|
Lilybaeum Stele
The Lilybaeum stele is a notable Phoenician gravestone stele found in Sicily and first published in 1882. The stele was published in the Corpus Inscriptionum Semiticarum, having been supplied to Renan by Count Francesco Hernandez di Carrera. It measures 0.37 x 0.22 m and is made from white calcareous stone. It was found in Marsala (Roman Lilybaeum), in an area known as ''il Timpone di S. Antonio''. It is currently in the Antonino Salinas Regional Archeological Museum in Palermo. Inscription The inscriptions is known as Kanaanäische und Aramäische Inschriften, KAI 63 and CIS I 138. It is a standard Punic votive inscriptions, Punic votive inscription, dedicated to Baal Hammon by Hanno, son of Adonbaal: Design The stele shows some important Phoenician religious symbols. These symbols include symbols of Tanit (Sign of Tanit) and Baal Hammon (a crescent and a disc), Caduceus, an incense burner and a Priest spreads his right hand up (a position related with the cult of Tanit), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthago Exhibition - Stela With Cultic Scene & Votive Inscription (49340901392)
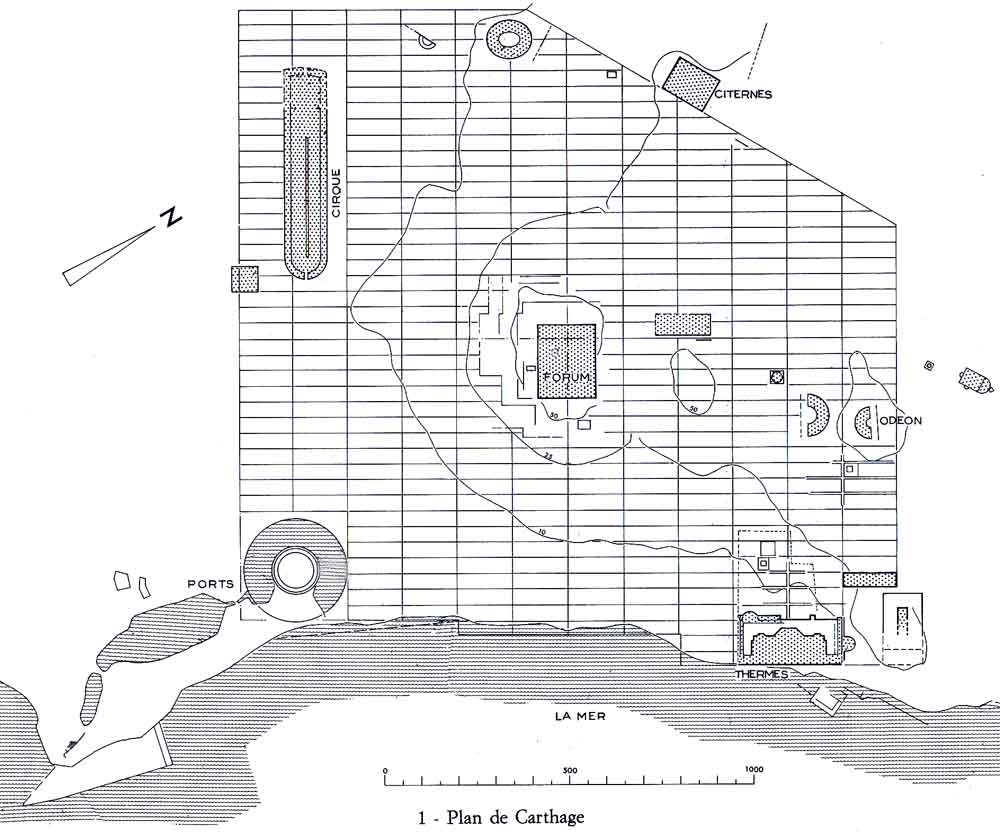
Roman Carthage was an important city in ancient Rome, located in Carthage (municipality), modern-day Tunisia. Approximately 100 years after the destruction of Ancient Carthage, Punic Carthage in 146 BC, a new city of the same name (Latin '':wikt:Carthago#Latin, Carthāgō'') was built on the same land by the Roman Republic, Romans in the period from 49 to 44 BC. By the 3rd century, Carthage had developed into one of the largest cities of the Roman Empire, with a population of several hundred thousand.Likely the fourth city in terms of population during the imperial period, following Rome, Alexandria and Antioch, in the 4th century also surpassed by Constantinople; also of comparable size were Ephesus, Smyrna and Pergamum. Stanley D. Brunn, Maureen Hays-Mitchell, Donald J. Zeigler (eds.), ''Cities of the World: World Regional Urban Development'', Rowman & Littlefield, 2012p. 27/ref> It was the center of the Roman province of Africa Province, Roman Empire, Africa, which was a major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; , ) is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was borne by other heralds like Iris (mythology), Iris, the messenger of Hera. The short staff is entwined by two serpent (mythology), serpents, sometimes surmounted by wings. In Roman iconography, it was depicted being carried in the left hand of Mercury (mythology), Mercury, the messenger of the gods. Some accounts assert that the oldest imagery of the caduceus is rooted in Mesopotamia with the Sumerian god Ningishzida; his symbol, a staff with two snakes intertwined around it, dates back to 4000 BC to 3000 BC. This iconography may have been a representation of two snakes copulating. As a symbol, it represents Hermes (or the Roman Mercury), and by extension trades, occupations, or undertakings associated with the god. In later Classical antiquity, Antiquity, the caduceus provided the basis for the astronomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Steles
Phoenician may refer to: * Phoenicia, an ancient civilization * Phoenician alphabet **Phoenician (Unicode block) * Phoenicianism, a form of Lebanese nationalism * Phoenician language * List of Phoenician cities See also * Phoenix (mythology) * Phoenix (other) * Phoenicia (other) * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Inscriptions
The Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, also known as Northwest Semitic inscriptions, are the primary extra-Biblical source for understanding of the societies and histories of the ancient Phoenicians, Ancient Hebrews, Hebrews and Arameans. Semitic inscriptions may occur on stone slabs, pottery ostraca, ornaments, and range from simple names to full texts. The older inscriptions form a Canaanite languages, Canaanite–Aramaic dialect continuum, exemplified by writings which scholars have struggled to fit into either category, such as the Stele of Zakkur and the Deir Alla Inscription. The Northwest Semitic languages are a language group that contains the Aramaic, Aramaic language, as well as the Canaanite languages including Phoenician language, Phoenician and Hebrew language, Hebrew. Languages The old Aramaic period (850 to 612 BC) saw the production and dispersal of inscriptions due to the rise of the Arameans as a major force in Ancient Near East. Their language was adopted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1882 Archaeological Discoveries
Year 188 (CLXXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in the Roman Empire as the Year of the Consulship of Fuscianus and Silanus (or, less frequently, year 941 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 188 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Publius Helvius Pertinax becomes pro-consul of Africa from 188 to 189. Japan * Queen Himiko (or Shingi Waō) begins her reign in Japan (until 248). Births * April 4 – Caracalla (or Antoninus), Roman emperor (d. 217) * Lu Ji (or Gongji), Chinese official and politician (d. 219) * Sun Shao, Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 241) Deaths * March 17 – Julian, pope and patriarch of Alexandria * Fa Zhen (or Gaoqing), Chinese scholar (b. AD 100) * Lucius Antistius Burrus, Roman politician (executed) * Ma Xiang, Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Chipiez
Charles Chipiez (; 1835–1901) was an influential French architect, Egyptologist, Iranologist, and an avid historian of the ancient world's architecture. He was a teacher at École Spéciale d'Architecture in Paris, France, and helped build the "École Nationale Professionnelle d'Armentières" or the National Professional building of Armentières in 1887. Chipiez with the help of architect, hellenist, and architectural historian Georges Perrot wrote some of the most detailed description of the architectural achievements of the ancient world in such places as Egypt, Greece, Persia, Lydia, Lycia and Assyria. Chipiez would also create some of the most detailed virtual architectural drawings of the ancient monuments that once stood erect, bringing them to life. Some of his prominent works with Perrot include ''History of art in primitive Greece: Mycenian art'' in 1894, ''A history of art in Phoenicia and its dependencies'' in 1885, ''History of art in Persia'' in 1892, A history of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Perrot
Georges Perrot (12 November 1832 – 30 June 1914) was a French archaeologist. He taught at the Sorbonne from 1875 and was director of the École Normale Supérieure from 1888 to 1902. In 1874 he was elected to the Academie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres, where he served as the permanent secretary from 1904 until his death. Dictionary of Art Historians After discovering in 1857 a first fragment of the , his most famous archaeological discovery was made while on an expedition to in 1861, where he found a |
Tel Hazor
Tel Hazor (), translated in LXX as Hasōr (), and in Arabic Tell Waqqas or Tell Qedah el-Gul (), is an archaeological Tell (archaeology), tell at the site of ancient Hazor, located in the Upper Galilee, north of the Sea of Galilee, in the northern Korazim Plateau. From the Middle Bronze Age (around 1750 BCE) to the Iron Age (ninth century BCE), Hazor was the largest fortified city in the region and one of the most important in the Fertile Crescent. It maintained commercial ties with Babylon and Syria, and imported large quantities of tin for the bronze industry. In the Book of Joshua, Hazor is described as "the head of all those kingdoms" () and archaeological excavations that have emphasized the city's importance. The Hazor expedition, headed by Yigael Yadin in the mid-1950s, was the most important dig undertaken by Israel in its early years of statehood. Tel Hazor is the largest archaeological site in northern Israel, featuring an upper tell of 30 acres and a lower city of more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities. Their office or position is the "priesthood", a term which also may apply to such persons collectively. A priest may have the duty to hear confessions periodically, give marriage counseling, provide prenuptial counseling, give spiritual direction, teach catechism, or visit those confined indoors, such as the sick in hospitals and nursing homes. Description According to the trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society, priests have existed since the earliest of times and in the simplest societies, most likely as a result of agricultural surplus#Neolithic, agricultural surplus and consequent social stratification. The necessity to read sacred text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incense Burner
A censer, incense burner, perfume burner or pastille burner is a vessel made for burning incense or perfume in some solid form. They vary greatly in size, form, and material of construction, and have been in use since ancient times throughout the world. They may consist of simple earthenware bowls or fire pots to intricately carved silver or gold vessels, small table top objects a few centimetres tall to as many as several metres high. Many designs use openwork to allow a flow of air. In many cultures, burning incense has spirituality, spiritual and religious connotations, and this influences the design and decoration of the censer. Often, especially in Western contexts, the term "censer" is used for pieces made for religious use, especially those on chains that are swung through the air to spread the incense smoke widely, while the term "perfume burner" is used for objects made for secular use. The original meaning of pastille was a small compressed mixture of aromatic plant m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Of Tanit
__NOTOC__ The sign of Tanit or sign of Tinnit is an anthropomorph symbol of the Punic goddess Tanit, present on many archaeological remains of the Carthaginian civilization. The symbol has many variants, but the basic form consists of a disc on top of a triangle, separated by a horizontal line, like a schematic image of a person. Punic stele containing the sign of Tannit were uncovered in the hundreds in the site of El-Hofra in Cirta (Constantine, Algeria) and are showcased in the Louvre Museum. A coin with the sign and a legend ''phanebalos'', presumably the Greek form of the Phoenician title of the goddess, i.e. ''tnt pn bʿl'', "Tanit ''the face of Baal (Hammon)''", was found in Ashkelon. The first report about the representations of the sign was in the beginning of the 19th century, on stele unearthed on the site of Carthage. Archaeological excavations have subsequently uncovered representations on other supports, such as mosaics or even on ceramics. The excavatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |