|
List Of Robert Burns Memorials
This is a list of over sixty known memorials (statues, busts, fountains, buildings and street names) to the Scottish people, Scottish poet Robert Burns. Of these, the oldest outdoor statue is given to be at Camperdown, Victoria, Australia (1830). Scotland * Aberdeen – statue near Union Terrace Gardens * Alloway – monument a short distance from Robert Burns Birthplace Museum, his birthplace. A greco-roman bust by Patrick Park stands within the monument, presented in 1847. * Arbroath – statue by Dundee sculptor Scott Sutherland in the grounds of Arbroath Library. Sutherland may be better known for his work of the Commando Memorial. * Ayr – statue in Burns Statue Square. Seated statue of Robert Burns and his dog luath. To mark the opening of the Central shopping centre in 2006. Artist David Annand was selected to create a sculpture out of steel and bronze, based on Burns' poem 'The Twa Dog.' * Bathgate – Statue or Rabbie Burns with Highland Mary in grounds of Partne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
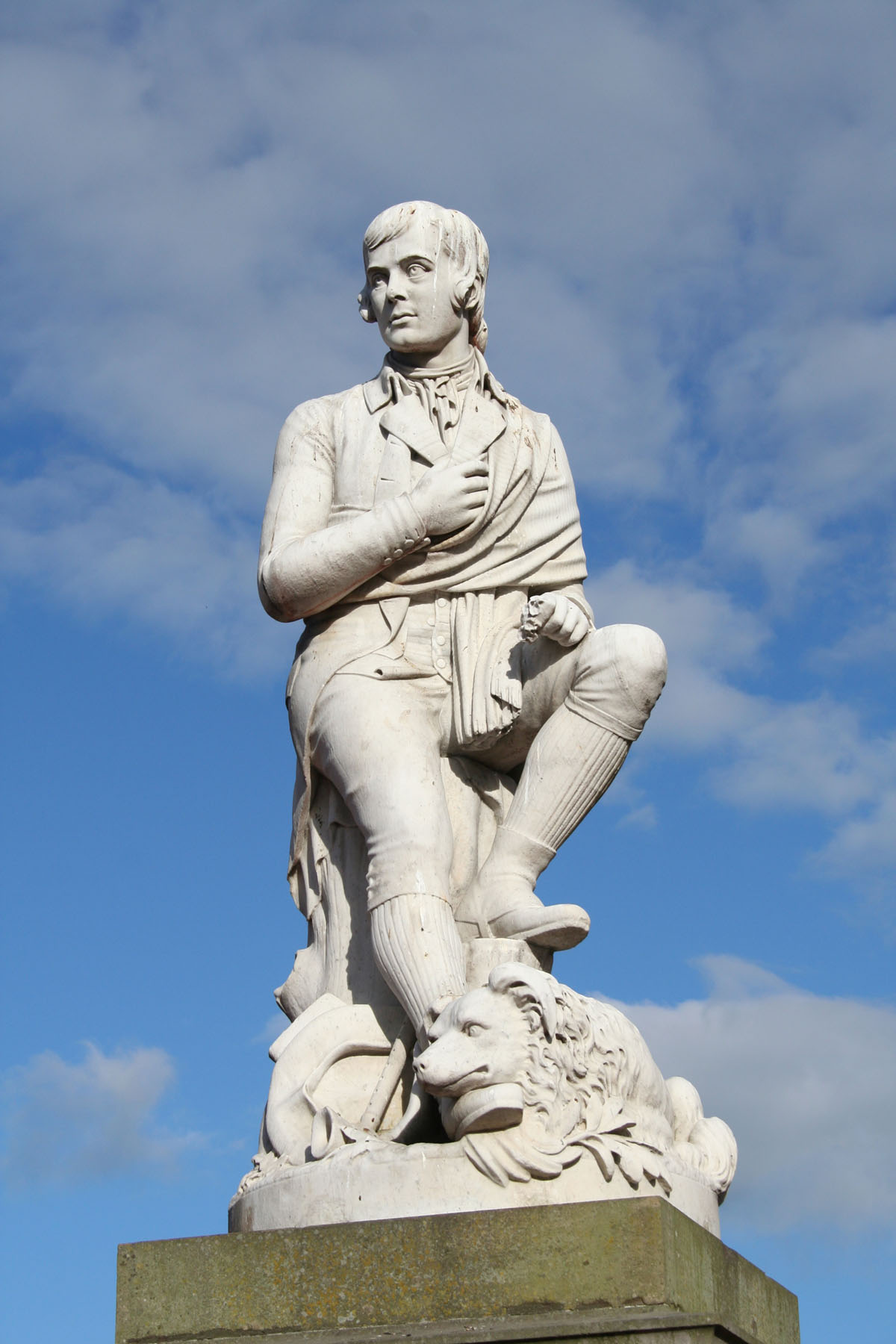
Burns Monument, Alloway 2017-05-17
Burns may refer to: Astronomy * 2708 Burns, an asteroid * Burns (crater), on Mercury People * Burns (surname), list of people and characters named Burns ** Burns (musician), Scottish record producer Places in the United States * Burns, Colorado * Burns, Kansas * Burns, Missouri * Burns, New York * Burns, Oregon * Burns, Tennessee * Burns, Wisconsin ** Burns (community), Wisconsin * Burns, Wyoming * H.B. Burns Memorial Building, Washington, D.C. Ships of the US Navy * USS Burns (DD-171), USS ''Burns'' (DD-171), a WWI destroyer (1919–1930) * USS Burns (DD-588), USS ''Burns'' (DD-588), a WWII destroyer (1943 –1946) * USS W. W. Burns (1861), USS ''W. W. Burns'' (1861), a Civil-War schooner Other uses * Burn, a skin injury * Burns London, an English guitar maker * Burns Night, a celebration of Scottish poet Robert Burns See also * Burn (other) * Burns Township (other) * Burnside (other) * Burnsville (other) * Berns (disambigua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries
Dumfries ( ; ; from ) is a market town and former royal burgh in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, near the mouth of the River Nith on the Solway Firth, from the Anglo-Scottish border. Dumfries is the county town of the Counties of Scotland, historic county of Dumfriesshire. Before becoming King of Scots, Robert the Bruce killed his rival John Comyn III of Badenoch at Greyfriars Kirk in the town in 1306. The Young Pretender had his headquarters here towards the end of 1745. In World War II, the Norwegian armed forces in exile in Britain largely consisted of a brigade in Dumfries. Dumfries is nicknamed ''Queen of the South''. This is also the name of the town's Queen of the South F.C., football club. People from Dumfries are known colloquially in Scots language as ''Doonhamers''. Toponymy There are a number of theories on the etymology of the name, with an ultimately Common Celtic, Celtic derivation (either from Common Brittonic, Brythonic, Old Irish, Gaelic or a mixture of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Grant Stevenson
William Grant Stevenson, (7 March 1849 – 6 May 1919) was a Scottish sculptor and portrait painter. Life and work Stevenson was born in Ratho in Midlothian on 7 March 1849. His parents were William Stevenson and Margaret Kay Stevenson. His elder brother, David Watson Stevenson (1842–1904), was also a sculptor and an elected member of the Royal Scottish Academy. Stevenson is most famous for his colossal bronze figure of Sir William Wallace, which stands on a high plinth of roughly hewn pink granite overlooking Union Terrace Gardens in Aberdeen. Stevenson was an admirer of Robert Burns's work and created several sculptures of the poet. His marble statue of Burns serves as the centerpiece of the Burns Burns Monument, Kilmarnock, Monument in Kilmarnock. Stevenson was also commissioned to produce bronze statues of Burns for monuments located in: * Denver, Colorado (Robert Burns Memorial (Denver), City Park) * Chicago, Illinois (Garfield Park (Chicago), Garfield Park) * Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilmarnock
Kilmarnock ( ; ; , ), meaning "the church of Mernóc", is a town and former burgh in East Ayrshire situated in southwest Scotland. The town has served as the administrative centre of East Ayrshire Council since 1996 and is the region's main commercial and industrial centre. The town has a total of 284 listed buildings and structures as designed by Historic Environment Scotland, including the Dick Institute, Dean Castle, Loanhead School and the original 1898 building of Kilmarnock Academy, with post–war developments of the controversial 1970s regeneration such as The Foregate and Clydesdale Bank building being considered for listed building status. The first passenger conveying railway in Scotland originated in Kilmarnock in 1812 as a horse-drawn plateway and became known as the Kilmarnock and Troon Railway. The first printed collection of works by Scottish poet Robert Burns was published in 1786 in Kilmarnock. '' Poems, Chiefly in the Scottish Dialect'', was pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Pittendrigh Macgillivray
James Pittendrigh MacGillivray (1856 – 29 April 1938) was a Scottish sculptor. He was also a keen artist, musician and poet. He was born in Inverurie, Aberdeenshire, the son of a sculptor, and studied under William Brodie and John Mossman. His works include public statues of Robert Burns in Irvine, Lord Byron in Aberdeen, the 3rd Marquess of Bute in Cardiff, John Knox in Edinburgh's St Giles Cathedral, and William Ewart Gladstone in Coates Crescent Gardens, Edinburgh. After training under Brodie in Edinburgh, Macgillivray worked for nine years in Glasgow as assistant to Mossman and James Steel. In 1894 he returned to Edinburgh, where he lived at "Ravelston Elms" on Murrayfield Road. Macgillivray was a Scottish nationalist, and associated both with Patrick Geddes' Fin de Siècle Scottish cultural revival and Hugh MacDiarmid's later Scottish Renaissance movement. He contributed illustrations to the Spring and Autumn volumes of ''The Evergreen: A Northern Seasonal'' pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irvine, Ayrshire
Irvine ( ; ; ) is a town and former royal burgh on the coast of the Firth of Clyde in North Ayrshire, Scotland. The 2011 Census recorded the town's population at 33,698 inhabitants, making it the largest settlement in North Ayrshire, and 22nd List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, largest settlement in Scotland. Irvine was designated at the fifth and final Scottish new town in November 1966. Irvine is the administrative centre and the seat of the North Ayrshire, North Ayrshire Council administration which has its headquarters based at Cunninghame House. Irvine was the site of Scotland's 12th century military capital and former headquarters of the Lord High Constable of Scotland, Hugh de Morville, Constable of Scotland, Hugh de Morville. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Edwin Ewing
George Edwin Ewing (8 July 1828 – 26 April 1884) was a Scottish sculptor. He was born in Birmingham, the son of sculptor James Ewing and the brother of sculptor James Alexander Ewing. He grew up in Edinburgh and Glasgow and learned his trade in Liverpool and London, including in the modelling room of Covent Garden Theatre, before setting up in business in Glasgow in 1859. He then spent some time in Rome in the 1860s studying under the sculptor John Gibson (sculptor), John Gibson before returning to Glasgow in 1862. He went on to be the most successful Scottish sculptor of his time. Whilst his reputation stemmed from his marble busts of prominent Scots and the Royal Family, his most well-known commission was the bronze statue of Robert Burns in George Square, Glasgow, created in 1874–77, which was later enhanced with three bronze panels by his brother James in 1885–7. Whereas much of his work on public buildings has been lost during demolition, significant works remain to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
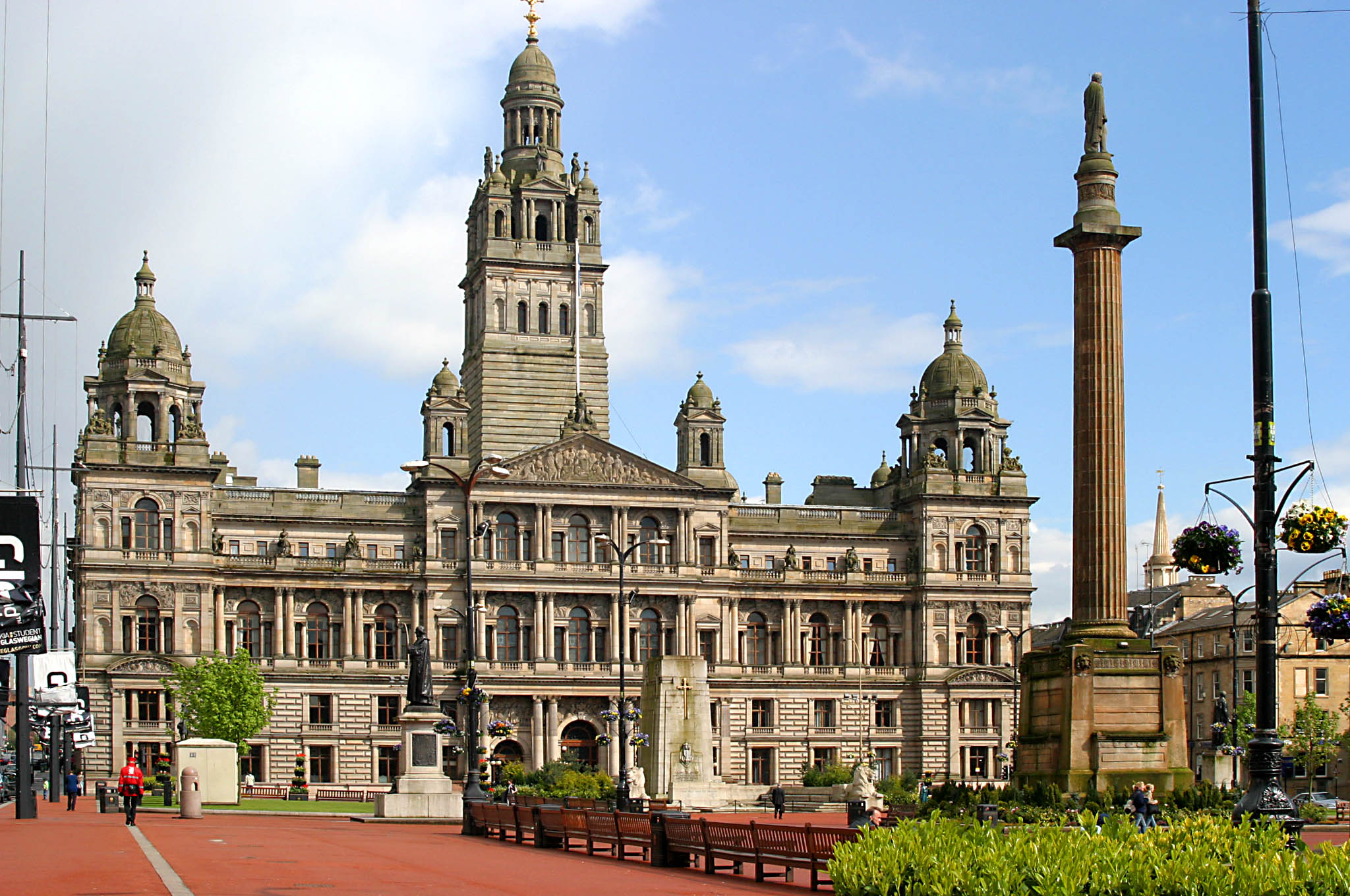
George Square
George Square () is the principal Town square, civic square in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is one of six squares in the city centre, the others being Cathedral Square, Glasgow, Cathedral Square, St Andrew's Square, Glasgow, St Andrew's Square, St Enoch Square, Royal Exchange Square, and Blythswood Square on Blythswood Hill. Named after King George III and initially laid out in 1781 but not developed for another twenty years, George Square is surrounded by architecturally important buildings including on the east side the palatial Municipal Chambers, also known as the Glasgow City Chambers, City Chambers, whose foundation stone was laid in 1883, and on the west side by the . Built by Glasgow Corporation, the Chambers are the continuing headquarters of Glasgow City Council. Joseph Swan's panoramic engraving of 1829 shows the early development of the square and its surrounding buildings. The square boasts an important collection of statues and monuments, including those de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom and the 27th-most-populous city in Europe, and comprises Wards of Glasgow, 23 wards which represent the areas of the city within Glasgow City Council. Glasgow is a leading city in Scotland for finance, shopping, industry, culture and fashion, and was commonly referred to as the "second city of the British Empire" for much of the Victorian era, Victorian and Edwardian eras. In , it had an estimated population as a defined locality of . More than 1,000,000 people live in the Greater Glasgow contiguous urban area, while the wider Glasgow City Region is home to more than 1,800,000 people (its defined functional urban area total was almost the same in 2020), around a third of Scotland's population. The city has a population density of 3,562 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eglinton Country Park
Eglinton Country Park is located on the grounds of the old Eglinton Castle estate in Kilwinning, North Ayrshire, Scotland (map reference NS 3227 4220). Eglinton Park is situated in the parish of Kilwinning, part of the former district of Cunninghame, and covers an area of ([] of which are woodland. The central iconic feature of the country park is the ruined Eglinton Castle, once home to the Eglinton family and later the Montgomeries, Earl of Eglinton, Earls of Eglinton and chiefs of the Clan Montgomery. Eglinton Country Park is managed and maintained by North Ayrshire Council and its Ranger Service. Spier's Parklands Spier's school, Spier's Old School Grounds on Barrmill Road, Beith is an amenity for the communities of the Garnock Valley (Dalry, Glengarnock, Kilbirnie, Longbar, Beith, Auchengree, Greenhills, Burnhouse, and Barrmill). Pedestrian access is 24x7. The Spier's parklands are patrolled by the NAC Ranger Service. The Friends of Spiers (FoS) are a group based at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
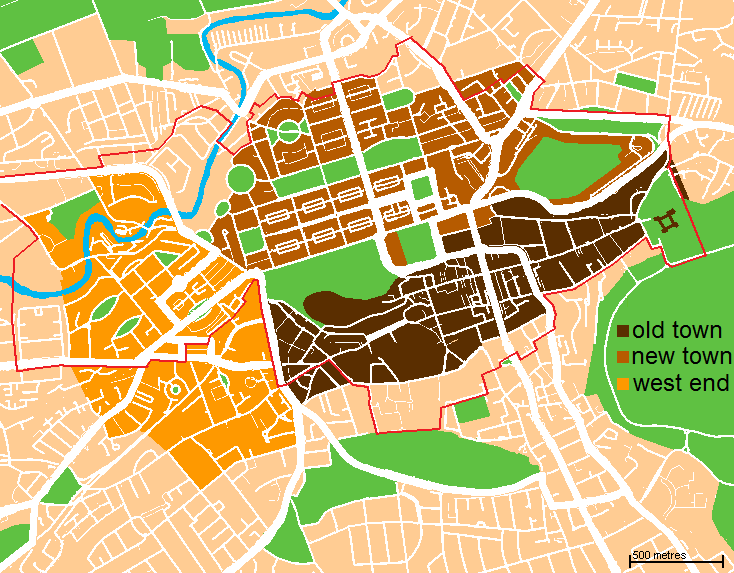
Old Town, Edinburgh
The Old Town () is the oldest part of Scotland's capital city of Edinburgh. The area has preserved much of its medieval street plan and many Scottish Reformation, Reformation-era buildings. Together with the 18th/19th-century New Town, Edinburgh, New Town, and West End, Edinburgh, West End, it forms part of a protected UNESCO World Heritage Site. Royal Mile The "Royal Mile" is a name coined in the early 20th century for the main street of the Old Town which runs on a downwards slope from Edinburgh Castle to Holyrood Palace and the ruined Holyrood Abbey. Narrow ''List of closes on the Royal Mile, closes'' (alleyways), often no more than a few feet wide, lead steeply downhill to both north and south of the main spine which runs west to east. Significant buildings in the Old Town include St. Giles' Cathedral, the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland, the National Museum of Scotland, the Old College, University of Edinburgh, Old College of the University of Edinburgh, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makars' Court
Makars' Court is a courtyard in central Edinburgh, Scotland. It forms part of Lady Stair's Close, which connects the Royal Mile#Lawnmarket, Lawnmarket with The Mound to the north, and is next to the Writers' Museum. Described as an "evolving national literary monument", the courtyard incorporates quotations from Scottish literature inscribed onto paving slabs. The quotations represent works in the languages used by Scots past and present: Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic, Scots language, Scots, English, and Latin. Selection The Scots language term ''makar'' denotes an author or writer, though stressing their role as a "skilled and versatile worker in the craft of writing". Since 2002 the city of Edinburgh has appointed its own official Makar. In 1997, twelve Scottish writers were selected by the Saltire Society, and quotations from their works were inscribed on stone slabs installed in the area adjacent to the museum. The first was unveiled by Ronald Harwood, then president of Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |