|
List Of Ambassadors Of Russia To Romania
The ambassador of Russia to Romania is the official representative of the president and the government of the Russian Federation to the president and the government of Romania. The ambassador and his staff work at large in the Russian embassy in Bucharest. There is a consulate general in Constanța. The current Russian ambassador to Romania is Vladimir Lipayev since June 2024. History of diplomatic relations Diplomatic relations between the regions that now constitute Romania and the Russian Federation date back to the medieval period. The Tsardom of Russia offered support for the Danubian Principalities during their struggle for independence from the Ottoman Empire. Moldavian ruler Stephen the Great concluded a military-political alliance with Russia in the fifteenth century, sealed by the marriage of his daughter Elena to Ivan the Young, the son and heir of Ivan III. Wallachian ruler Michael the Brave also advocated an alliance with Russia towards the end of the sixteenth cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
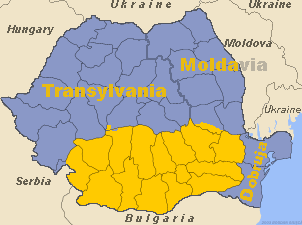
Danubian Principalities
The Danubian Principalities (, ) was a conventional name given to the Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia, which emerged in the early 14th century. The term was coined in the Habsburg monarchy after the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (1774) in order to designate an area on the lower Danube with a common geopolitical situation.Heppner Harald, ''Österreich und die Donaufürstentümer 1774–1812. Ein Beitrag zur habsburgischen Südosteuropapolitik'', Habilitationsschrift, Graz, 1984, pp. 8–9 The term was largely used then by foreign political circles and public opinion until the union of the two principalities in 1859. Alongside Transylvania, the United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia became the basis for the Kingdom of Romania, and by extension the modern nation-state of Romania. In a wider context, the concept may also apply to the Principality of Serbia as one of ''The Principalities of the Danube'', Wikisource:The Principalities of the Danube which came under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantin Brâncoveanu
Constantin Brâncoveanu (; 1654 – August 15, 1714) was List of Wallachian rulers, Prince of Wallachia between 1688 and 1714. Biography Ascension Constantin Brâncoveanu was the son of Pope Brâncoveanu (Matthew) and his wife, Stanca Cantacuzino. Maternally, he was a descendant of the noble Greeks, Greek family Cantacuzino family, Cantacuzino. Paternally, he was a descendant of the Craiovești boyar family and heir through his grandfather Preda of a considerable part of Matei Basarab′s fortune. Brâncoveanu was born on the Estate (land), estate of Brâncoveni and raised in the house of his uncle, ''stolnic'' Constantin Cantacuzino (stolnic), Constantin Cantacuzino. He rose to the throne after the death of his uncle, prince Şerban Cantacuzino. He was initially supported by his maternal uncles Constantin and Mihai Cantacuzino, but grew increasingly independent from them in the course of his reign. Constantin Cantacuzino retreated to one of his estates and began advocatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimitrie Cantemir
Dimitrie or Demetrius; Cantemir (; ; 26 October 1673 – 21 August 1723), also known by other spellings, was a Moldavian prince, statesman, and man of letters. He twice served as voivode of Moldavia (March–April 1693 and 1710–1711). During his second term, he allied his state with Russia in a war against Moldavia's Ottoman overlords; Russia's defeat forced Cantemir's family into exile and the replacement of the native voivodes by Greek phanariots. Cantemir was also a prolific writer, variously a: philosopher, historian, composer, musicologist, linguist, ethnographer and geographer. His son, Antioch, Russia's ambassador to Great Britain and France and a friend of Montesquieu and Voltaire, would become known as "the father of Russian poetry". Name Dimitrie is the Romanian form of the name Latinized as Demetrius and, less often, anglicized as Demeter. The Russian form of his name was (). He is also known as ''Dimitri Kantemiroğlu'' in Turkish contexts, ''Dymitr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great
Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned jointly with his half-brother Ivan V of Russia, Ivan V until 1696. From this year, Peter was an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch, an autocrat who remained the ultimate authority and organized a well-ordered police state. Much of Peter's reign was consumed by lengthy wars against the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Swedish Empire, Swedish empires. His Azov campaigns were followed by the foundation of the Imperial Russian Navy, Russian Navy; after his victory in the Great Northern War, Russia annexed a Treaty of Nystad, significant portion of the eastern Baltic Sea, Baltic coastline and was officially renamed from a Tsardom of Russia, tsardom to an Russian Empire, empire. Peter led a cultural revolution that replaced some of the traditionalist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Lutsk
The Treaty of Lutsk was a secret agreement signed in Lutsk, Poland-Lithuania (now in Ukraine), between the Tsardom of Russia and the Ottoman Protectorate of Moldavia on 13 April 1711, shortly after the outbreak of the Russo-Ottoman War of 1710–11. The Ottoman Protectorate of Kara Bogdan (Moldavia) supported Russia in its war against the Ottomans with troops and by allowing the Russian army to cross its territory and to place garrisons in Moldavian fortresses. The Moldavians were represented by the Metropolitan of Moldavia Ghedeon. The text of the treaty was elaborated entirely by Moldavian Hospodar Dimitrie Cantemir, who broke his oath to the Sultan and promised to become the vassal of the Russian tsar. Terms In the preamble and in Article I, Dimitrie Cantemir worships the tsar, receiving in return protection from Peter I for himself and for all the people of Moldavia. It is provided that the lord of Moldavia "with all the great boyars and her nobles and with the inhabitants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael The Brave
Michael the Brave ( or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593–1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Transylvania (1599–1600). He is considered one of Romania's greatest national heroes. Since the 19th century, Michael the Brave has been regarded by Romanian nationalism, Romanian nationalists as a symbol of Romanian unity, as his reign marked the first time in history all principalities inhabited by Romanians were under the same ruler. His rule over Wallachia began in the autumn of 1593. Two years later, Long Turkish War, war with the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans began, a conflict in which the Prince fought the Battle of Călugăreni, resulting in a victory against an army nearly three times the size of the army of Michael the Brave, considered one of the most important battles of his reign. Although the Wallachians emerged victorious from the battle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Muntenia (Greater Wallachia) and Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia). Dobruja could sometimes be considered a third section due to its proximity and brief rule over it. Wallachia as a whole is sometimes referred to as Muntenia through identification with the larger of the two traditional sections. Wallachia was founded as a principality in the early 14th century by Basarab I after a rebellion against Charles I of Hungary, although the first mention of the territory of Wallachia west of the river Olt dates to a charter given to the voivode Seneslau in 1246 by Béla IV of Hungary. In 1417, Wallachia was forced to accept the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire; this lasted until the 19th century. In 1859, Wallachia united with Moldavia to form the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan III Of Russia
Ivan III Vasilyevich (; 22 January 1440 – 27 October 1505), also known as Ivan the Great, was Grand Prince of Moscow and Sovereign of all Russia, all Russia from 1462 until his death in 1505. Ivan served as the co-ruler and regent for his blind father Vasily II before he officially ascended the throne. He multiplied the territory of his state through conquest, purchase, inheritance and the seizure of lands from his dynastic relatives, and laid the foundations of the centralized Russian state. He also renovated the Kremlin, Moscow Kremlin and introduced a new Sudebnik of 1497, legal code. Ivan is credited with ending the dominance of the Tatars over Russia; his Great Stand on the Ugra River, victory over the Great Horde in 1480 formally restored its independence. Ivan began using the title tsar, and used the title tentatively until the House of Habsburg, Habsburgs recognized it. While officially using "tsar" in his correspondence with other monarchs, he was satisfied with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan The Young
Ivan Ivanovich () or Ioann Ioannovich (), also known as Ivan the Young (; 15 February 1458 – 6 March 1490), was the eldest son and heir of Ivan III of Russia from his first marriage to Maria of Tver. In 1471, he was given the title of grand prince by his father and made co-ruler. In 1485, he was given Tver as an appanage. Biography Ivan Ivanovich was born on 15 February 1458, the son of Ivan III by his first wife Maria of Tver, who later died in 1467. In 1471, as Ivan III marched off on his campaign against Novgorod, he bestowed upon the young Ivan the title of grand prince, so the Muscovite ambassadors and government officials used to speak on behalf of the two grand princes. Ambassadors from different Russian cities (e.g. Novgorod), as well ambassadors from foreign countries, could equally address both Ivan III and Ivan the Young with the same requests or problems. Russian chronicles continued to give the young Ivan the title of grand prince after his father returned fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elena Of Moldavia
Elena Stefanovna of Moldavia (), also known as Elena of Wallachia (; – 18 January 1505), was a Moldavian princess as a daughter of Stephen III, who later became the grand princess consort of Moscow in 1483 as the wife of Ivan the Young, the heir of Ivan III of Russia. After her husband's death in 1490, their son Dmitry Ivanovich was made co-ruler in 1498 until her faction lost in 1502; she and her son were then imprisoned. Biography Elena was born in . Her parents were Stephen III ("the Great"), the sovereign prince of Moldavia, and his first (or second) wife Princess Evdochia of Kiev. Negotiations to marry her to Ivan Ivanovich ("the Young"), heir to the throne of Moscow, began in the late 1470s. Elena married Ivan the Young on 12 January 1483, and gave birth to Dmitry Ivanovich on 10 October 1483. After the death of her spouse in 1490, her son, who had borne only the title ''prince'', was appointed as the heir to the Russian throne and made co-ruler in 1498. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |