|
List Of Conflicts In The Land Of Israel
This is a list of conflicts in the southern Levant arranged chronologically from ancient to modern times. This region has also been referred to historically as the Land of Canaan, the Land of Israel, the Holy Land, the Promised Land, and Palestine. This region has been ruled over by many nations, including the Canaanites, Israelites, Judeans, Romans, Rashidun Caliphates, Crusaders, Ottoman Empire, British Empire, and today, Israel and Palestine. In addition to wars and battles, there may also be periods of violent, civil unrest included in this list, such as: massacres, riots, rebellions, and revolution In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements ...s. 1050 BCE–551 BCE 550 BCE–1 BCE 1–999 1000–1499 1500–1899 1900–1999 2000–2024 References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Levant
The Southern Levant is a geographical region that corresponds approximately to present-day Israel, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southern Syria and the Sinai Peninsula. As a strictly geographical description, it is sometimes used by archaeologists and historians to avoid the religious and political connotations of other names for this area. Like much of Southwestern Asia, the Southern Levant is an arid region consisting mostly of desert and dry steppe, with a thin strip of wetter, temperate climate along the Mediterranean coast. Geographically it is dominated by the Jordan Valley, a section of the Great Rift Valley bisecting the region from north to south, and containing the Sea of Galilee, the Jordan River and the Dead Sea—the lowest point on the Earth's land surface. The Southern Levant has a long history and is one of the world's most intensively investigated areas by archaeologists. It is considered likely to be the first place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip, collectively known as the occupied Palestinian territories, within the broader geographic and historical Palestine (region), Palestine region. Palestine shares most of its borders with Israel, and it borders Jordan to the east and Egypt to the southwest. It has a total land area of while Demographics of the State of Palestine, its population exceeds five million people. Its Status of Jerusalem, proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, while Ramallah serves as its administrative center. Gaza City was its largest city prior to Gaza Strip evacuations, evacuations in 2023. Situated at a Levantine corridor, continental crossroad, the region of Palestine was ruled by various empires and experienced Demographic history of Palestine (region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries. Jews are named after Judah, and primarily descend from people who lived in the region. The Hebrew Bible depicts the Kingdom of Judah as one of the two successor states of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel, a term denoting the united monarchy under biblical kings Saul, David, and Solomon and covering the territory of Judah and Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel. However, during the 1980s, Biblical minimalism, some biblical scholars began to argue that the archaeological evidence for an extensive kingdom before the late 8th century BCE is too weak, and that the methodology used to obtain the evidence is flawed. In the 10th and early 9th centuries BCE, the territory of Judah might have been limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
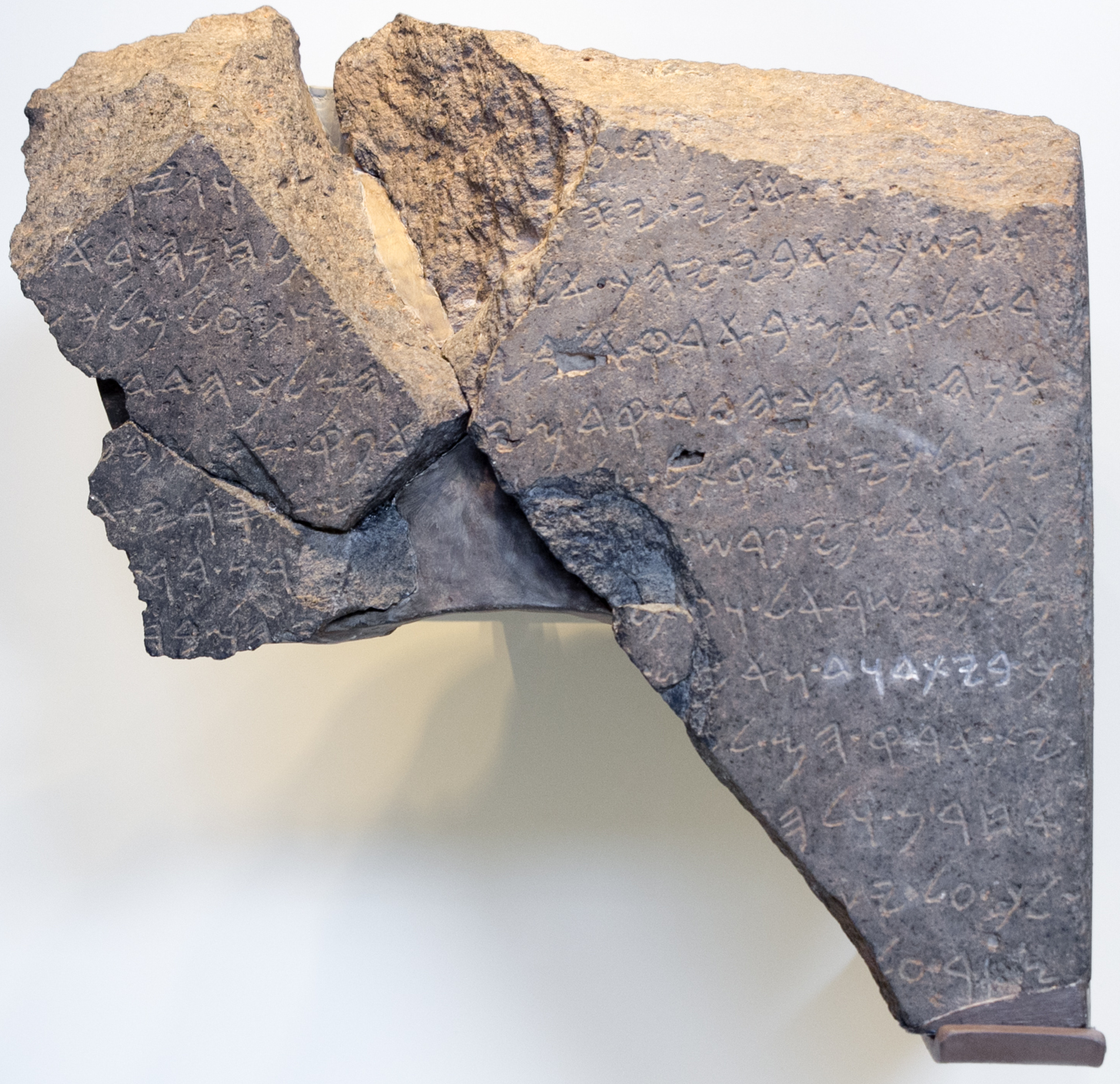
Battle Of Zephath
The Battle of Zephath, according to the Hebrew Bible (), occurred during the period of 911-870 BCE in the reign of King Asa of Judah. It was fought in the Valley of Zephath near Maresha in modern-day Israel between the armies of the Kingdom of Judah under the command of King Asa and that of the Kushites and ancient Egyptians under the command of Zerah the Cushite, who, given the time frame with Asa's reign, may have been a military commander under Osorkon I. The warriors of Judah were victorious in the battle, utterly defeating the Egyptians and Kushites, which the Chronicler attributes to divine intervention, and Asa's forces collected a large volume of war spoils. Asa's forces pursued the enemy stragglers as far as the coastal city of Gerar, where they halted due to exhaustion. The result of the battle created peace between Judah and Egypt until the time of Josiah some centuries later, when Egypt would again make encroachments in the region. See also * Battle of Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jebusites
The Jebusites (; ) were, according to the Book of Joshua and Books of Samuel from the Hebrew Bible, a Canaanite tribe that inhabited Jerusalem, called Jebus () before the conquest initiated by Joshua (, ) and completed by David (). According to some Chronology of the Bible, biblical chronologies, it was conquered in 1003 BC. A majority of scholars agree that the Book of Joshua holds little historical value for early Israel and reflects a much later period. 1 Chronicles 11:4 states that Jerusalem was known as Jebus before this event. Scholars sometimes dispute the identification of Jebus with Jerusalem. Identification of Jebus The identification of Jebus with Jerusalem has been disputed, principally by Niels Peter Lemche. Supporting his case, every non-biblical mention of Jerusalem found in the ancient Near East refers to the city as "Jerusalem". An example of these records are the Amarna letters, several of which were written by the chieftain of Jerusalem Abdi-Heba and call Jeru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Jebus
The siege of Jebus is described in passages of the Hebrew Bible as having occurred when the Israelites, led by King David, besieged and conquered the Canaanite city of Jerusalem, then known as ''Jebus'' (, , ). The Israelites gained access to the city by conducting a surprise assault, and Jebus (or Jerusalem) was subsequently installed as the capital city of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel under its initial name as the City of David (historic), City of David. The identification of Jebus with Jerusalem has been challenged. Danes, Danish biblical scholar Niels Peter Lemche notes that every non-biblical mention of Jerusalem found in the ancient Near East refers to the city with the name of Jerusalem, offering as an example the Amarna letters, which are dated to the 14th century BCE and refer to Jerusalem as . He states that "There is no evidence of Jebus and the Jebusites outside of the Old Testament. Some scholars reckon Jebus to be a different plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistia
Philistia was a confederation of five main cities or pentapolis in the Southwest Levant, made up of principally Gaza, Ashkelon, Ashdod, Ekron, Gath, and for a time, Jaffa (part of present-day Tel Aviv-Yafo). Scholars believe the Philistines were made up of people of an Aegean background that from roughly 1200 BC onwards settled in the area and mixed with the local Canaanite population, and came to be known as '' Peleset'', or Philistines. At its maximum territorial expansion, its territory may have stretched along the Canaanite coast from Arish in the Sinai (today's Egypt) to the Yarkon River (today's Tel Aviv), and as far inland as Ekron and Gath. Nebuchadnezzar II invaded Philistia in 604 BC, burned Ashkelon, and incorporated the territory into the Neo-Babylonian Empire; Philistia and its native population the Philistines disappear from the historic record after that year. History Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic records from the New Kingdom period record a group of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Of Israel
The Kingdom of Israel (Hebrew: מַמְלֶכֶת יִשְׂרָאֵל, ''Mamleḵeṯ Yīśrāʾēl'') was an Israelite kingdom that may have existed in the Southern Levant. According to the Deuteronomistic history in the Hebrew Bible, a United Monarchy or United Kingdom of Israel existed under the reigns of Saul, Ish-bosheth, David, and Solomon, encompassing the territories of both the later kingdoms of Kingdom of Judah, Judah and Kingdom of Israel (northern kingdom), Israel. Whether the United Monarchy existed—and, if so, to what extent—is a matter of ongoing academic debate. During the 1980s, some biblical scholars began to argue that the archaeological evidence for an extensive kingdom before the late 8th century BCE is too weak, and that the methodology used to obtain the evidence is flawed. Scholars remain divided among those who support the historicity of the biblical narrative, those who doubt or dismiss it, and those who support the kingdom's theoretic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Michmash
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Battle of Michmash (alternate spelling, ''Michmas'') was fought between Israelites under Jonathan (Samuel), Jonathan, son of King Saul and a force of Philistines at Michmash, a town east of Bethel and south of Migron, Mateh Binyamin, Migron. Strength of combatant armies According to the Bible, Saul's army consisted entirely of infantry, about 3,000 soldiers and militia men. According to Josephus and 1 Samuel 13:2, Saul himself initially retained 2,000 of these as his guard in Bethel while providing Jonathan with 1,000 which he used to take back Gibeah from Philistine rule.Josephus, ''Antiquities of the Jews'', VI.6.1 Saul kept a standing army of three thousand soldiers after the Battle of Jabesh-Gilead. However, none of the soldiers carried swords or spears with them and had to rely on axes, sickles, mattocks, and plow points as weapons; 1 Samuel 13:19 mentions that "Not a blacksmith could be found in the whole land of Israel, because the Phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolution
In political science, a revolution (, 'a turn around') is a rapid, fundamental transformation of a society's class, state, ethnic or religious structures. According to sociologist Jack Goldstone, all revolutions contain "a common set of elements at their core: (a) efforts to change the political regime that draw on a competing vision (or visions) of a just order, (b) a notable degree of informal or formal mass mobilization, and (c) efforts to force change through noninstitutionalized actions such as Political demonstration, mass demonstrations, Protest, protests, strikes, or violence." Revolutions have occurred throughout human history and varied in their methods, durations and outcomes. Some revolutions started with List_of_peasant_revolts, peasant uprisings or guerrilla warfare on the periphery of a country; others started with urban insurrection aimed at seizing the country's capital city. Revolutions can be inspired by the rising popularity of certain political Ideology, ideo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebellion
Rebellion is an uprising that resists and is organized against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a portion of a state. A rebellion is often caused by political, religious, or social grievances that originate from a perceived inequality or marginalization. ''Rebellion'' comes from Latin ''re'' and ''bellum'', and in Lockian philosophy refers to the Right of revolution, responsibility of the people to overthrow unjust government. Classification Uprisings which revolt, Resistance movement, resisting and taking direct action against an authority, law or policy, as well as organize, are rebellions. An insurrection is an uprising to change the government. If a government does not recognize rebels as belligerents, then they are insurgents and the revolt is an insurgency. In a larger conflict, the rebels may be recognized as belligerents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riot
A riot or mob violence is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people. Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted varies depending on the riot and the inclinations of those involved. Targets can include Shopping mall, shops, cars, restaurants, state-owned institutions, and religious buildings. Riots often occur in reaction to a grievance or out of dissent. Historically, riots have occurred due to poverty, unemployment, poor quality of life, living conditions, governmental oppression, taxation or conscription, conflicts between ethnic groups (race riot) or religions (e.g., sectarian violence, pogrom), the outcome of a sporting event (e.g., sports riot, football hooliganism) or frustration with legal channels through which to air grievances. While individuals may attempt to lead or control a riot, riots typically consist of disorganize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |