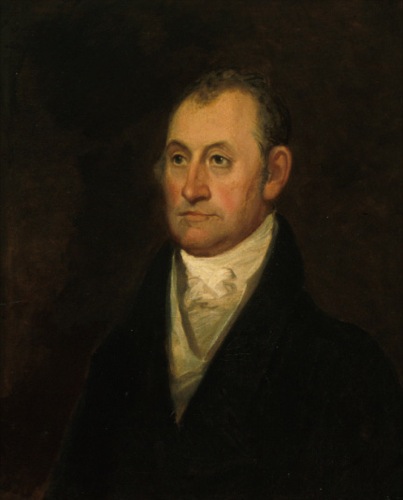|
List Of Governors Of Kentucky
The governor of the Commonwealth of Kentucky is the head of government of Kentucky, and serves as commander-in-chief of the state's Kentucky National Guard, military forces. The governor has a duty to enforce state laws; the power to either approve or veto Bill (law), bills passed by the Kentucky General Assembly; the power to convene the legislature; and the power to grant pardons, except in cases of treason and Impeachment in the United States, impeachment. The governor is also empowered to reorganize the state government or reduce it in size. Historically, the office has been regarded as one of the most powerful executive positions in the United States. Fifty-nine individuals have held the office of governor. Prior to a 1992 amendment to the Kentucky Constitution, state's constitution, the governor was prohibited from succeeding himself or herself in office, though four men (Isaac Shelby, John L. Helm, James B. McCreary and Happy Chandler) served multiple non-consecutive terms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor Of The Commonwealth Of Kentucky
The governor of the Commonwealth of Kentucky is the head of government of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Kentucky. Sixty-two men and one woman have served as governor of Kentucky. The governor's term is four years in length; since 1992, incumbents have been able to seek re-election once before becoming ineligible for four years. Throughout the state's history, four men have served two non-consecutive terms as governor, and four others have served two consecutive terms, the most recent being current governor Andy Beshear, who was re-elected to a second term on November 7, 2023. Kentucky is one of only five U.S. states that hold gubernatorial elections in Off-year election, odd-numbered years. The governor's powers are enumerated in the Kentucky Constitution, state constitution. There have been four constitutions of Kentucky—adopted in 1792, 1799, 1850, and 1891, respectively—and each has enlarged the governor's authority. Among the powers assigned to the gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Garrard
James Garrard ( ; January 14, 1749 – January 9, 1822) was an American farmer, Baptist minister and politician who served as the List of Governors of Kentucky, second governor of Kentucky from 1796 to 1804. Because of Term limits in the United States, term limits imposed by the Kentucky Constitution, state constitution adopted in 1799, he was the last Kentucky governor elected to two consecutive terms until the restriction was eased by a 1992 amendment, allowing Paul E. Patton's re-election in 1999. After serving in the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, Garrard moved west to the part of Virginia that is now Bourbon County, Kentucky. He held several local political offices and represented the area in the Virginia House of Delegates. He was chosen as a delegate to five of the ten statehood conventions that secured Kentucky's separation from Virginia and helped write the state's first constitution. Garrard was among the delegates who unsuccessfully tried to exclude gua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Shelby
Isaac Shelby (December 11, 1750 – July 18, 1826) was an American politician and military officer who was the List of governors of Kentucky, first and fifth Governor of Kentucky and served in the state legislatures of Virginia and North Carolina. He also fought in Lord Dunmore's War, the American Revolutionary War, and the War of 1812. While governor, he led the Kentucky militia in the Battle of the Thames, an action that was rewarded with a Congressional Gold Medal. Counties in nine states, and several cities and military bases, have been named in his honor. His fondness for John Dickinson (delegate), John Dickinson's "The Liberty Song" is believed to be the reason Kentucky adopted the state motto "United we stand, divided we fall". Issac Shelby's military service began when he served as second-in-command to his father at the Battle of Point Pleasant, the only major battle of Lord Dunmore's War. He gained the reputation of an expert woodsman and surveyor and spent the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant Governor Of Kentucky
The lieutenant governor of Kentucky was created under the state's second constitution, which was ratified in 1799. The inaugural officeholder was Alexander Scott Bullitt, who took office in 1800 following his election to serve under James Garrard in 1799. The lieutenant governor becomes governor of Kentucky under circumstances similar to those under which the vice president of the United States assumes the presidency. The current lieutenant governor is Democrat Jacqueline Coleman, who has been office since December 10, 2019. Duties of the Kentucky lieutenant governor As specified in Kentucky Revised Statute 11.400, it states: 11.400 Duties of Lieutenant Governor.Kentucky Revised Statute 11.400 (1) In addition to the duties prescribed for the office by the Constitution of the Commonwealth of Kentucky, the duties of the Lieutenant Governor shall be as follows: (a) To serve as vice chairman of the State Property and Buildings Commission as prescribed by KRS 56.450; (b) To serve a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ticket (election)
The term ticket can mean different things in relation to elections of councils or legislative bodies. First, it may refer to a single election choice which fills more than one political office or seat. For example, in Guyana, the candidates for President and Parliament run on the same "ticket", because they are elected together on a single ballot question — as a vote for a given party-list in the Parliamentary election counts as a vote for the party's corresponding presidential candidate — rather than separately. A ticket can also refer to a political group or political party. In this case, the candidates for a given party are said to be running on the party's ticket. " Straight party voting" (most common in some U.S. states) is voting for the entire party ticket, including every office for which the party has a candidate running. Particularly in the era of mechanical voting machines, it was possible to accomplish this in many jurisdictions by the use of a "party lever" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral College
An electoral college is a body whose task is to elect a candidate to a particular office. It is mostly used in the political context for a constitutional body that appoints the head of state or government, and sometimes the upper parliamentary chamber, in a democracy. Its members, called ''electors'', are either elected by the people for this purpose (making the whole process an indirect election) or by certain subregional entities or social organizations. If a constituent body that is not only summoned for this particular task, like a parliament, elects or appoints certain officials, it is not referred to as "electoral college" (see e.g. parliamentary system). Also, other appointing bodies (like committees appointing judges, as in Canada or Germany) normally do not fall into this definition. Examples United States The United States Electoral College is the only remaining electoral college in democracies where an executive president (a head of state who is also head of go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an List of historical unrecognized states and dependencies, unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States from 1861 to 1865. It comprised eleven U.S. states that declared Secession in the United States, secession: South Carolina in the American Civil War, South Carolina, Mississippi in the American Civil War, Mississippi, Florida in the American Civil War, Florida, Alabama in the American Civil War, Alabama, Georgia in the American Civil War, Georgia, Louisiana in the American Civil War, Louisiana, Texas in the American Civil War, Texas, Virginia in the American Civil War, Virginia, Arkansas in the American Civil War, Arkansas, Tennessee in the American Civil War, Tennessee, and North Carolina in the American Civil War, North Carolina. These states fought against the United States during the American Civil War. With Abraham Lincoln's 1860 Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (American Civil War)
The Union was the central government of the United States during the American Civil War. Its civilian and military forces resisted the Confederate State of America, Confederacy's attempt to Secession in the United States, secede following the 1860 United States presidential election, election of Abraham Lincoln as president of the United States. Presidency of Abraham Lincoln, Lincoln's administration asserted the permanency of the federal government of the United States, federal government and the continuity of the Constitution of the United States, United States Constitution. Nineteenth-century Americans commonly used the term Union to mean either the federal government of the United States or the unity of the states within the Federalism in the United States, federal constitutional framework. The Union can also refer to the people or territory of the states that remained loyal to the national government during the war. The loyal states are also known as the North, although fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admitted To The Union
Admission to the Union is provided by the Admissions Clause of the United States Constitution in Article IV, Section 3, Clause 1, which authorizes the United States Congress to admit new states into the Union beyond the thirteen states that already existed when the Constitution came into effect. The Constitution went into effect on June 21, 1788, in the nine states that had ratified it, and the U.S. federal government began operations under it on March 4, 1789, when it was in effect in 11 out of the 13 states. Since then, 37 states have been admitted into the Union. Each new state has been admitted on an equal footing with those already in existence. Of the 37 states admitted to the Union by Congress, all but six have been established within existing U.S. organized incorporated territories. A state that was so created might encompass all or part of a territory. When the people of a territory or a region have grown to a sufficient population and have made their desire for st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky County, Virginia
Kentucky County (aka Kentucke County), later the District of Kentucky, was formed by the Commonwealth of Virginia from the western portion (beyond the Big Sandy River and Cumberland Mountains) of Fincastle County effective 1777. The name of the county was taken from a Native American place name that came to be associated with a river in east central Kentucky, and gave the Kentucky River its name and eventually the U.S. state of Kentucky. During the almost four years of Kentucky County's existence, its seat of government was Harrodstown (then also known as Oldtown, later renamed Harrodsburg). The entire existence of Kentucky County was in the context of the Western theater of the American Revolutionary War. Except for the old French settlements in Illinois country, Kentucky was the western theater, and several major battles of the War occurred during its existence including the siege of Boonesborough, siege of Logan's Fort, and Bird's invasion of Kentucky. Other eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martha Layne Collins
Colonel Martha Layne Collins (née Hall; born December 7, 1936) is an American former businesswoman and politician from the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Kentucky; she served as the state's List of Governors of Kentucky, 56th governor from 1983 to 1987, the first woman to hold the office and the only one to date. Prior to that, she served as the 48th Lieutenant Governor of Kentucky, under John Y. Brown Jr. Her election made her the highest-ranking Democratic Party (United States), Democratic woman in the U.S. She was considered as a possible running mate for Democratic presidential nominee Walter Mondale in the 1984 United States presidential election, 1984 presidential election, but Mondale chose Congresswoman Geraldine Ferraro instead. After graduating from the University of Kentucky, Collins worked as a school teacher while her husband finished a degree in dentistry. She became interested in politics, and worked on both Wendell Ford's gubernatorial campaign in 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1899 Kentucky Gubernatorial Election
The 1899 Kentucky gubernatorial election was held on November 7, 1899, to choose the 33rd governor of Kentucky. The incumbent, Republican William O'Connell Bradley, was term-limited and unable to seek re-election. During a contentious and chaotic convention at the Music Hall in Louisville, the Democratic Party nominated state Senator William Goebel. A dissident faction of the party, styling themselves the "Honest Election Democrats", were angered by Goebel's political tactics at the Music Hall convention and later held their own convention. They nominated former Governor John Y. Brown. Republicans nominated state Attorney General William S. Taylor, although Governor Bradley favored another candidate and lent Taylor little support in the ensuing campaign. In the general election, Taylor won by a vote of 193,714 to 191,331. Brown garnered 12,040 votes, more than the difference between Taylor and Goebel. The election results were challenged on grounds of voter fraud, but th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |