|
Lifeboat Ethics
Lifeboat ethics is a metaphor for resource distribution proposed by the ecologist Garrett Hardin in two articles published in 1974, building on his earlier 1968 article detailing "The tragedy of the commons". Hardin's 1974 metaphor describes a lifeboat bearing fifty people with room for ten more. The lifeboat is in an ocean surrounded by a hundred swimmers. The ethics of the situation stem from the dilemma of whether (and under what circumstances) swimmers should be taken aboard the lifeboat. Hardin compared the lifeboat metaphor to the Spaceship Earth model of resource distribution, which he criticizes by asserting that a spaceship would be directed by a single leader which the Earth lacks. Hardin asserts that the spaceship model leads to the ''tragedy of the commons''. In contrast, the lifeboat metaphor presents individual lifeboats as rich nations and the swimmers as poor nations. Development Lifeboat ethics is closely related to issues in environmental ethics, utilitariani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanic Lifeboat
RMS ''Titanic'' was a British ocean liner that Sinking of the Titanic, sank in the early hours of 15 April 1912 as a result of striking Iceberg that struck the Titanic, an iceberg on her maiden voyage from Southampton, England, to New York City, United States. Of the Sinking of the Titanic#Casualties and survivors, estimated 2,224 passengers and crew aboard, approximately 1,500 died (estimates vary), making the incident one of List of accidents and disasters by death toll#Peacetime maritime, the deadliest peacetime sinkings of a single ship. ''Titanic'', operated by White Star Line, carried some of the wealthiest people in the world, as well as hundreds of emigrants from the British Isles, Scandinavia, and elsewhere in Europe who were seeking a new life in the United States and Canada. The disaster drew public attention, spurred major changes in maritime safety regulations, and inspired a Titanic in popular culture, lasting legacy in popular culture. It was the second time Whit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology Today
''Psychology Today'' is an American media organization with a focus on psychology and human behavior. The publication began as a bimonthly magazine, which first appeared in 1967. The print magazine's reported circulation is 275,000 as of 2023. The ''Psychology Today'' website features therapist and health professional directories and hundreds of blogs written by a wide variety of psychologists, psychiatrists, counselors, social workers, medical doctors, marriage and family therapists, anthropologists, sociologists, and science journalists. ''Psychology Today'' is among the oldest media outlets with a focus on behavioral science. Its mission is to cover all aspects of human behavior so as to help people better manage their own health and wellness, adjust their mindset, and manage a range of mental health and relationship concerns. ''Psychology Today'' content and its therapist directory are found in 20 countries worldwide. ''Psychology Today'''s therapist directory is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repugnant Conclusion
The mere addition paradox (also known as the repugnant conclusion) is a problem in ethics identified by Derek Parfit and discussed in his book ''Reasons and Persons'' (1984). The paradox identifies the mutual incompatibility of four intuitively compelling assertions about the relative value of populations. Parfit’s original formulation of the repugnant conclusion is that "For any perfectly equal population with very high positive welfare, there is a population with very low positive welfare which is better, other things being equal." The paradox Parfit considers four populations, as depicted in the following diagram: A, A+, B− and B. Each bar represents a distinct group of people. The bars' width represents group size while the bar's height represents group happiness. Unlike A and B, A+ and B− are complex populations, each comprising two distinct groups of people. It is also stipulated that the lives of the members of each group are good enough that they would rather be ali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratchet Effect
The ratchet effect is a concept in sociology and economics illustrating the difficulty with reversing a course of action once a specific thing has occurred, analogous with the mechanical ratchet (device), ratchet that allows movement in one direction and seizes or tightens in the opposite. The concept has been applied to multiple fields of study and is related to the phenomena of scope creep, mission creep, and feature creep. Background The ratchet effect first came to light in Alan T. Peacock, Alan Peacock and Jack Wiseman (economist), Jack Wiseman's 1961 report "The Growth of Public Expenditure in the United Kingdom." Peacock and Wiseman found that public spending increases like a ratchet following periods of crisis. The term was later expanded upon by American historian Robert Higgs in the 1987 book ''Crisis and Leviathan,'' highlighting Peacock and Wiseman's research as it relates to governments experiencing difficulty in Rollback (legislation), rolling back huge bureaucra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Control
Population control is the practice of artificially maintaining the size of any population. It simply refers to the act of limiting the size of an animal population so that it remains manageable, as opposed to the act of protecting a species from excessive rates of extinction, which is referred to as conservation biology. While many abiotic and biotic factors influence population control, humans are notably influential against animal populations. Whether humans need to hunt animals for food, exterminate a pest, or reduce competition for resources, managing populations involves providing nourishment, or neutering to prevent reproduction, culling individuals or the use of pesticides. Population control plays an important role in wildlife populations. Based on the species being dealt with, there are numerous ways populations of the wild are controlled. Wildlife contraception is the act of preventing reproduction in the wild, which subsequently decreases populations. An example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food For Peace
Since the 1950s, in different administrative and organizational forms, the United States' Food for Peace program has used America's agricultural surpluses to provide food assistance around the world, broaden international trade, and advance U.S. international diplomacy. Approximately 4 billion people in 150 countries have benefited directly from U.S. food assistance."Are Trump and Musk ending a Kansas legacy by shuttering USAID's Food for Peace?," February 2, 2025, '','' retrieved March 2, 2025 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrying Capacity
The carrying capacity of an ecosystem is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available. The carrying capacity is defined as the environment's maximal load, which in population ecology corresponds to the population equilibrium, when the number of deaths in a population equals the number of births (as well as immigration and emigration). Carrying capacity of the environment implies that the resources extraction is not above the rate of regeneration of the resources and the wastes generated are within the assimilating capacity of the environment. The effect of carrying capacity on population dynamics is modelled with a logistic function. Carrying capacity is applied to the maximum population an environment can support in ecology, agriculture and fisheries. The term carrying capacity had been applied to a few different processes in the past before finally being appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balloon Debate
A balloon is a flexible membrane bag that can be inflated with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, or air. For special purposes, balloons can be filled with smoke, liquid water, granular media (e.g. sand, flour or rice), or light sources. Modern day balloons are made from materials such as rubber, latex, polychloroprene, or a nylon fabric, and can come in many different colors. Some early balloons were made of dried animal bladders, such as the pig bladder. Some balloons are used for decorative purposes or entertaining purposes, while others are used for practical purposes such as meteorology, medical treatment, military defense, or transportation. A balloon's properties, including its low density and low cost, have led to a wide range of applications. The rubber balloon was invented by Michael Faraday in 1824, during experiments with various gases. He invented them for use in the lab. Applications Play Decoration Balloons are used for decorating bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
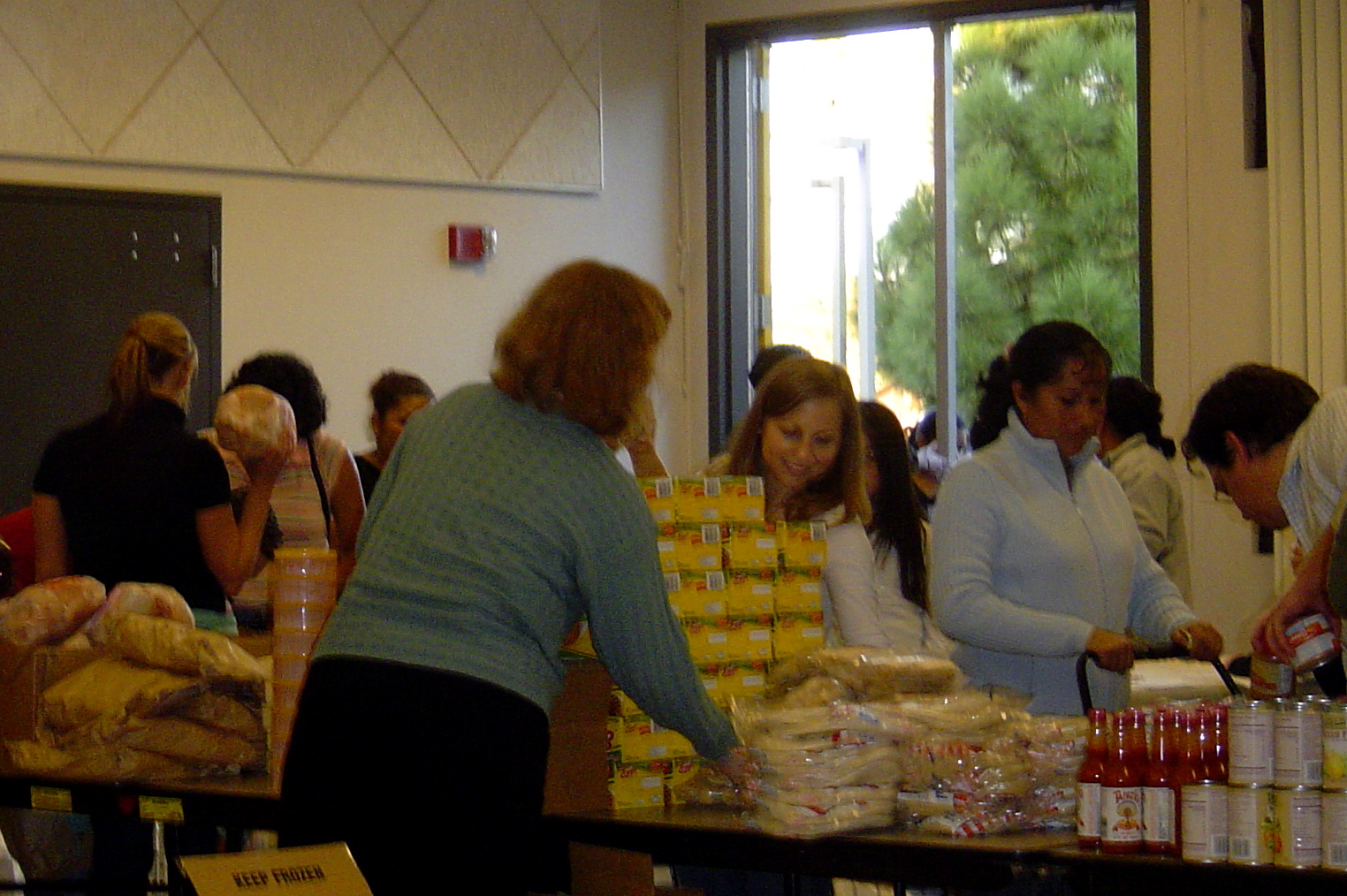
Food Bank
A food bank or food pantry is a non-profit, charitable organization that distributes food to those who have difficulty purchasing enough to avoid hunger, usually through intermediaries like food pantries and soup kitchens. Some food banks distribute food directly with their food pantries. St. Mary's Food Bank Alliance, St. Mary's Food Bank was the world's first food bank, established in the US in 1967. Since then, many thousands have been set up all over the world. In Europe, their numbers grew rapidly after the 2007–2008 world food price crisis, global increase in the price of food which began in late 2006, and especially after the 2008 financial crisis began to worsen economic conditions for those on low incomes. Likewise, the 2020s in economic history, inflation and economic crisis of the 2020s has exponentially driven low and even some middle income class consumers to at least partially get their food. The growth of food banks has been welcomed by commentators who see them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
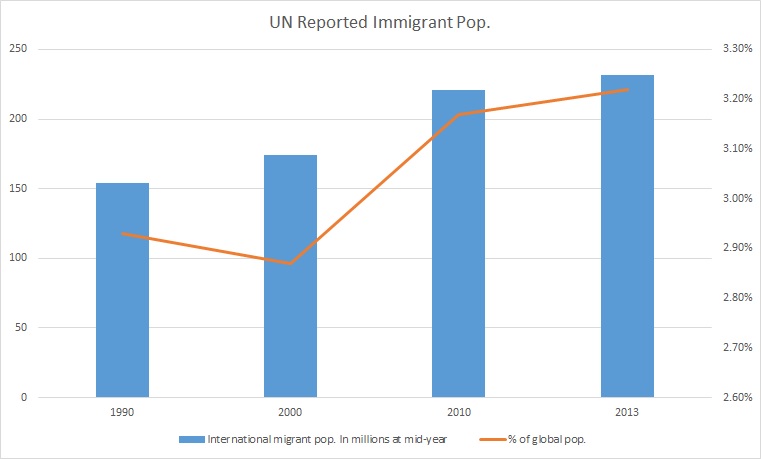
Immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as Permanent residency, permanent residents. Commuting, Commuters, Tourism, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; Seasonal industry, seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however. Economically, research suggests that migration can be beneficial both to the receiving and sending countries. The academic literature provides mixed findings for the relationship between immigration and crime worldwide. Research shows that country of origin matters for speed and depth of immigrant assimilation, but that there is considerable assimilation overall for both first- and second-generation immigrants. Discrimination based on nationality is legal in most countries. Extensive evidence of discrimination against foreign-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Aid
In international relations, aid (also known as international aid, overseas aid, foreign aid, economic aid or foreign assistance) is – from the perspective of governments – a voluntary transfer of resources from one country to another. The type of aid given may be classified according to various factors, including its intended purpose, the terms or conditions (if any) under which it is given, its source, and its level of urgency. For example, aid may be classified based on urgency into emergency aid and development aid. Emergency aid is rapid assistance given to a people in immediate distress by individuals, organizations, or governments to relieve suffering, during and after man-made emergencies (like wars) and natural disasters. Development aid is aid given to support development in general which can be economic development or social development in developing countries. It is distinguished from humanitarian aid as being aimed at alleviating poverty in the long term, rathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Policies
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an organization. Policies can assist in both ''subjective'' and ''objective'' decision making. Policies used in subjective decision-making usually assist senior management with decisions that must be based on the relative merits of a number of factors, and as a result, are often hard to test objectively, e.g. work–life balance policy. Moreover, governments and other institutions have policies in the form of laws, regulations, procedures, administrative actions, incentives and voluntary practices. Frequently, resource allocations mirror policy decisions. Policies intended to assist in objective decision-making are usually operational in nature and can be objectively tested, e.g. a password policy. The term may apply to government, public secto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |