|
List Of Ancient Philippine Consorts
This is a list of the queen consorts of the major kingdoms and states that existed in present-day Philippines. Only the senior queens—i.e. those with the rank of ''Dayang'' (''"Lady"'') and ''Lakambini'' (''"Queen"'')—are listed. Rankings of consorts Prior to the History of the Philippines (900–1521), Archaic epoch (c. 900–1565), the consorts of the List of sovereign state leaders in the Philippines, Filipino monarchs were organized in three general tiers: ''Dayang'' (), ''Lakan, Lakambini'' (), and ''Binibini'' (), or even the word ''Hara'' () is a Malayo-Sanskrit terms in which referred to a Queen regnant, Queen in western sense, also meant the chief queen of the states and polities which is in the influence of Indianized kingdoms, India or Animist states (see also Indianized kingdoms). The title Sultana (title), Sultana or ''sultanah'' is an Islamic title and a feminine form of the word Sultan. This term has been legally used for some Muslim women monarchs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Consort
A queen consort is the wife of a reigning king, and usually shares her spouse's social Imperial, royal and noble ranks, rank and status. She holds the feminine equivalent of the king's monarchical titles and may be crowned and anointed, but historically she does not formally share the king's political and military powers, unless on occasion acting as regent. In contrast, a queen regnant is a female monarch who rules ''suo jure'' (Latin for, "in her own right") and usually becomes queen by inheriting the throne upon the death of the previous monarch. A queen dowager is a widowed queen consort, and a queen mother is a queen dowager who is the mother of the current monarch. Titles When a title other than king is held by the sovereign, his wife can be referred to by the feminine equivalent, such as princess consort or empress consort. In monarchies where polygamy has been practised in the past (such as Morocco and Thailand), or is practised today (such as the Zulu people, Zulu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
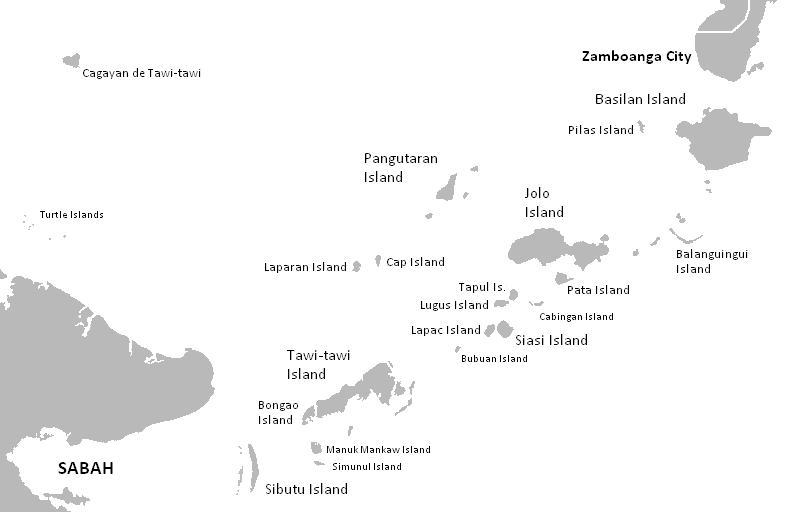
Sultanate Of Sulu
The Sultanate of Sulu (; ; ) is a Sunni Muslim subnational monarchy in the Philippines, Republic of the Philippines that includes the Sulu Archipelago, coastal areas of Zamboanga City and certain portions of Palawan in today's Philippines. Historically, the Sultanate included parts of present-day Sabah and North Kalimantan in north-eastern Borneo, but Malaysia does not recognize the territory of North Borneo as part of the Sultanate. The sultanate was founded either on 17 November 1405 or 1457 by Johore-born explorer and Sunni religious scholar Sharif ul-Hāshim of Sulu, Sharif ul-Hashim. ''Paduka Mahasari Maulana al Sultan Sharif ul-Hashim'' became his full regnal name; ''Sharif-ul Hashim'' is his abbreviated name. He settled in Buansa, Sulu. The sultanate gained its independence from the Bruneian Empire in 1578. At its peak, it stretched over the islands that bordered the western peninsula of Zamboanga Peninsula, Zamboanga in Mindanao in the east to Palawan in the north. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daragang Magayon
Daragang Magayon () is the heroine that appears in the legend of Mt. Mayon in Albay, Philippines. Basic legend Magayon was the only daughter of Makusog (strong), the tribal chief of Rawis, and Dawani (rainbow), who died shortly after giving birth to her. She grew up to be a very beautiful and sweet woman that struck the swains from faraway tribes who vied for her attention. However, none of these young men could captivate the heart of Magayon, not even the handsome but haughty Pagtuga (eruption A volcanic eruption occurs when material is expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure. Several types of volcanic eruptions have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has ...), a hunter and the chief of the Iriga tribe. He gave fabulous gifts to Magayon, yet it was not enough to capture her attention. One day, Daragang Magayon was bathing in the Yawa River when she slipped on the rocks. Unfortunately, she did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Makiling
Mount Makiling (also spelled Maquiling) is an inactive stratovolcano located in the provinces of Laguna and Batangas on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The mountain rises to an elevation of above mean sea level and is the highest feature of the Laguna Volcanic Field. The volcano has no recorded historic eruption but volcanism is still evident through geothermal features like mud spring and hot springs. South of the mountain is the Makiling–Banahaw Geothermal Plant. The Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS) classifies the volcano as " Inactive". Mount Makiling is a state-owned forest reserve administered by the University of the Philippines Los Baños. Prior to its transfer to the university, the mountain was the first national park of the Philippines. Mount Makiling National Park was established on February 23, 1933, by Proclamation No. 552. However, it was decommissioned as a national park on June 20, 1963, by Republic Act No. 3523 when i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genius Loci
In classical Roman religion, a ''genius loci'' (: ''genii locorum'') was the protective spirit of a place. It was often depicted in religious iconography as a figure holding attributes such as a cornucopia, patera (libation bowl), or snake. Many Roman altars found throughout the Western Roman Empire were dedicated to a particular ''genius loci''. The Roman imperial cults of the Emperor and the imperial house developed in part in connection with the sacrifices made by neighborhood associations ''( vici)'' to the local ''genius''. These 265 local districts had their cult organised around the ''Lares Compitales'' (guardian spirits or ''lares'' of the crossroads), which the emperor Augustus transformed into ''Lares Augusti'' along with the ''Genius Augusti''. The emperor's ''genius'' is then regarded as the ''genius loci'' of the Roman Empire as a whole. Roman examples of these ''genii'' can be found, for instance, at the church of St. Giles, Tockenham, Wiltshire, England, where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Makiling
Maria Makiling, more properly Mariang Makiling, is a '' diwata'' in Philippine mythology, associated with Mount Makiling in Laguna, Philippines. She is the most widely known ''diwatà'' or ''lambana (fairy)'' in Philippine mythology and was venerated in pre-colonial Philippines as a goddess known as Dayang Masalanta or Dian Masalanta who was invoked to stop deluges, storms, and earthquakes. Maria Makiling is a beautiful fairy or goddess who watches over the mountain. She is known for her beauty and is often shown with accompanied by tiny winged fairies called lambana. She protects the mountain and helps the people who rely on it for food and resources. Some stories also say that the nearby lake, Laguna de Bay, and its fish are part of her care. According to legend, she was sent by Bathalà, a powerful god, to help the people in their daily lives. Mount Makiling resembles the profile of a woman, said to be Maria herself. This phenomenon is described as true from several diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (1985), reported statements from present generation which "specifies that the message must be oral statements spoken, sung or called out on musical instruments only"; "There must be transmission by word of mouth over at least a generation". He points out, "Our definition is a working definition for the use of historians. Sociologists, linguists or scholars of the verbal arts propose their own, which in, e.g., sociology, stresses common knowledge. In linguistics, features that distinguish the language from common dialogue (linguists), and in the verbal arts features of form and content that define art (folklorists)."Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: "Methodology and African Pre-history", 1990, ''UNESCO International Scientific Committee for the Drafting of a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folktale
Oral literature, orature, or folk literature is a genre of literature that is spoken or sung in contrast to that which is written, though much oral literature has been transcribed. There is no standard definition, as anthropologists have used varying descriptions for oral literature or folk literature. A broad conceptualization refers to it as literature characterized by oral transmission and the absence of any fixed form. It includes the stories, legends, and history passed through generations in a spoken form. Background Pre-literate societies, by definition, have no written literature, but may possess rich and varied oral traditions—such as folk epics, folk narratives (including fairy tales and fables), folk drama, proverbs and folksongs—that effectively constitute an oral literature. Even when these are collected and published by scholars such as folklorists and paremiographers, the result is still often referred to as "oral literature". The different genres of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datu
''Datu'' is a title which denotes the rulers (variously described in historical accounts as chiefs, sovereign princes, and monarchs) of numerous Indigenous peoples throughout the Philippine archipelago. The title is still used today, though not as much as early Philippine history. It is a cognate of ''datuk'', ''dato'', and ''ratu'' in several other Austronesian languages. Overview In early Philippine history, ''datus'' and a small group of their Cognatic kinship, close relatives formed the "apex stratum" of the traditional three-tier social hierarchy of lowland Philippine societies. Only a member of this birthright aristocracy (called ''maginoo'', ''nobleza'', ''maharlika'', or ''timagua'' by various early chroniclers) could become a ''datu''; members of this elite could hope to become a ''datu'' by demonstrating prowess in war or exceptional leadership. In large coastal polities such as those in Maynila (historical polity), Maynila, Tondo (historical polity), Tondo, Pangasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja
Raja (; from , IAST ') is a noble or royal Sanskrit title historically used by some Indian subcontinent, Indian rulers and monarchs and highest-ranking nobles. The title was historically used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. The title has a long history in South Asia and History of Southeast Asia, Southeast Asia, being attested from the ''Rigveda'', where a ' is a Rigvedic tribes, ruler, see for example the Battle of the Ten Kings, ', the "Battle of Ten Kings". The title has equivalent cognates in other Indo-European languages, notably the Latin Rex (title), Rex and the Celtic languages, Celtic Rix. Raja-ruled Indian states While most of the British Raj, Indian salute states (those granted a Salute#Heavy arms: gun salutes, gun salute by the The Crown, British Crown) were ruled by a Maharaja (or variation; some promoted from an earlier Raja- or equivalent style), even exclusively from 13 guns up, a number had Rajas: ; Hereditary salutes of 11-guns : * the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jawi Alphabet
Jawi (; ; ; ) is a writing system used for writing several languages of Southeast Asia, such as Acehnese language, Acehnese, Banjarese language, Banjarese, Betawi language, Betawi, Maguindanao language, Magindanao, Malay language, Malay, Maranao language, Mëranaw, Minangkabau language, Minangkabau, Tausug language, Tausūg, Ternate language, Ternate and many other languages in Southeast Asia. Jawi is based on the Arabic script, consisting of all 31 original Arabic letters, six letters constructed to fit phonemes native to Malay, and one additional phoneme used in foreign loanwords, but not found in Classical Arabic, which are ''ca'' ( ), ''nga'' ( ), ''pa'' ( ), ''ga'' ( ), ''va'' ( ), and ''nya'' ( ). Jawi was developed during the Spread of Islam in Southeast Asia, advent of Islam in Maritime Southeast Asia, supplanting the earlier Brahmic scripts used during Hindu-Buddhist era. The oldest evidence of Jawi writing can be found on the 14th century Terengganu Inscription Ston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |