|
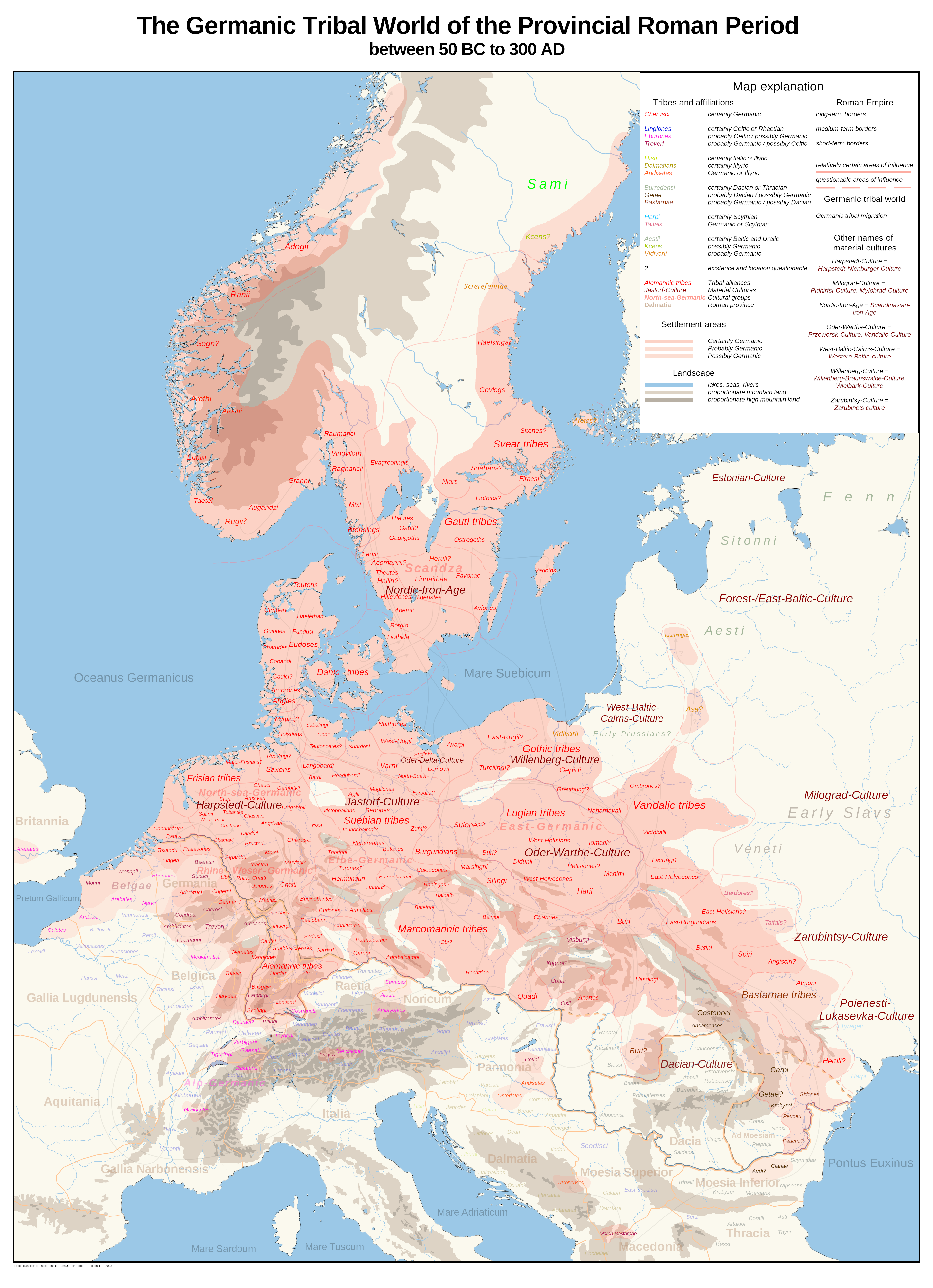
List Of Ancient Germanic Peoples And Tribes
The list of early Germanic peoples is a catalog of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groups, and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilizations from antiquity. This information is derived from various ancient historical sources, beginning in the 2nd century BC and extending into late antiquity. By the Early Middle Ages, early forms of kingship had started to shape historical developments across Europe, with the exception of Northern Europe. In Northern Europe, influences from the Vendel Period (c.AD 550- 800) and the subsequent Viking Age (c. AD 800- 1050) played a significant role in the germanic historical context. The associations and locations of the numerous peoples and groups in ancient sources are often subject to heavy uncertainty and speculation, and classifications of ethnicity regarding a common culture or a temporary alliance of heterogeneous groups are disputed. It is uncertain whether certain groups are Germanic in the broader linguistic sense or whether they c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of the Roman Empire, but also all Germanic speaking peoples from this era, irrespective of where they lived, most notably the Goths. Another term, ancient Germans, is considered problematic by many scholars since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. Although the first Roman descriptions of ''Germani'' involved tribes west of the Rhine, their homeland of ''Germania'' was portrayed as stretching east of the Rhine, to southern Scandinavia and the Vistula in the east, and to the upper Danube in the south. Other Germanic speakers, such as the Bastarnae and Goths, lived further east in what is now Moldova and Ukraine. The term ''Germani ''is generally only used to refer to historical peoples from the 1st to 4th centuries CE. Different ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Getica
''De origine actibusque Getarum'' (''The Origin and Deeds of the Getae''), commonly abbreviated ''Getica'' (), written in Late Latin by Jordanes in or shortly after 551 AD, claims to be a summary of a voluminous account by Cassiodorus of the origin and history of the Goths, Gothic people, which is now lost. However, the extent to which Jordanes actually used the work of Cassiodorus is unknown. It is significant as the only remaining contemporaneous resource that gives an extended account of the Origin stories of the Goths, origin and history of the Goths, although to what extent it should be considered history or origin mythology is a matter of dispute. Synopsis of the work The ''Getica'' begins with a discussion of a large island named Scandza, which faces the mouth of the Vistula river and had been described by the writers Claudius Ptolemy and Pomponius Mela. Jordanes reports this island to be the original home of many different peoples including the Goths, who have swarmed lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrabaecampi
The Adrabaecampi () and Parmaecampi (, ''Parmaikampoi'') were two divisions of the Kampoi (Κάμποι), a tribe of greater Germany who, according to Ptolemy, dwelled on the north bank of the Danube south of the Gabreta Forest after the Marcomanni and Sudini. They were located, per Ptolemy, immediately north of the Danube and south of Bohemia, i.e. in the immediate vicinity of the Roman imperial border. The name Kampoi is traced back to the Celtic river name Kamp (from Celtic *''cambo'', "curved"). The Chamb, which flows into the Regen near Cham, and the Kamp in Lower Austria are considered tributaries of the Danube that flow on the left side. The Kambaioi, an Illyrian people, have a related name. The derivation of the names of the Kampoi tribes from Latin ''campi'' (fields) is implausible, as no good sense can be made of the prefixes ''adrabae'' and ''parmae''. The second has been linked to Gallo-Latin ''parma Parma (; ) is a city in the northern Italian region of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troms
Troms (; ; ; ) is a Counties of Norway, county in northern Norway. It borders Finnmark county to the northeast and Nordland county in the southwest. Norrbotten Län in Sweden is located to the south and further southeast is a shorter border with Lapland (Finland), Lapland Province in Finland. To the west is the Norwegian Sea (Atlantic Ocean). The county had a population of 169,610 in 2024. The entire county, which was established in 1866, is located north of the Arctic Circle. The Troms County Municipality is the governing body for the county, elected by the people of Troms, while the Troms County governor (Norway), county governor is a representative of the King of Norway, King and Government of Norway. From 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2023 Troms was merged with the neighboring Finnmark county to create the new Troms og Finnmark county. This merger was reversed by the government resulting from the 2021 Norwegian parliamentary election. General information Name Until 1919, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyngen (fjord)
, , or is a fjord in Troms county, Norway. The long fjord is the longest fjord in Troms county and it is often used as the dividing line between "northern Troms" and "southern Troms". The fjord is located within the municipalities of Skjervøy, Nordreisa, Lyngen, Gáivuotna–Kåfjord, and Storfjord. It stretches from the village of Hatteng in Storfjord Municipality in the south all the way north to the islands of Skjervøy Municipality. The Lyngen Alps lie on the Lyngen Peninsula along the western shore of the fjord. The European route E06 highway runs along the eastern shore of the fjord. The Kåfjorden branches off of the main fjord on the east side, and the southernmost part of the fjord is also known as the Storfjorden. Media gallery View to Lyngenfjorden from east coast, 2010 06.jpg, A view of the Lyngenfjord Cod drying in Lyngen.JPG, Cod drying along the fjord Aurora borealis above Lyngenfjorden, 2012 March-2.jpg, View of the fjord under the northern lights Zwisc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nord-Trøndelag
Nord-Trøndelag (; "North Trøndelag") was a counties of Norway, county constituting the northern part of the present-day Trøndelag county in Norway. It bordered the old Sør-Trøndelag ("South Trøndelag") county as well as the county of Nordland. To the west is the Norwegian Sea (Atlantic Ocean), and to the east is Jämtland in Sweden. The county was established in 1804 when the old Trondhjems amt was divided into two: Nordre Trondhjems amt and Sør-Trøndelag, Søndre Trondhjems amt. In 2016, the two county councils voted to merge (back) into a single county on 1 January 2018. As of 1 January 2014, the county had 135,142 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-least populated county. The largest municipalities are Stjørdal Municipality, Stjørdal, Steinkjer Municipality, Steinkjer (the county seat), Levanger Municipality, Levanger, Namsos Municipality, Namsos, and Verdal Municipality, Verdal, all with between 24,000 and 12,000 inhabitants. The economy is primarily cente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namdalen
Namdalen () is a Districts of Norway, traditional district in the central part of Norway, consisting of the municipalities of Namsos Municipality, Namsos, Grong Municipality, Grong, Overhalla Municipality, Overhalla, Røyrvik Municipality, Røyrvik, Nærøysund Municipality, Nærøysund, Høylandet Municipality, Høylandet, Flatanger Municipality, Flatanger, Lierne Municipality, Lierne, Leka Municipality, Leka, and Namsskogan Municipality, Namsskogan, all in Trøndelag county. The district has three List of towns and cities in Norway, towns: Namsos (town), Namsos, Rørvik and Kolvereid. The whole district covers about and has about 35,000 residents (2009). The district surrounds the Namdalen valley and the river Namsen, one of the best salmon rivers in Europe (only the Tana River (Norway), Tana river in Finnmark yields a larger catch of salmon). Agriculture and forestry have always been important in Namdalen. Norway spruce is the most prevalent tree species. The grain fields in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
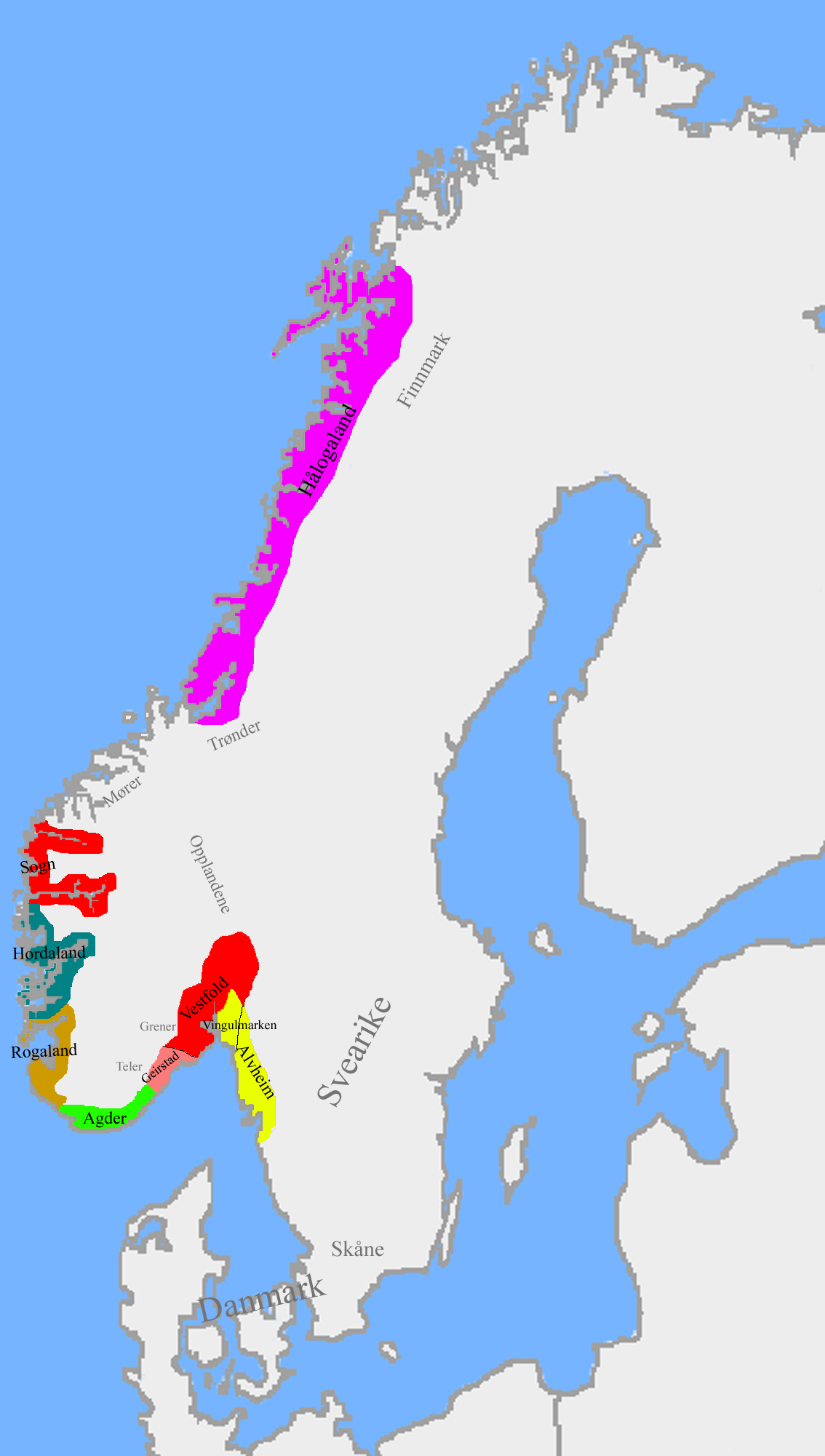
Petty Kingdoms Of Norway
The petty kingdoms of Norway () were the entities from which the later Kingdom of Norway was founded. Before the unification of Norway in 872 and during the period of fragmentation after King Harald Fairhair's death, Norway was divided in several small kingdoms. Some could have been as small as a cluster of villages, and others comprised several of today's counties. By the time of the first historical records of Scandinavia, about the 8th century, a number of small political entities existed in Norway. The exact number is unknown, and would probably also fluctuate with time. It has been estimated that there were 9 petty realms in Western Norway during the early Viking Age. Archaeologist Bergljot Solberg on this basis estimates that there would have been at least 20 in the whole country. There are no written sources from this time to tell us the title used by these rulers, or the exact borders between their realms. The main written sources we have on this period, the kings' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hålogaland
Hålogaland was the northernmost of the Norwegian provinces in the medieval Norse sagas. In the early Viking Age, before Harald Fairhair, Hålogaland was a kingdom extending between the Namdalen valley in Trøndelag county and the Lyngen fjord in Troms county. Etymology and history Ancient Norwegians said that was named after a royal named Hǫlgi. The Norse form of the name was '. The first element of the word is the genitive plural of ', a 'person from Hålogaland'. The last element is ', as in 'land' or 'region'. The meaning of the demonym ' is unknown. Thorstein Vikingson's Saga, 1, describes it as a compound of Hial, "Hel" or "spirit," and "loge", "fire" – although this is largely discredited. The Gothic historian Jordanes in his work ' (also known as ''Getica''), written in Constantinople , mentions a people "Adogit" living in the far North. This could be an old form of ' and a possible reference to the petty kingdom of Hålogaland. Alex Woolf links the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania (book)
The ''Germania'', written by the Roman historian Publius Cornelius Tacitus around 98 AD and originally titled ''On the Origin and Situation of the Germans'' (), is a historical and ethnographic work on the Germanic peoples outside the Roman Empire. Contents The ''Germania'' begins with a description of the lands, laws, and customs of the Germanic people (chapters 1–27); it then describes individual peoples, beginning with those dwelling closest to Roman lands and ending on the uttermost shores of the Baltic, among the amber-gathering Aesti, the Fenni, and the unknown peoples beyond them. Tacitus says (chapter 2) that physically, the Germanic peoples appear to be a distinct nation, not an admixture of their neighbors, since nobody would desire to migrate to a climate as horrid as that of Germania. They are divided into three large branches, the Ingaevones, the Irminones, and the Istaevones, deriving their ancestry from three sons of Mannus, son of Tuisto, their comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |