|
List Of Geological Features On 21 Lutetia
This is a list of named geological features on 21 Lutetia. There are 37 officially named features on Lutetia, of which: * 19 are craters, * 8 are Regiones, * 3 are Labes, * 2 are Fossae, * 2 are Rimae, * 2 are Rupes, and * 1 is a Dorsum. 21 Lutetia was flown by in July 2010 by the '' Rosetta spacecraft'', while en route to comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. During this visit, ''Rosetta'' imaged Lutetia with a resolution of per pixel. As Lutetia is named after the Roman town that would later become Paris, most features on Lutetia are named after places in Europe during the Roman era. Craters Impact craters on 21 Lutetia are named after cities in Europe around the Roman era. Based on the images taken of the northern side of Lutetia by ''Rosetta'', it is suspected there is a large crater named Suspicio crater on the southern side of Lutetia, however it has not been directly imaged, so it remains unconfirmed, and therefore is not included in this list. Dorsa Dorsa on 21 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1567216776412-annotated-map-of-asteroid-21-lutetia 625
Year 1567 ( MDLXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 20 – Battle of Rio de Janeiro: Portuguese forces under the command of Estácio de Sá definitively drive the French out of Rio de Janeiro. * January 23 – After 45 years' reign, the Jiajing Emperor, Zhu Houcong, dies in the Forbidden City of China. * January – A Spanish force under the command of Captain Juan Pardo establishes Fort San Juan, in the Native American settlement of Joara. The fort is the first European settlement in present-day North Carolina. * February 4 – Prince Zhu Zaiji, son of the Jiajing Emperor, becomes the ascends the throne of Ming Dynasty China as the Longqing Emperor. * February 10 – Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley, husband of Mary, Queen of Scots, is murdered at the Provost's House in Kirk o' Field, Edinburgh. * March 13 – Battle of Oosterweel: A Spanish mercenary army surprises and kills a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21 Lutetia
21 Lutetia is a large M-type asteroid in the main asteroid belt. It measures about 100 kilometers in diameter (120 km along its major axis). It was discovered in 1852 by Hermann Goldschmidt, and is named after Lutetia, the Latin name of Paris. Lutetia has an irregular shape and is heavily cratered, with the largest impact crater reaching 45 km in diameter. The surface is geologically heterogeneous and is intersected by a system of grooves and scarps, which are thought to be fractures. It has a high overall bulk density, suggesting that it is made of metal-rich rock. The '' Rosetta'' probe passed within of Lutetia in July 2010. It was the largest asteroid visited by a spacecraft until ''Dawn'' arrived at Vesta in July 2011, and it is currently the 3rd largest asteroid to have ever been imaged in high quality by a spacecraft (after Vesta and Ceres). Discovery and exploration Lutetia was discovered on 15 November 1852, by Hermann Goldschmidt from the balc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a depression (geology), depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact event, impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Impact craters are typically circular, though they can be elliptical in shape or even irregular due to events such as landslides. Impact craters range in size from microscopic craters seen on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program to simple bowl-shaped depressions and vast, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury (planet), Mercury, Callisto (moon), Callisto, Ganymede (moon), Ganymede, and most small moons and asteroids. On other planet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regio (astronomy)
Planetary geology, alternatively known as astrogeology or exogeology, is a planetary science discipline concerned with the geology of celestial bodies such as planets and their Natural satellite, moons, asteroids, comets, and meteorites. Although the geo- prefix typically indicates topics of or relating to Earth, planetary geology is named as such for historical and convenience reasons; due to the subject matter, it is closely linked with more traditional Earth-based geology. Planetary geology includes such topics as determining the properties and processes of the internal structure of the terrestrial planets, Planetary surface, surface processes such as volcanism, impact craters, even fluvial and aeolian processes, aeolian action where applicable. Despite their outermost layers being dominated by gases, the giant planets are also included in the field of planetary geology, especially when it comes to their interiors. Fields within Planetary geology are largely derived from fields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossa (geology)
In planetary nomenclature, a fossa (pl. fossae ) is a long, narrow depression (trough) on the surface of an extraterrestrial body, such as a planet or moon. The term, which means "ditch" or "trench" in Latin, is not a geological term as such but a descriptor term used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the International Astronomical Union (IAU) for topographic features whose geology or geomorphology is uncertain due to lack of data or knowledge of the exact processes that formed them. Fossae are believed to be the result of a number of geological processes, such as geological fault, faulting or subsidence. Many fossae on Mars are probably graben. On Mars The Tharsis quadrangle is home to large troughs (long narrow depressions) called fossae in the geographical language used for Mars. This term is derived from Latin; therefore fossa is singular and fossae is plural. Troughs form when the crust is stretched until it breaks. The stretching can be due to the larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupes
Rupes (plural ) is the Latin word for 'cliff'. It is used in planetary geology to refer to escarpments on other worlds. , the International Astronomical Union, IAU has named 62 such features in the Solar System, on Mercury (planet), Mercury (17), Venus (7), the Moon (8), Mars (23), the asteroids 4 Vesta, Vesta (2) and 21 Lutetia, Lutetia (2), and Uranus's satellites Miranda (moon), Miranda (2) and Titania (moon), Titania (1). How rupes formed is, , a matter of speculation. Compressional Deformation (mechanics), strain from the cooling of the crust of terrestrial planets and large-scale displacement due to impacts are the two dominant theories. See also * List of lunar features#Rupes, Rupes on the Earth's moon * List of geological features on Mercury, Rupes on Mercury * List of geological features on Venus#Rupes, Rupes on Venus * Rousillon Rupes * Rupes Tenuis * Verona Rupes References Planetary geology Escarpments, Extraterrestrial cliffs, * {{planetary-geology-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrinkle Ridge
A wrinkle ridge is a type of feature commonly found on lunar maria, or basalt plains. These features are low, sinuous ridges formed on the mare surface that can extend for up to several hundred kilometers. Wrinkle ridges are tectonic features created after the lava cooled and solidified. They frequently outline ring structures buried within the mare, follow circular patterns outlining the mare, or intersect protruding peaks. They are sometimes called ''veins'' due to their resemblance to the veins that protrude from beneath the skin. Wrinkle ridges are named with the Latin designation ''dorsum'' (plural ''dorsa''). The standard IAU nomenclature uses the names of people (generally scientists) to identify wrinkle ridges on the Moon. For example, the Dorsa Burnet are named for Thomas Burnet, and the Dorsum Owen is named after George Owen of Henllys. Wrinkle ridges can also be found on Mars, for example in Chryse Planitia, on several of the asteroids that have been visited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
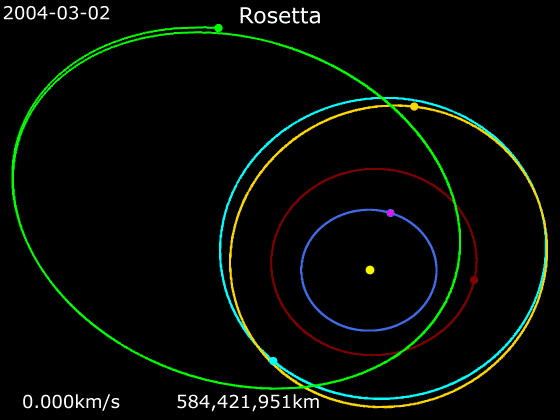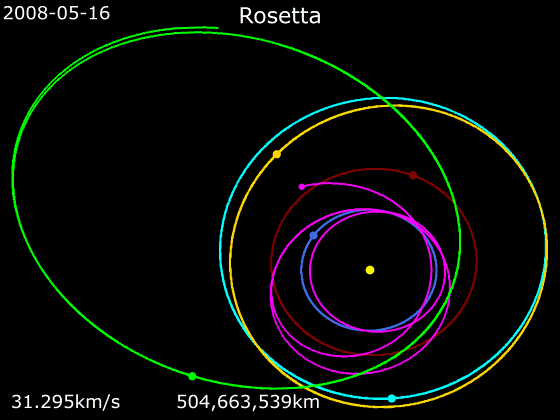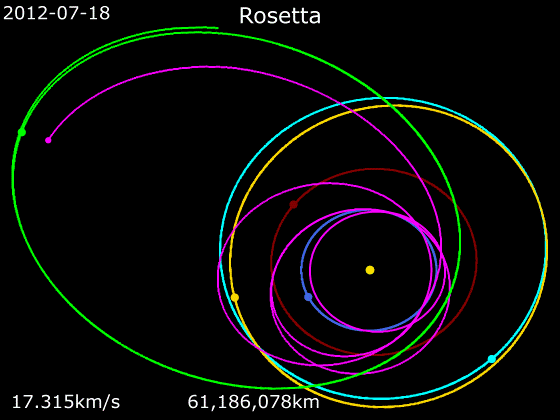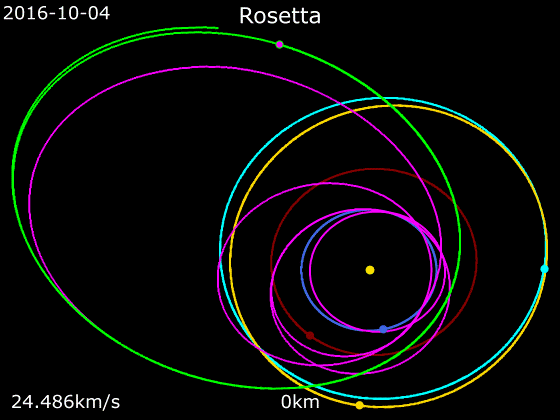
Rosetta (spacecraft)
''Rosetta'' was a space probe built by the European Space Agency that launched on 2 March 2004. Along with ''Philae'', its lander module, ''Rosetta'' performed a detailed study of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P). During its journey to the comet, the spacecraft performed flybys of Earth, Mars, and the asteroids 21 Lutetia and 2867 Šteins. It was launched as the third cornerstone mission of the ESA's Horizon 2000 programme, after ''SOHO' Cluster'' and '' XMM-Newton''. On 6 August 2014, the spacecraft reached the comet and performed a series of manoeuvers to eventually orbit the comet at distances of . On 12 November, its lander module ''Philae'' performed the first successful landing on a comet, though its battery power ran out two days later. Communications with ''Philae'' were briefly restored in June and July 2015, but due to diminishing solar power, ''Rosetta'' communications module with the lander was turned off on 27 July 2016. On 30 September 2016, the ''Rosett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko
67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (abbreviated as 67P or 67P/C–G) is a Jupiter-family comet. It is originally from the Kuiper belt and has an orbital period of 6.45 years as of 2012, a rotation period of approximately 12.4 hours, and a maximum velocity of . Churyumov–Gerasimenko is approximately at its longest and widest dimensions. It was first observed on photographic plates in 1969 by Soviet astronomers Klim Churyumov, Klim Ivanovych Churyumov and Svetlana Gerasimenko, Svetlana Ivanovna Gerasimenko, after whom it is Naming of comets, named. It most recently came to Perihelion and aphelion, perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) on 2 November 2021, and will next come to perihelion on 9 April 2028. Churyumov–Gerasimenko was the destination of the European Space Agency's Rosetta (spacecraft), ''Rosetta'' mission, launched on 2 March 2004. ''Rosetta'' space rendezvous, rendezvoused with Churyumov–Gerasimenko on 6 August 2014 and entered orbit on 10 September 2014. ''Rosetta' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, Fashion capital, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the French art, arts and Science and technology in France, sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |