|
List Of Bell Labs Alumni
The American research and development (R&D) company Bell Labs is known for its many alumni who have won various awards, including the Nobel Prize and the ACM Turing Award. List * Nobel Prize * __ Turing Award References {{Reflist Scientists at Bell Labs Lists of people by company, Bell Labs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research And Development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage of development of a potential new service or the production process. Although R&D activities may differ across businesses, the primary goal of an R&D department is to new product development, develop new products and services. R&D differs from the vast majority of corporate activities in that it is not intended to yield immediate profit, and generally carries greater risk and an uncertain return on investment. R&D is crucial for acquiring larger shares of the market through new products. ''R&D&I'' represents R&D with innovation. Background New product design and development is often a crucial factor in the survival of a company. In a global industrial landscape that is changing fast, firms must continually revise their design and range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos E
Amos or AMOS may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Amos'' (album), an album by Michael Ray * Amos (band), an American Christian rock band * ''Amos'' (film), a 1985 American made-for-television drama film * Amos (guitar), a 1958 Gibson Flying V * Amos Records, an independent record label established in Los Angeles, California, in 1968 People and religious figures * Amos (name), a given name, nickname and surname * Amos (prophet), a Jewish prophet from the 8th century BCE, and the author of the Book of Amos Technology * AMOS, or Advanced Mortar System, a 120 mm automatic twin-barreled, breech-loaded mortar turret * AMOS (programming language), a dialect of BASIC on the Amiga computer * Alpha Micro Operating System, a proprietary operating system used in Alpha Microsystems minicomputers * IBM SPSS Amos, a statistical software package by IBM used in structural equation modeling, companion software in the SPSS family * Air Force Maui Optical and Superco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
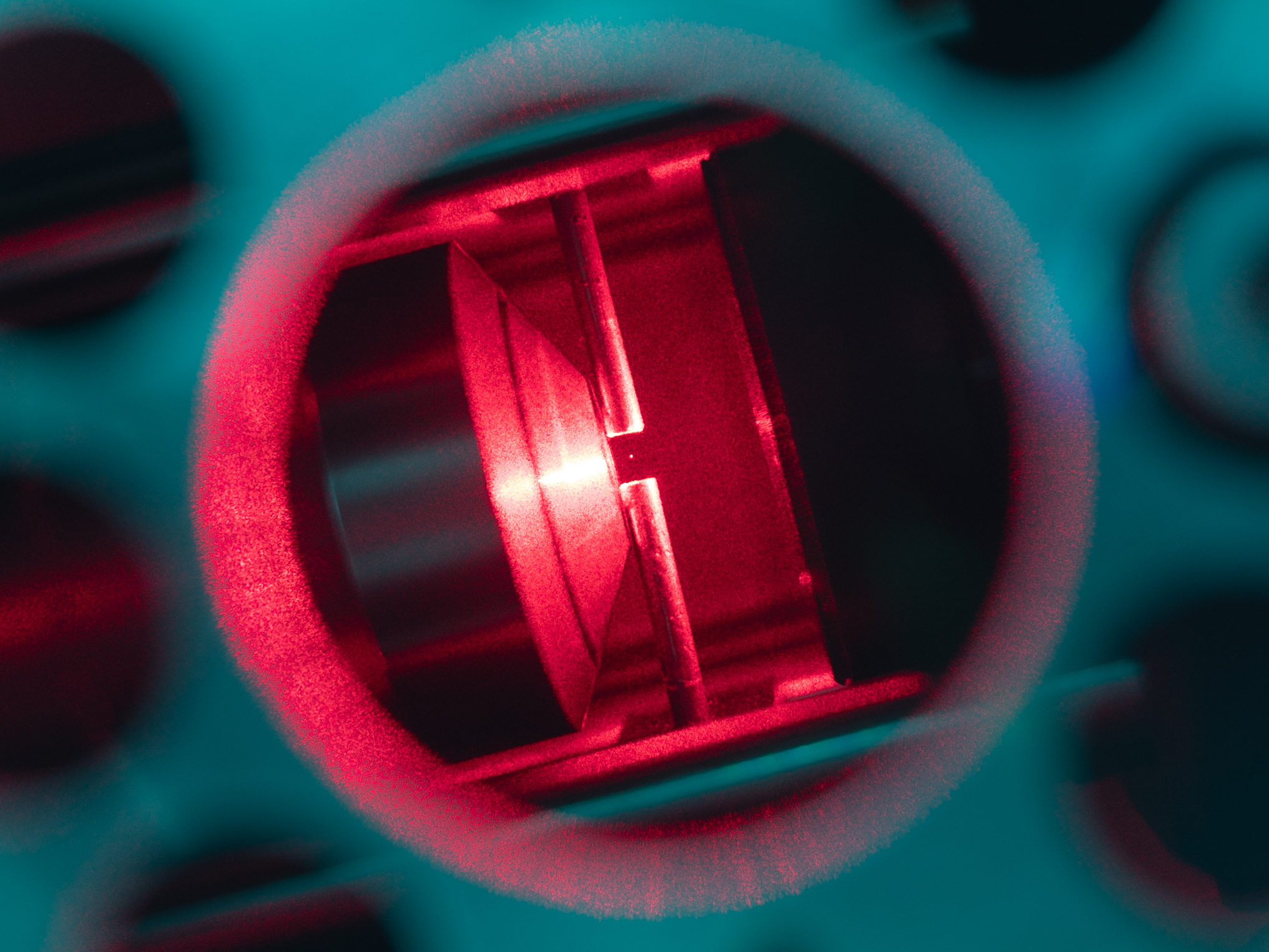
Optical Tweezers
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers. If the object is held in air or vacuum without additional support, it can be called optical levitation. The laser light provides an attractive or repulsive force (typically on the order of piconewtons), depending on the relative refractive index between particle and surrounding medium. Levitation is possible if the force of the light counters the force of gravity. The trapped particles are usually micron-sized, or even smaller. Dielectric and absorbing particles can be trapped, too. Optical tweezers are used in biology and medicine (for example to grab and hold a single bacterium, a cell like a sperm cell or a blood cell, or a molecule like DNA), nanoengineering and nanochemistry (to study and build materials from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Ashkin
Arthur Ashkin (September 2, 1922 – September 21, 2020) was an American scientist and Nobel laureate who worked at Bell Labs. Ashkin has been considered by many as the father of optical tweezers, "LaserFest – the 50th anniversary of the first laser" for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics 2018 at age 96, becoming the oldest Nobel laureate until 2019 when John B. Goodenough was awarded at 97. He resided in Rumson, New Jersey. Ashkin started his work on manipulation of microparticles with laser light in the late 1960s which resulted in the invention of optical tweezers in 1986. He also pioneered the optical trapping process that eventually was used to manipulate atoms, molecules, and biological cells. The key phenomenon is the radiation pressure of light; this pressure can be dissected down into optical gradient and scattering forces. Early life and family Arthur Ashkin was born in Brooklyn, New York, in 1922, to a family of Ukrainian-Jewish background. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Ashkin EM1B5678 (44417135450)
Arthur is a masculine given name of uncertain etymology. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text ''Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th century Romano-British general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still a matter of debate and the poem only survives in a late 13th century manuscript entitled the Book of Aneirin. A 9th-century Breton landowner named Arthur witnessed several charters collected in the '' Cartulary of Redon''. The Irish borrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Inventors Hall Of Fame
The National Inventors Hall of Fame (NIHF) is an American not-for-profit organization, founded in 1973, which recognizes individual engineers and inventors who hold a US patent of significant technology. Besides the Hall of Fame, it also operates a museum in Alexandria, Virginia, sponsors educational programs, and a collegiate competition. As of 2025, 652 inventors have been inducted, mostly constituting historic persons from the past three centuries, but also including living inductees. Nominees must hold a US patent of significant contribution to the US welfare, and which advances science and useful arts. History The National Inventors Hall of Fame was founded in 1973 on the initiative of H. Hume Mathews, then the chairman of the National Council of Patent Law Associations (now the National Council of Intellectual Property Law Associations). It was launched by Ed Sobey, who was also the first director. In 1974, it gained a major sponsor in the U.S. Patent and Trademar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Medal Of Technology
The National Medal of Technology and Innovation (formerly the National Medal of Technology) is an honor granted by the president of the United States to American inventors and innovators who have made significant contributions to the development of new and important technology. The award may be granted to a specific person, to a group of people or to an entire organization or corporation. It is the highest honor the United States can confer to a U.S. citizen for achievements related to technological progress. History The National Medal of Technology was created in 1980 by the United States Congress under the Stevenson-Wydler Technology Innovation Act. It was a bipartisan effort to foster technological innovation and the technological competitiveness of the United States in the international arena. The first National Medals of Technology were issued in 1985 by then-U.S. President Ronald Reagan to 12 individuals and one company. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handoff
In cellular telecommunications, handover, or handoff, is the process of transferring an ongoing call or data session from one channel connected to the core network to another channel. In satellite communications it is the process of transferring satellite control responsibility from one earth station to another without loss or interruption of service. Terminology American English uses the term ''handoff'', and this is most commonly used within some American organizations such as 3GPP2 and in American originated technologies such as CDMA2000. In British English the term ''handover'' is more common, and is used within international and European organisations such as ITU-T, IETF, ETSI and 3GPP, and standardised within European originated standards such as GSM and UMTS. The term handover is more common in academic research publications and literature, while handoff is slightly more common within the IEEE and ANSI organisations. Purpose In telecommunications there may be differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic Service Position System
The Traffic Service Position System (TSPS) was developed by Bell Labs in Columbus, Ohio to replace traditional cord switchboards. The first TSPS was deployed in Morristown, New Jersey in 1969 and used the Stored Program Control-1A CPU, "Piggyback" twistor memory (a proprietary technology developed by Bell Labs similar to core memory) and Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistor solid state memory devices similar to dynamic random access memory. Features The TSPS system utilized special analog trunks that originated at Class 5 end office circuit switch systems and Class 4 toll access circuit switch systems that were connected to Class 3 primary toll circuit switch systems such as the 4A-ETS/PBC and 4ESS switch systems. The TSPS system did not perform switching between the originating end office switch and the toll switch for the subscriber voice path. The TSPS system included the "Remote Trunking Arrangement" (RTA) feature that consolidated the trunk connection at the origina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling disclosure of the invention."A patent is not the grant of a right to make or use or sell. It does not, directly or indirectly, imply any such right. It grants only the right to exclude others. The supposition that a right to make is created by the patent grant is obviously inconsistent with the established distinctions between generic and specific patents, and with the well-known fact that a very considerable portion of the patents granted are in a field covered by a former relatively generic or basic patent, are tributary to such earlier patent, and cannot be practiced unless by license thereunder." – ''Herman v. Youngstown Car Mfg. Co.'', 191 F. 579, 584–85, 112 CCA 185 (6th Cir. 1911) In most countries, patent rights fall under private la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1ESS Switch
The Number One Electronic Switching System (1ESS) was the first large-scale stored program control (SPC) telephone exchange or electronic switching system in the Bell System. It was manufactured by Western Electric and first placed into service in Succasunna, New Jersey, in May 1965. The switching fabric was composed of a reed relay matrix controlled by wire spring relays which in turn were controlled by a central processing unit (CPU). The 1AESS central office switch was a plug compatible, higher capacity upgrade from 1ESS with a faster 1A processor that incorporated the existing instruction set for programming compatibility, and used smaller remreed switches, fewer relays, and featured disk storage. It was in service from 1976 to 2017. Switching fabric The voice switching fabric plan was similar to that of the earlier 5XB switch in being bidirectional and in using the call-back principle. The largest full-access matrix switches (the 12A line grids had partial acces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, computer scientist, cryptographer and inventor known as the "father of information theory" and the man who laid the foundations of the Information Age. Shannon was the first to describe the use of Boolean algebra—essential to all digital electronic circuits—and helped found artificial intelligence (AI). Roboticist Rodney Brooks declared Shannon the 20th century engineer who contributed the most to 21st century technologies, and mathematician Solomon W. Golomb described his intellectual achievement as "one of the greatest of the twentieth century". At the University of Michigan, Shannon dual degreed, graduating with a Bachelor of Science in electrical engineering and another in mathematics, both in 1936. A 21-year-old master's degree student in electrical engineering at MIT, his thesis, "A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits", demonstrated that electric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |