|
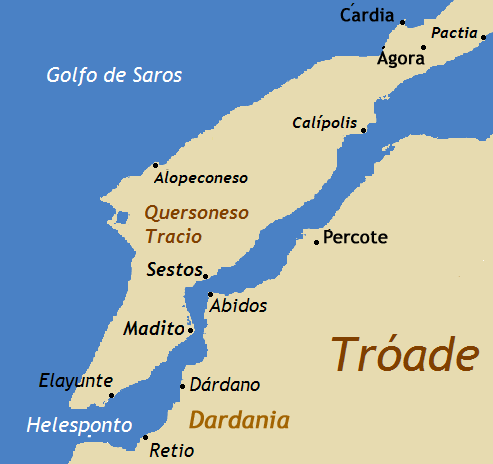
List Of Ancient Greek Tyrants
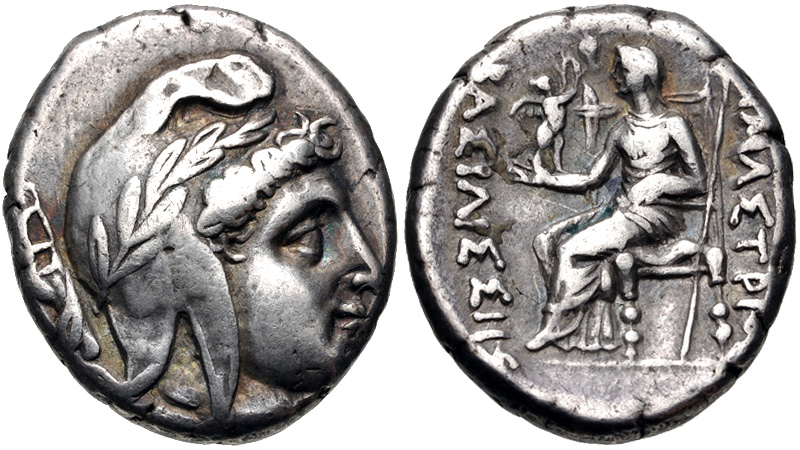
This is a list of tyrants from Ancient Greece. Abydus * Daphnis, c. 500 BC under Darius I (pro persian)Herodotus, Historie4.138/ref> * Philiscus, c. 368-360 BC (assassinated) * Iphiades, 360-? BC Agrigentum (Acragas) * Phalaris, 570-554 BC (overthrown and roasted) * Telemachus, after 554 BC * Alcamenes, 6th/5th century BCHeraclides Lembus, Excerpta Politiarum, 69."Ἀκραγαντίνων: ��μεθ’ ὃν Ἀλκαμένης παρέλαβε τὰ πράγματα, καὶ μετὰ τοῦτον Ἄλκανδρος προέστη, ἀνὴρ ἐπιεικής. καὶ εὐθένησαν οὕτως ὡς περιπόρφυρα ἔχειν ἱμάτια." (Constitution of the Acragantines. ��After him .e. PhalarisAlcamenes seized the power, and after him, Alcander, a righteous man, governed. And they flourished to such an extent that they had himations fringed with purple”.) (DILTS 1971) * Alcandros (Alcander), 6th/5th century BC * Theron, 488-472 BC * Thrasydaeus, 47 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to repressive means. The original Greek term meant an absolute sovereign who came to power without constitutional right, yet the word had a neutral connotation during the Archaic and early Classical periods. However, Greek philosopher Plato saw ''tyrannos'' as a negative form of government, and on account of the decisive influence of philosophy on politics, deemed tyranny the "fourth and worst disorder of a state."Plato, ''The Republic'' Book VIII The philosophers Plato and Aristotle defined a tyrant as a person who rules without law, using extreme and cruel methods against both his own people and others. The ''Encyclopédie'' defined the term as a usurper of sovereign power who makes "his subjects the victims of his passions and unjust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tyrants Of Syracuse
Syracuse (; ) was an ancient Greek city-state, located on the east coast of Sicily, Magna Graecia. The city was founded by settlers from Corinth in 734 or 733 BC, and was conquered by the Romans in 212 BC, after which it became the seat of Roman rule in Sicily. Throughout much of its history as an independent city, it was governed by a succession of tyrants, with only short periods of democracy and oligarchy. While Pindar addressed the Deinomenids as kings (basileus) in his odes, it is not clear that this (or any other title) was officially used by any of the tyrants until Agathocles adopted the title in 304.''A Dictionary of the Ancient Greek World'' by David Sacks, Oswyn Murray, Margaret Bunson Page 10 Tyrants of Syracuse Deinomenids (485–465) * Gelon I (485 BC–478 BC) * Hiero I (478 BC–466 BC) * Thrasybulus (466 BC–465 BC) Thrasybulus was deposed in 465 and Syracuse had a republican government for the next sixty years. This period is usually known as the Second Democr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Argos
Argos (; ; ) is a city and former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece and is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, and the oldest in Europe. It is the largest city in Argolis and a major center in the same prefecture, having nearly twice the population of the prefectural capital, Nafplio. Since the 2011 local government reform it has been part of the municipality of Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 138.138 km2. It is from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour. A settlement of great antiquity, Argos has been continuously inhabited as at least a substantial village for the past 7,000 years. A resident of the city of Argos is known as an Argive ( , ; ). However, this term is also used to refer to those ancient Greeks generally who assaulted the city of Troy during the Trojan War; the term is more widely applied by the Homeric bards. Numerous ancient monuments can be found in the cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memnon Of Heraclea
Memnon of Heraclea (; , ''gen''.: Μέμνονος; fl. c. 1st century) was a Greek historical writer, probably a native of Heraclea Pontica. He described the history of that city in a large work, known only through the ''Excerpta of '' ''Photius'' (I of Constantinople), and describing especially the various tyrants who had at times ruled Heraclea. Memnon's history encompassed an unknown number of books, but Photius had read the ninth through the sixteenth, and made a tolerably copious abstract of that portion. The first eight books he had not read, and he speaks of other books after the sixteenth. The ninth book begins with an account of the tyrant Clearchus, the disciple of Plato and Isocrates. The thirteenth book contains a long account of the rise of Rome. The last event mentioned in the sixteenth book was the death of Brithagoras, who was sent by the Heracleians as ambassador to Julius Caesar, after the latter had obtained the supreme power (48 BC). From this Gerardus Voss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Pontus
Pontus ( ) was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus in modern-day Turkey, and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty of Persian origin, which may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty. The kingdom was proclaimed by Mithridates I in 281BC and lasted until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 63BC. The Kingdom of Pontus reached its largest extent under Mithridates VI the Great, who conquered Colchis, Cappadocia, Bithynia, the Greek colonies of the Tauric Chersonesos, and for a brief time the Roman province of Asia. After a long struggle with Rome in the Mithridatic Wars, Pontus was defeated. The kingdom had three cultural strands, which often fused together: Greek (mostly on the coast), Persian, and Anatolian, with Greek becoming the official language in the 3rd century BC. Features of Pontus The Kingdom of Pontus was divided into two distinct areas: the coastal region and the Pontic interior. The coastal region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumenes Of Amastris
Eumenes (; ; ) was a Greek general, satrap, and Successor of Alexander the Great. He participated in the Wars of Alexander the Great, serving as Alexander's personal secretary and later on as a battlefield commander. Eumenes depicted himself as a lifelong loyalist of Alexander's dynasty and championed the cause of the Macedonian Argead royal house. In the Wars of the Diadochi after Alexander's death, Eumenes initially supported the regent Perdiccas in the First Diadochi War, and later the Argead royalty in the Second Diadochi War. Despite less experience as a commander, Eumenes defeated Craterus, one of Alexander's most accomplished generals, at the Battle of the Hellespont in 321 BC. After Perdiccas' murder in 320 BC Eumenes became a public enemy of the new Post-Alexander regime under Antipater and Antigonus. In 319 BC he was defeated by Antigonus at the Battle of Orkynia and confined to Nora. Eumenes escaped and then allied with Polyperchon and Olympias, Ale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amastrine
Amastris (; c. 340/39–284 BC) also called Amastrine, was a Persian princess, and Tyrant-ruler of the city of Heraclea from circa 300 to her death. She was the daughter of Oxyathres, the brother of the Persian King Darius III. Arrian, '' Anabasis Alexandri'', VII. 4. She was the first woman in the Mediterranean publicly identified as the political, economic, and administrative royal authority.Monica D'Agostini. (2020). Can Powerful Women Be Popular?: Amastris: Shaping a Persian Wife into a Famous Hellenistic Queen. In ''Celebrity, Fame, and Infamy in the Hellenistic World.'' Edid. Riemer Faber. Canada: University of Toronto Press. Life Little is known about Amastris' life before her first marriage. From her paternal namesake, it can be concluded that she did not have brothers. As a Persian royal woman, she would have been trained in managerial duty. Amastris was given by Alexander the Great in marriage to Craterus. However, in 322 BC, she married Dionysius, tyrant of Hera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amasra
Amasra (from Greek language, Greek Amastris Ἄμαστρις, ''gen''. Ἀμάστριδος) is a small Black Sea port town in the Bartın Province, Turkey. It is the seat of Amasra District.İlçe Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 30 January 2023. Its population is 6,098 (2021). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archinus (tyrant)
Archinus () was an Athenian democratic politician who wielded substantial influence between the restoration of democracy in 403 BC and the beginning of the Corinthian War in 395 BC. In the early days of the restored democracy, he acted to weaken the oligarchic exiles at Eleusis by ending the period during which citizens could register to emigrate to Eleusis before its announced ending date. He seems to have advocated a moderate democratic policy, opposing motions to expand the franchise and restore the levels of pay for civil service that had typified the golden days of Periclean democracy in Athens in the mid-5th century BC. Archinus is also said to have encouraged the official adoption by Athens of the 24-letter Ionic alphabet in 403–2 (Suda, ), alongside the archon Eucleides Eucleides () was eponymous archon of Athens for the year running from July/August 403 BC until June/July 402 BC. His year in office was marked by Athens' official adoption of the Ionic alphabet. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periander Of Ambracia
Periander (; ; died c. 585 BC) was the second tyrant of the Cypselid dynasty that ruled over ancient Corinth. Periander's rule brought about a prosperous time in Corinth's history, as his administrative skill made Corinth one of the wealthiest city states in Greece. Several accounts state that Periander was a cruel and harsh ruler, but others claim that he was a fair and just king who worked to ensure that the distribution of wealth in Corinth was more or less even. He is often considered one of the Seven Sages of Greece The Seven Sages or Seven Wise Men was the title given to seven philosophers, statesmen, and law-givers of the 7th–6th centuries BCE who were renowned for their wisdom Wisdom, also known as sapience, is the ability to apply knowledge, ..., men of the 6th century BC who were renowned for centuries for their wisdom. (The other Sages were most often considered to be Thales, Solon, Cleobulus, Chilon, Bias of Priene, Bias and Pittacus of Mytilene, Pittacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cypselus
Cypselus (, ''Kypselos'') was the first tyrant of Corinth in the 7th century BC. With increased wealth and more complicated trade relations and social structures, Greek city-states tended to overthrow their traditional hereditary priest-kings; Corinth, the richest archaic ''polis,'' led the way. Like the '' signori'' of late medieval and Renaissance Italy, the tyrants usually seized power at the head of some popular support. Often the tyrants upheld existing laws and customs and were highly conservative as to cult practices, thus maintaining stability with little risk to their own personal security. As in Renaissance Italy, a cult of personality naturally substituted for the divine right of the former legitimate royal house. After the last traditional king of Corinth, Telestes, was assassinated by Arieus and Perantas, there were no more kings; instead '' prytanes'' taken from the former royal house of the Bacchiadae ruled for a single year each. Cypselus, the son of Eë ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambracia
Ambracia (; , occasionally , ''Ampracia'') was a city of ancient Greece on the site of modern Arta. It was founded by the Corinthians in 625 BC and was situated about from the Ambracian Gulf, on a bend of the navigable river Arachthos (or Aratthus), in the midst of a fertile wooded plain. Name It was named after Ambracia, who according to some myths was Augeas daughter, while others describe her as Apollo's granddaughter and the daughter of Melaneus, king of the Dryope. According to a different story, the town was named after Ambrax, Thesprotus son and Lycaon's grandson. History Ambracia was founded between 650 and 625 BC by Gorgus, son of the Corinthian tyrant Cypselus, at which time its economy was based on farmlands, fishing, timber for shipbuilding, and the exportation of the produce of Epirus. After the expulsion of Gorgus's son Periander its government developed into a strong democracy. The early policy of Ambracia was determined by its loyalty to Corinth (for wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |