|
List Of MeSH Codes (D12.776.543)
The following is a partial list of the "D" codes for Medical Subject Headings (MeSH), as defined by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM). This list covers membrane proteins. For other protein-related codes, see List of MeSH codes (D12.776). Codes before these are found at List of MeSH codes (D12.776) § MeSH D12.776.532.510.750. Codes following these are found at List of MeSH codes (D12.776) § MeSH D12.776.556. For other MeSH codes, see List of MeSH codes. The source for this content is the set o2006 MeSH Treesfrom the NLM. – membrane proteins – ankyrins – arrestins – arrestin – bacterial outer membrane proteins – adhesins, bacterial * – adhesins, escherichia coli – fimbriae proteins – calnexin – connexins – connexin 43 – dystrophin – dystrophin-associated proteins – dystroglycans – sarcoglycans – ephrins – ephrin-A1 – ephrin-A2 – ephrin-A3 – ephrin-A4 – ephrin-A5 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/ PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials. MeSH was introduced in the 1960s, with the NLM's own index catalogue and the subject headings of the Quarterly Cumulative Index Medicus (1940 edition) as precursors. The yearly printed version of MeSH was discontinued in 2007; MeSH is now available only online. It can be browsed and downloaded free of charge through PubMed. Originally in English, MeSH has been translated into numerous other languages and allows retrieval of documents from different origins. Structure MeSH vocabulary is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dystroglycans
Dystroglycan is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DAG1'' gene. Dystroglycan is one of the dystrophin-associated glycoproteins, which is encoded by a 5.5 kb transcript in ''Homo sapiens'' on chromosome 3. There are two exons that are separated by a large intron. The spliced exons code for a protein product that is finally cleaved into two non-covalently associated subunits, lpha(N-terminal) and eta(C-terminal). Function In skeletal muscle the dystroglycan complex works as a transmembrane linkage between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. lphadystroglycan is extracellular and binds to merosin lpha2 laminin in the basement membrane, while etadystroglycan is a transmembrane protein and binds to dystrophin, which is a large rod-like cytoskeletal protein, absent in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. Dystrophin binds to intracellular actin cables. In this way, the dystroglycan complex, which links the extracellular matrix to the intracellular actin cable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
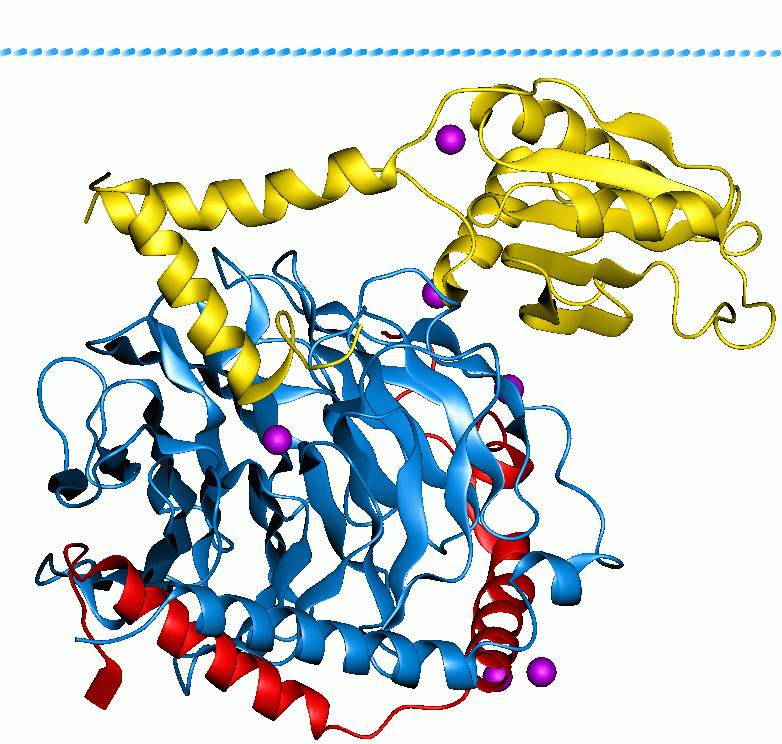
Gtp-binding Protein Alpha Subunits, Gq-g11
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable dimeric complex referred to as the beta-gamma complex . Heterotrimeric G proteins located within the cell ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gtp-binding Protein Alpha Subunit, Gi2
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be c ... that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gtp-binding Protein Alpha Subunits, Gi-go
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable dimeric complex referred to as the beta-gamma complex . Heterotrimeric G proteins located within the cell ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
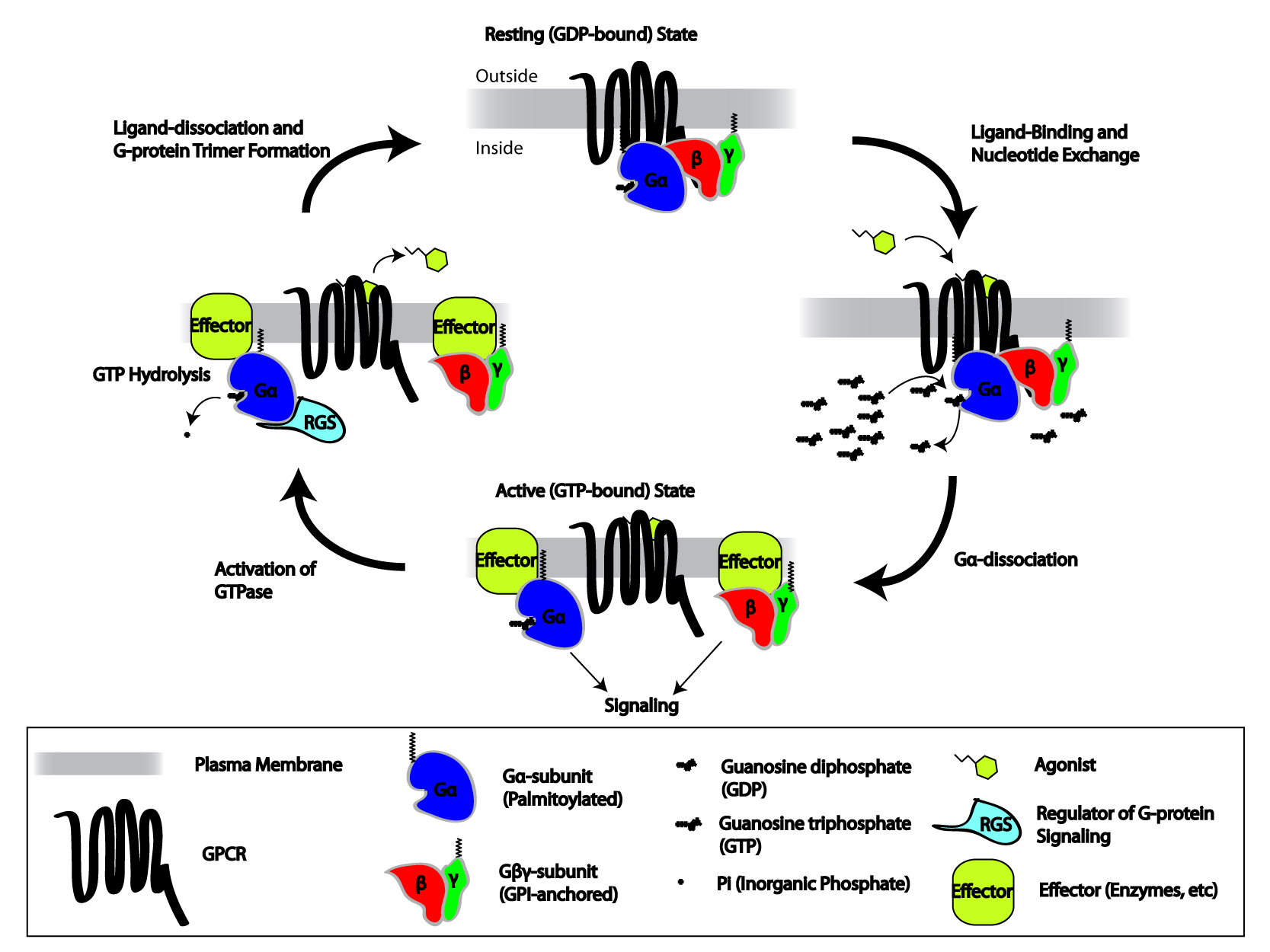
Heterotrimeric Gtp-binding Proteins
Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the ''"large" G proteins'' (as opposed to the subclass of smaller, monomeric small GTPases) are membrane-associated G proteins that form a heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-structural difference between heterotrimeric and monomeric G protein is that heterotrimeric proteins bind to their cell-surface receptors, called G protein-coupled receptors, directly. These G proteins are made up of ''alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) subunits. The alpha subunit is attached to either a GTP or GDP, which serves as an on-off switch for the activation of G-protein. When ligands bind a GPCR, the GPCR acquires GEF ( guanine nucleotide exchange factor) ability, which activates the G-protein by exchanging the GDP on the ''alpha'' subunit to GTP. The binding of GTP to the ''alpha'' subunit results in a structural change and its dissociation from the rest of the G-protein. Generally, the ''alpha'' subunit binds membrane-bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephrin-B2
Ephrin-B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFNB2'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the ephrin (EPH) family. The ephrins and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, especially in the nervous system and in erythropoiesis. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. This gene encodes an EFNB class ephrin which binds to the EPHB4 and EPHA3 receptors. Cancer EFNB2 gene has been observed progressively downregulated in Human papillomavirus-positive neoplastic keratinocytes derived from uterine cervical preneoplastic lesions at different levels of malignancy. For this reason, EFNB2 is likely to be associated with tumorigenesis and may be a poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephrin-A5
Ephrin A5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFNA5'' gene. Ephrin A5 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein of the ephrin-A subclass of ephrin ligands that binds to the EphA subclass of Eph receptors. Ephrin A5 has also been shown to bind to the EphB2 receptor. Reverse signaling in growth cone survival "Reverse" signaling is one unique property of ephrin ligands that allows for the transmission of an intracellular signal in ephrin-expressing cells that is distinct from the signal transmitted in Eph receptor-expressing cells. Although the mechanism of "reverse" signaling by ephrin-As is not well understood, it is relatively surprising considering that ephrin-A ligands are attached to the cell membrane solely by a GPI linkage and unlike ephrin-Bs, lack a potential intracellular signaling domain. Nonetheless, certain ephrin-A ligands are known to initiate reverse signaling cascades like ephrin A5, which has been shown to stimu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephrin-A3
Ephrin A3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFNA3'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the ephrin (EPH) family. The ephrins and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, especially in the nervous system and in erythropoiesis. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. This gene encodes an EFNA class ephrin. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephrin-A2
Ephrin-A2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFNA2'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the ephrin family. The protein is composed of a signal sequence, a receptor-binding region, a spacer region, and a hydrophobic region. The EPH and EPH-related receptors comprise the largest subfamily of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and have been implicated in mediating developmental events, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. Posttranslational modifications determine whether this protein localizes to the nucleus or the cytoplasm. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |