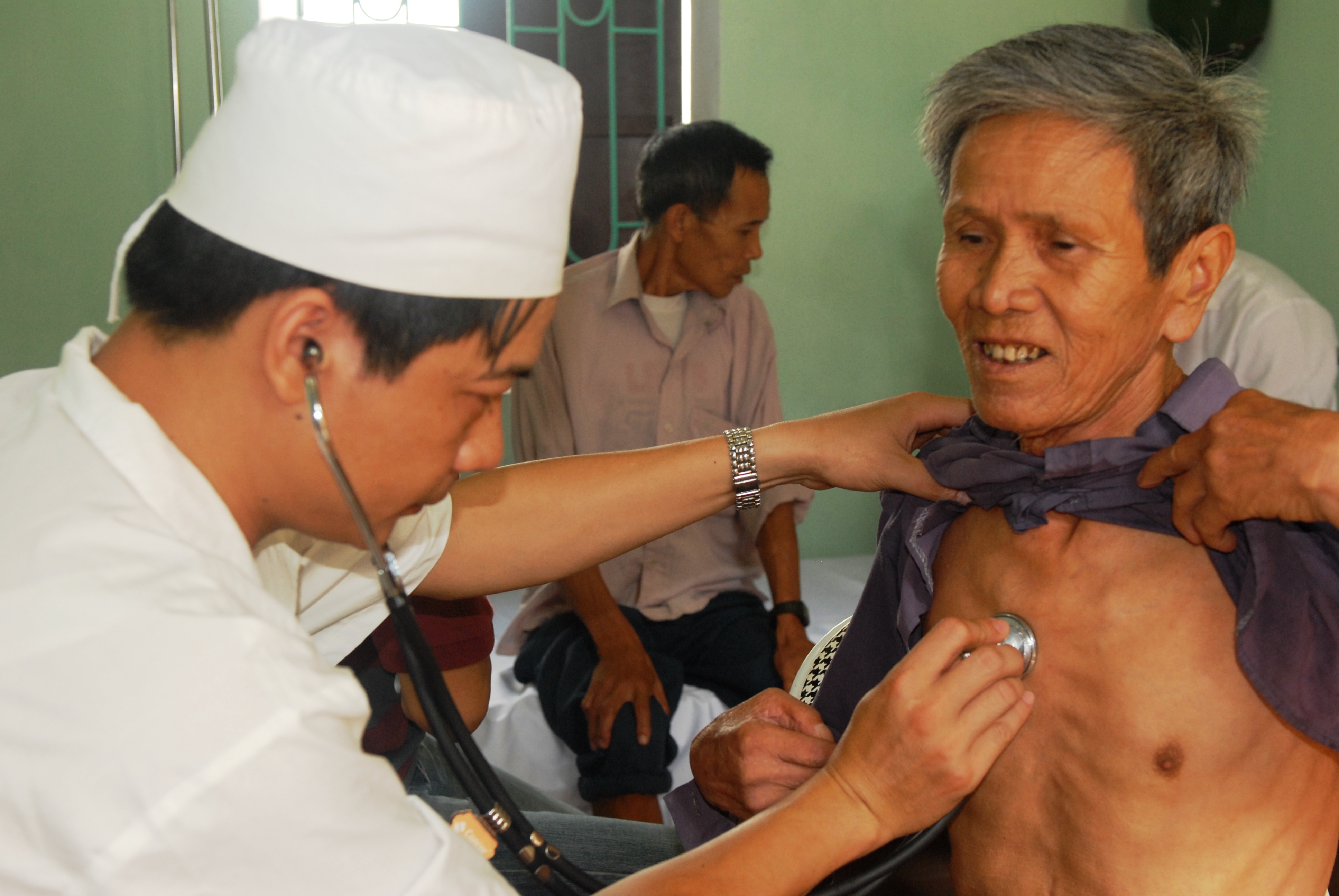
Stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medicine, medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, with either one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. A stethoscope can be used to listen to the sounds made by the heart sounds, heart, lungs or intestines, as well as blood flow in artery, arteries and veins. In combination with a manual sphygmomanometer, it is commonly used when measuring blood pressure. It was invented in 1816 by René Laennec and the binaural version by Arthur Leared in 1851. Less commonly, "mechanic's stethoscopes", equipped with rod shaped chestpieces, are used to listen to internal sounds made by machines (for example, sounds and vibrations emitted by worn ball bearings), such as diagnosing a malfunctioning automobile engine by listening to the sounds of its internal parts. Stethoscopes can also be used to check scientific vacuum chambers for leaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Device
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase. Discovery of what would be considered a medical device by modern standards dates as far back as in Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. Study of Archaeology, archeology and Roman medical literature also indicate that many types of medical devices were in widespread use during the time of ancient Rome. In the United States it was not until the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a medical diagnosis, diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical History
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and eventually people close to them, so to collect reliable/objective information for managing the medical diagnosis and proposing efficient medical treatments. The medically relevant complaints reported by the patient or others familiar with the patient are referred to as symptoms, in contrast with clinical signs, which are ascertained by direct examination on the part of medical personnel. Most health encounters will result in some form of history being taken. Medical histories vary in their depth and focus. For example, an ambulance paramedic would typically limit their history to important details, such as name, history of presenting complaint, allergies, etc. In contrast, a psychiatric history is frequently lengthy and in depth, as man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signs And Symptoms
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body, which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, including diagnosis, screening or monitoring. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood sugar in a person suspected of having diabetes mellitus after periods of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnosis
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine "causality, cause and effect". In systems engineering and computer science, it is typically used to determine the causes of symptoms, mitigations, and solutions. Computer science and networking * Bayesian network * Complex event processing * Diagnosis (artificial intelligence) * Event correlation * Fault management * Fault tree analysis * Grey problem * RPR problem diagnosis * Remote diagnostics * Root cause analysis * Troubleshooting * Unified Diagnostic Services Mathematics and logic * Bayesian probability * Hickam's dictum, Block Hackam's dictum * Occam's razor * Regression analysis#Regression diagnostics, Regression diagnostics * Sutton's law Medicine * Medical diagnosis * Molecular diagnostics Methods * CDR computerized assessment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene ( autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delayed Puberty
Delayed puberty is when a person lacks or has incomplete development of specific sexual characteristics past the usual age of onset of puberty. The person may have no physical or hormone, hormonal signs that puberty has begun. In the United States, girls are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack breast development by age 13 or have not started menstruating by age 15. Boys are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack enlargement of the testicles by age 14. Delayed puberty affects about 2% of adolescents. Most commonly, puberty may be delayed for several years and still occur normally, in which case it is considered constitutional delay of growth and puberty, a common variation of healthy physical development. Delay of puberty may also occur due to various causes such as malnutrition, various systemic diseases, or defects of the reproductive system (hypogonadism) or the body's responsiveness to sex hormones. Initial workup for delayed puberty not due to a chronic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |