|
List Of Animals With Humps
This is a list of animals that have a naturally occurring hump or humps as a part of their anatomy. Humps may evolve, as a store of fat, as a heat control mechanism, as a development of muscular strength, as a form of display to other animals, or be apparent as a consequence of some behaviour such as the diving of whales. Enlarged humps have also been selected for by some animal breeders for aesthetic or religious reasons. * Dromedary - also known as Arabian camel, is a large even-toed ungulate, of the genus ''Camelus'', with one hump on its back. The hump stores up to 80 lb (36 kg) of fat, which the camel can break down into energy to meet its needs when resources are scarce; the hump also helps dissipate body heat. Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M., eds. (2005). ''Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference'' (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 646. . OCLC 62265494. * Bactrian camel - also known as the Mongolian camel or domestic Bactrian camel, is a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Largest Cervids
Cervids are one of the most common families of wild herbivores in the world. Of these the moose can grow up to 2.33 m tall and weigh as much as 820 kg. The smallest cervid is the northern pudu. See also * List of cervids References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Mammoth
The woolly mammoth (''Mammuthus primigenius'') is an extinct species of mammoth that lived from the Middle Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. It was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with the African ''Mammuthus subplanifrons'' in the early Pliocene. The woolly mammoth began to diverge from the steppe mammoth about 800,000 years ago in Siberia. Its closest extant relative is the Asian elephant. The Columbian mammoth (''Mammuthus columbi'') lived alongside the woolly mammoth in North America, and DNA studies show that the two Hybrid (biology), hybridised with each other. Mammoth remains were long known in Asia before they became known to Europeans. The origin of these remains was long debated and often explained as the remains of legendary creatures. The mammoth was identified as an extinct elephant species by Georges Cuvier in 1796. The appearance and behaviour of the woolly mammoth are among the best studied of any Prehistory, prehi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
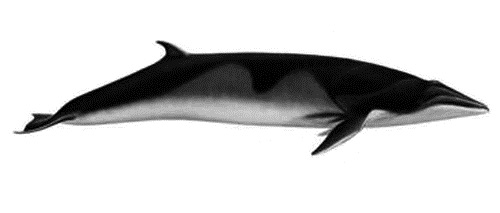
Baleen Whale
Baleen whales (), also known as whalebone whales, are marine mammals of the order (biology), parvorder Mysticeti in the infraorder Cetacea (whales, dolphins and porpoises), which use baleen plates (or "whalebone") in their mouths to sieve plankton from the water. Mysticeti comprises the family (biology), families Balaenidae (right whale, right and Bowhead whale, bowhead whales), Balaenopteridae (rorquals), Eschrichtiidae (the gray whale) and Cetotheriidae (the pygmy right whale). There are currently 16 species of baleen whales. While cetaceans were historically thought to have descended from Mesonychia, mesonychians, molecular phylogenetics, molecular evidence instead supports them as a clade of even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla). Baleen whales split from toothed whales (Odontoceti) around 34 mya (unit), million years ago. Baleen whales range in size from the and pygmy right whale to the and blue whale, the Largest organisms, largest known animal to have ever existed. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humpback Whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the monotypic taxon, only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The humpback has a distinctive body shape, with long pectoral fins and tubercles on its head. It is known for Cetacean surfacing behaviour, breaching and other distinctive surface behaviors, making it popular with whale watching, whale watchers. Males produce a complex Whale sound, song that typically lasts from 4 to 33 minutes. Found in oceans and list of seas, seas around the world, humpback whales typically animal migration, migrate between feeding areas towards the poles and breeding areas near the equator. They feed in Polar region, polar waters and migrate to tropics, tropical or subtropical waters to breed and give birth. Their diet consists mostly of krill and small fish, and they usually Bubble-net feeding, use bubbles to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartebeest
The hartebeest (; ''Alcelaphus buselaphus''), also known as kongoni or kaama, is an Fauna of Africa, African antelope. It is the Monotypic taxon, only member of the genus ''Alcelaphus''. Eight subspecies have been described, including two sometimes considered to be independent species. A large antelope, the hartebeest stands just over at the shoulder, and has a typical head-and-body length of . The weight ranges from . It has a particularly elongated forehead and oddly-shaped horn (anatomy), horns, a short neck, and pointed ears. Its legs, which often have black markings, are unusually long. The animal coat, coat is generally short and shiny. Coat colour varies by the subspecies, from the sandy brown of the western hartebeest to the chocolate brown of the Swayne's hartebeest. Sexual dimorphism, Both sexes of all subspecies have horns, with those of females being more slender. Horns can reach lengths of . Apart from its long face, the large chest and the sharply sloping back di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
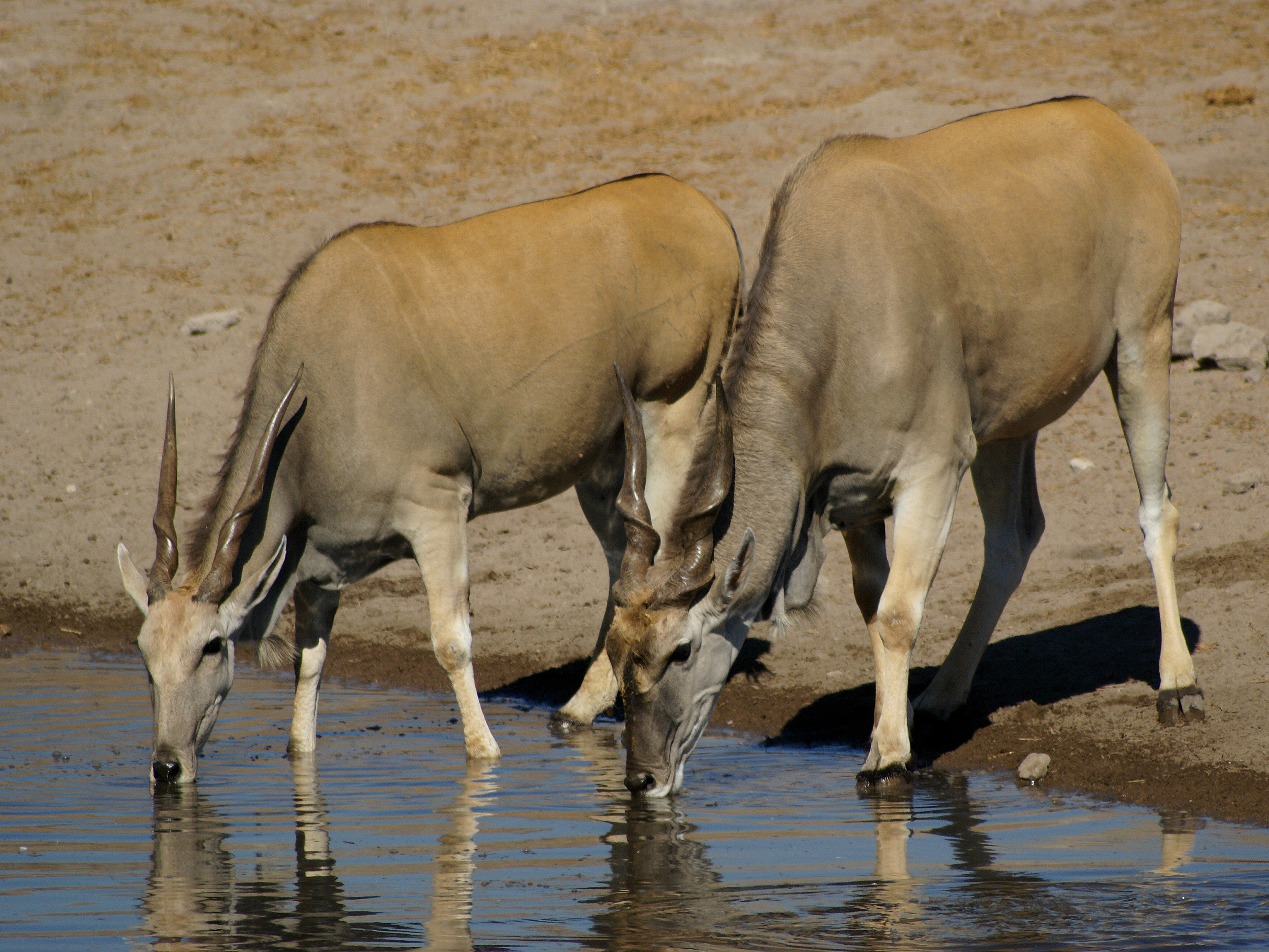
Giant Eland
The giant eland (''Taurotragus derbianus''), also known as the Lord Derby's eland or greater eland, is an open-forest and savanna antelope. A species of the family Bovidae and genus ''Taurotragus'', it was described in 1847 by John Edward Gray. The giant eland is the largest species of antelope, with a body length ranging from . There are two subspecies: ''T. d. derbianus'' and ''T. d. gigas''. The giant eland is a herbivore, eating grasses, foliage and branches. They usually form small herds consisting of 15–25 members, both males and females. Giant elands are not territorial, and have large home ranges. They are naturally alert and wary, which makes them difficult to approach and observe. They can run at up to and use this speed as a defence against predators. Mating occurs throughout the year but peaks in the wet season. They mostly inhabit broad-leafed savannas, woodlands and glades. The giant eland is native to Cameroon, Central African Republic, Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Eland
The common eland (''Taurotragus oryx''), also known as the southern eland or eland antelope, is a large savannah and plains antelope found in East Africa, East and Southern Africa. An adult male is around tall at the shoulder and can weigh up to with a typical range of . Females are around tall and weigh . It is the second-largest antelope in the world, being slightly smaller on average than the giant eland. It was scientifically described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766. Mainly a herbivore, its diet is primarily grasses and leaves. Common elands form herds of up to 500 animals, but are not Territory (animal), territorial. The common eland prefers habitats with a wide variety of flowering plants such as savannah, woodlands, and open and Montane ecology, montane grasslands; it avoids dense forests. It uses loud barks, visual and postural movements, and the flehmen response to Animal communication, communicate and warn others of danger. The common eland is used by humans for leat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PMID (identifier)
PubMed is an openly accessible, free database which includes primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health maintains the database as part of the Entrez system of information retrieval. From 1971 to 1997, online access to the MEDLINE database was provided via computer and phone lines primarily through institutional facilities, such as university libraries. PubMed, first released in January 1996, ushered in the era of private, free, home- and office-based MEDLINE searching. The PubMed system was offered free to the public starting in June 1997. Content In addition to MEDLINE, PubMed provides access to: * older references from the print version of ''Index Medicus'', back to 1951 and earlier * references to some journals before they were indexed in Index Medicus and MEDLINE, for instance ''Science'', '' BMJ'', and ''Annals of Surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISSN (identifier)
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit to uniquely identify a periodical publication (periodical), such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature. The ISSN system was first drafted as an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) international standard in 1971 and published as ISO 3297 in 1975. ISO subcommittee TC 46/SC 9 is responsible for maintaining the standard. When a serial with the same content is published in more than one media type, a different ISSN is assigned to each media type. For example, many serials are published both in print and electronic media. The ISSN system refers to these types as print ISSN (p-ISSN) and electronic ISSN (e-ISSN). Consequently, as defined in ISO 3297:2007, every serial in the ISSN system is also assigned a linking ISSN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are called cows and mature male cattle are bulls. Young female cattle are called heifers, young male cattle are oxen or bullocks, and castrated male cattle are known as steers. Cattle are commonly raised for meat, for dairy products, and for leather. As draft animals, they pull carts and farm implements. Cattle are considered sacred animals within Hinduism, and it is illegal to kill them in some Indian states. Small breeds such as the miniature Zebu are kept as pets. Taurine cattle are widely distributed across Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus are found mainly in India and tropical areas of Asia, America, and Australia. Sanga cattle are found primarily in sub-Saharan Africa. These types, sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus''), also known as indicine cattle and humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of Bos taurus, domestic cattle originating in South Asia. Zebu, like many Sanga cattle breeds, differs from taurine cattle by a fatty hump on their shoulders, a large dewlap, and sometimes drooping ears. They are well adapted to withstanding Tropical climate, high temperatures and are farmed throughout the tropics. The zebu is used as a draught animal, draught and riding animal, dairy cattle and beef cattle, as well as for byproducts such as Hide (skin), hides and Feces, dung for fuel and manure. Some small breeds such as Nadudana also known as the Miniature Zebu, miniature zebu are also kept as pets. In some regions, zebu have significant Cattle in religion#In Indian religions, religious meaning. Taxonomy Both scientific names ''Bos taurus'' and ''Bos indicus'' were introduced by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, with the latter used for humped cattle in China proper, China. The ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |