|
Lipid-gated Ion Channels
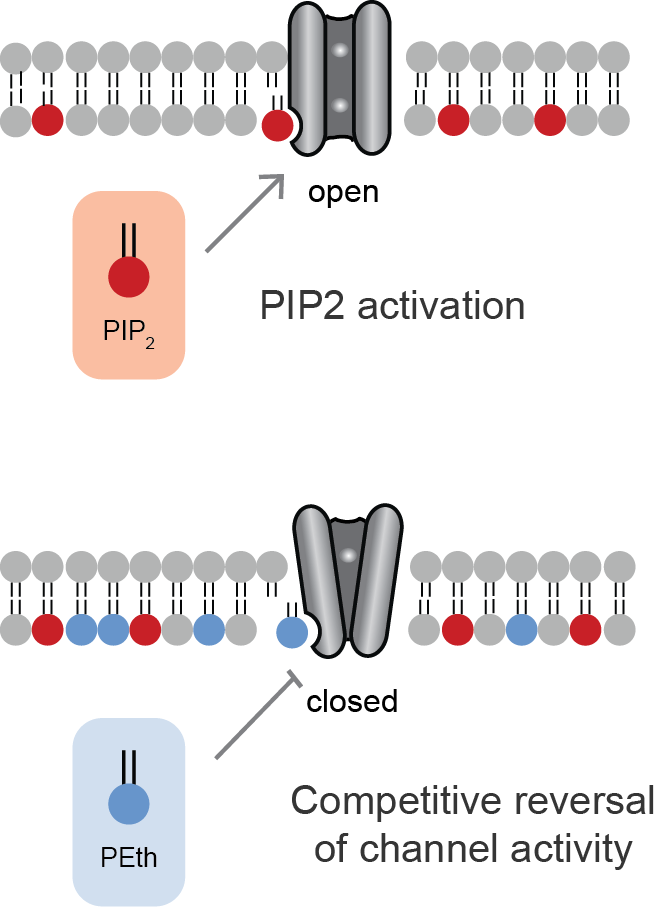
Lipid-gated ion channels are a class of ion channels whose conductance of ions through the membrane depends directly on lipids. Classically the lipids are membrane resident anionic signaling lipids that bind to the transmembrane domain on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane with properties of a classic ligand. Other classes of lipid-gated channels include the mechanosensitive ion channels that respond to lipid tension, thickness, and hydrophobic mismatch. A lipid ligand differs from a lipid Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in that a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand derives its function by dissociating from the channel while a cofactor typically derives its function by remaining bound. PIP2-gated channels Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) was the first and remains the best studied lipid to gate ion channels. PIP2 is a cell membrane lipid, and its role in gating ion channels represents a novel role for the molecule. Kir channels: PIP2 binds to and directly activate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inward-rectifier Potassium Ion Channel
Inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir, IRK) are a specific Lipid-gated_ion_channels, lipid-gated subset of potassium channels. To date, seven subfamilies have been identified in various mammalian cell types, plants, and bacteria. They are activated by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PIP2). The malfunction of the channels has been implicated in several diseases. IRK channels possess a pore domain, homologous to that of voltage-gated ion channels, and flanking transmembrane domain, transmembrane segments (TMSs). They may exist in the membrane as Homo-oligomer, homo- or Hetero-oligomers, heterooligomers and each monomer possesses between 2 and 4 TMSs. In terms of function, these proteins transport potassium, potassium (K+), with a greater tendency for K+ uptake than K+ export. The process of inward-rectification was discovered by Denis Noble in cardiac muscle cells in 1960s and by Richard Adrian, 2nd Baron Adrian, Richard Adrian and Ala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KCNK2
Potassium channel subfamily K member 2, also known as TREK-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNK2'' gene. This gene encodes K2P2.1, a lipid-gated ion channel belonging to the two-pore-domain background potassium channel protein family. This type of potassium channel is formed by two homodimers that create a channel that releases potassium out of the cell to control resting membrane potential. The channel is opened by anionic lipid, certain anesthetics, membrane stretching, intracellular acidosis, and heat. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Function in neurons TREK-1 is part of the subfamily of mechano-gated potassium channels that are present in mammalian neurons. They can be gated in both chemical and physical ways and can be opened via both physical stimuli and chemical stimuli. TREK-1 channels are found in a variety of tissues, but are particularly abundant in the brain and heart and are seen in various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are Receptor (biochemistry), receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PEth Competition
Phosphatidylethanols (PEth) are a group of phospholipids formed only in the presence of ethanol via the action of phospholipase D (PLD). It accumulates in blood and is removed slowly, making it a useful biomarker for alcohol consumption. PEth is also thought to contribute to the symptoms of alcohol intoxication. Structure Chemically, phosphatidylethanols are phospholipids carrying two fatty acid side chain, chains, which are variable in structure, and one phosphate ethyl group, ethyl ester. Biosynthesis When ethanol is present, PLD substitutes ethanol for water and covalently attaches the alcohol as the head group of the phospholipid; hence the name phosphatidylethanol. Normally PLD incorporates water to generate phosphatidic acid (PA); the process is termed transphosphatidylation. PLD continues to generate PA in the presence of ethanol and while PEth is generated and the effects of ethanol transphosphatidlyation are through the generation of the unnatural lipid not depletion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small-conductance Mechanosensitive Channel
Small conductance mechanosensitive ion channels (MscS) provide protection against hypo-osmotic shock in bacteria, responding both to stretching of the cell membrane and to membrane depolarization. In eukaryotes, they fulfill a multitude of important functions in addition to osmoregulation. They are present in the membranes of organisms from the three domains of life: bacteria, archaea, fungi and plants. Structure There are two families of mechanosensitive (MS) channels: large-conductance MS channels (MscL) and small-conductance MS channels (MscS or YGGB). The MscS family is much larger and more variable in size and sequence than the MscL family. MscS family homologues vary in length between 248 and 1120 amino acyl residues and in topology, but the homologous region that is shared by most of them is only 200-250 residues long, exhibiting 4-5 transmembrane regions (TMSs). Much of the diversity in MscS proteins occurs in the number of TMSs, which ranges from three to eleven TM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large-conductance Mechanosensitive Channel
Large conductance mechanosensitive ion channels (MscLs)TC# 1.A.22 are a family of pore-forming membrane proteins that are responsible for translating stresses at the cell membrane into an electrophysiological response. MscL has a relatively large conductance, 3 nS, making it permeable to ions, water, and small proteins when opened. MscL acts as stretch-activated osmotic release valve in response to osmotic shock. History MscL was first discovered on the surface of giant ''Escherichia coli'' spheroplasts using patch-clamp technique. Subsequently, the ''Escherichia coli'' MscL (Ec-MscL) gene was cloned in 1994. Following the cloning of MscL, the crystal structure of ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' MscL (Tb-MscL), was obtained in its closed conformation. In addition, the crystal structure of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' MscL (Sa-MscL) and Ec-MscL have been determined using X-ray crystallography and molecular model A molecular model is a physical model of an atomistic system that rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanosensitive Channels
Mechanosensitive channels (MSCs), mechanosensitive ion channels or stretch-gated ion channels are membrane proteins capable of responding to mechanical stress over a wide dynamic range of external mechanical stimuli. They are present in the membranes of organisms from the three domains of life: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. They are the sensors for a number of systems including the senses of touch, hearing and balance, as well as participating in cardiovascular regulation and osmotic homeostasis (e.g. thirst). The channels vary in selectivity for the permeating ions from nonselective between anions and cations in bacteria, to cation selective allowing passage Ca2+, K+ and Na+ in eukaryotes, and highly selective K+ channels in bacteria and eukaryotes. All organisms, and apparently all cell types, sense and respond to mechanical stimuli. MSCs function as mechanotransducers capable of generating both electrical and ion flux signals as a response to external or internal stimuli. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLIC
The GLIC receptor is a bacterial ( Gloeobacter) Ligand-gated Ion Channel, homolog to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. It is a proton-gated (the channel opens when it binds a proton, ion), cation-selective channel (it selectively lets the positive ions through). Like the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors is a functional pentameric oligomer (the channel normally works as an assembly of five subunits). However while its eukaryotic homologues are hetero-oligomeric (assembled from different subunits), all until now known bacteria known to express LICs encode a single monomeric unit, indicating the GLIC to be functionally homo-oligomeric (assembled from identical subunits). The similarity of amino-acid sequence to the eukaryotic LGICs is not localized to any single or particular tertiary domain, indicating the similar function of the GLIC to its eukaryotic equivalents. Regardless, the purpose of regulating the threshold for action potential excitation in the nerve signal transmiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup. They are a major component of biological membranes and can easily be obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soybeans, from which they are mechanically or chemically extracted using hexane. They are also a member of the lecithin group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (lecithin) is a major component of the pulmonary surfactant, and is often used in the lecithin–sphingomyelin ratio to calculate fetal lung maturity. While phosphatidylcholines are found in all plant and animal cells, they are absent in the membranes of most bacteria, including ''Escherichia coli ''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylglycerol
Phosphatidylglycerol is a glycerophospholipid found in pulmonary surfactant and in the plasma membrane where it directly activates lipid-gated ion channels. The general structure of phosphatidylglycerol consists of a L-glycerol 3-phosphate backbone ester-bonded to either saturated or unsaturated fatty acids on carbons 1 and 2. The head group substituent glycerol is bonded through a phosphomonoester. It is the precursor of surfactant and its presence (>0.3) in the amniotic fluid of the newborn indicates fetal lung maturity. Approximately 98% of alveolar wall surface area is due to the presence of type I cells, with type II cells producing pulmonary surfactant covering around 2% of the alveolar walls. Once surfactant is secreted by the type II cells, it must be spread over the remaining type I cellular surface area. Phosphatidylglycerol is thought to be important in spreading of surfactant over the Type I cellular surface area. The major surfactant deficiency in premature infants r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inotropic
An inotrope or inotropic is a drug or any substance that alters the force or energy of muscular contractions. Negatively inotropic agents weaken the force of muscular contractions. Positively inotropic agents increase the strength of muscular contraction. The term ''inotropic state'' is most commonly used in reference to various drugs that affect the strength of contraction of heart muscle. However, it can also refer to pathological conditions. For example, enlarged heart muscle can increase inotropic state, whereas dead heart muscle can decrease it. Medical uses Both positive and negative inotropes are used in the management of various cardiovascular conditions. The choice of agent depends largely on specific pharmacological effects of individual agents with respect to the condition. One of the most important factors affecting inotropic state is the level of calcium in the cytoplasm of the muscle cell. Positive inotropes usually increase this level, while negative inotropes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase D
Phospholipase D (PLD) (EC 3.1.4.4; also known as lipophosphodiesterase II, lecithinase D, choline phosphatase; systematic name: phosphatidylcholine phosphatidohydrolase) is an anesthetic-sensitive and mechanosensitive enzyme of the phospholipase protein superfamily that catalyzes the hydrolysis of membrane phospholipids. The canonical reaction is: :\text + \text_2\text \rightarrow \text + \text Phospholipases occur widely across bacteria, yeast, plants, animals, and viruses. PLD's principal substrate is phosphatidylcholine, which it hydrolyzes to produce the membrane lipid phosphatidic acid (PA) and soluble choline in a cholesterol-dependent process termed substrate presentation. Plants encode numerous PLD isoenzymes, with molecular weights ranging from approximately 90 to 125 kilodalton, kDa. In mammals, six PLD isoenzymes (PLD1–PLD6) are expressed. PLD1 and PLD2 are the best characterized, responsible for classical phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis and PA signaling. Other is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |