|
Liberty Of Ely Act 1837
The Isle of Ely () is a historic region around the city of Ely in Cambridgeshire, England. Between 1889 and 1965, it formed an administrative county. Etymology Its name has been said to mean "island of eels", a reference to the fish that were often caught in the local rivers for food. This etymology was first recorded by the Venerable Bede. History Until the 17th century, the area was an island surrounded by a large area of fenland, a type of swamp. It was coveted as an area easy to defend, and was controlled in the very early medieval period by the Gyrwas, an Anglo-Saxon tribe. Upon their marriage in 652, Tondbert, a prince of the Gyrwas, presented Æthelthryth (who became St. Æthelthryth), the daughter of King Anna of the East Angles, with the Isle of Ely. She afterwards founded a monastery at Ely, which was destroyed by Viking raiders in 870, but was rebuilt and became a famous Abbey and Shrine. The area's natural defences led to it playing a role in the military hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenland Hall, March
Fenland Hall is a municipal building on County Road, March, Cambridgeshire, England, which serves as the headquarters of Fenland District Council. The building was originally called "County Hall", and was built in 1908–1909 by Isle of Ely County Council to be its meeting place and offices. History Isle of Ely County Council was created in 1889 under the Local Government Act 1888. The Isle of Ely Quarter Sessions, which preceded the county council, had met alternately at Ely and Wisbech. The county council decided instead to hold its meetings in March, being a more central location within the Isle, and with better railway connections. For the first twenty years after its creation the county council met at the Temperance Hall in March, an assembly hall and hotel which had been built in 1885 opposite March railway station (and which was later renamed the Station Hotel). After nearly twenty years of meeting at the Temperance Hall, in which time the council's staff were based in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Of East Anglia
Anna (or Onna; killed 653 or 654) was List of monarchs of East Anglia, king of East Anglia from the early 640s until his death. He was a member of the Wuffingas family, the ruling dynasty of the East Angles, and one of the three sons of Eni of East Anglia, Eni who ruled the kingdom of East Anglia, succeeding some time after Ecgric of East Anglia, Ecgric was killed in battle by Penda of Mercia. Anna was praised by Bede for his devotion to Christianity and was renowned for the saintliness of his family: his son Jurmin and all his daughters – Seaxburh of Ely, Seaxburh, Æthelthryth, Æthelburh of Faremoutiers, Æthelburh and possibly a fourth, Wihtburh – were canon (priest), canonised. Little is known of Anna's life or his reign, as few records have survived from this period. In 631 he may have been at Exning, close to the Devil's Dyke, Cambridgeshire, Devil's Dyke. In 645 Cenwalh of Wessex was driven from his kingdom by Penda and, due to Anna's influence, he was conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
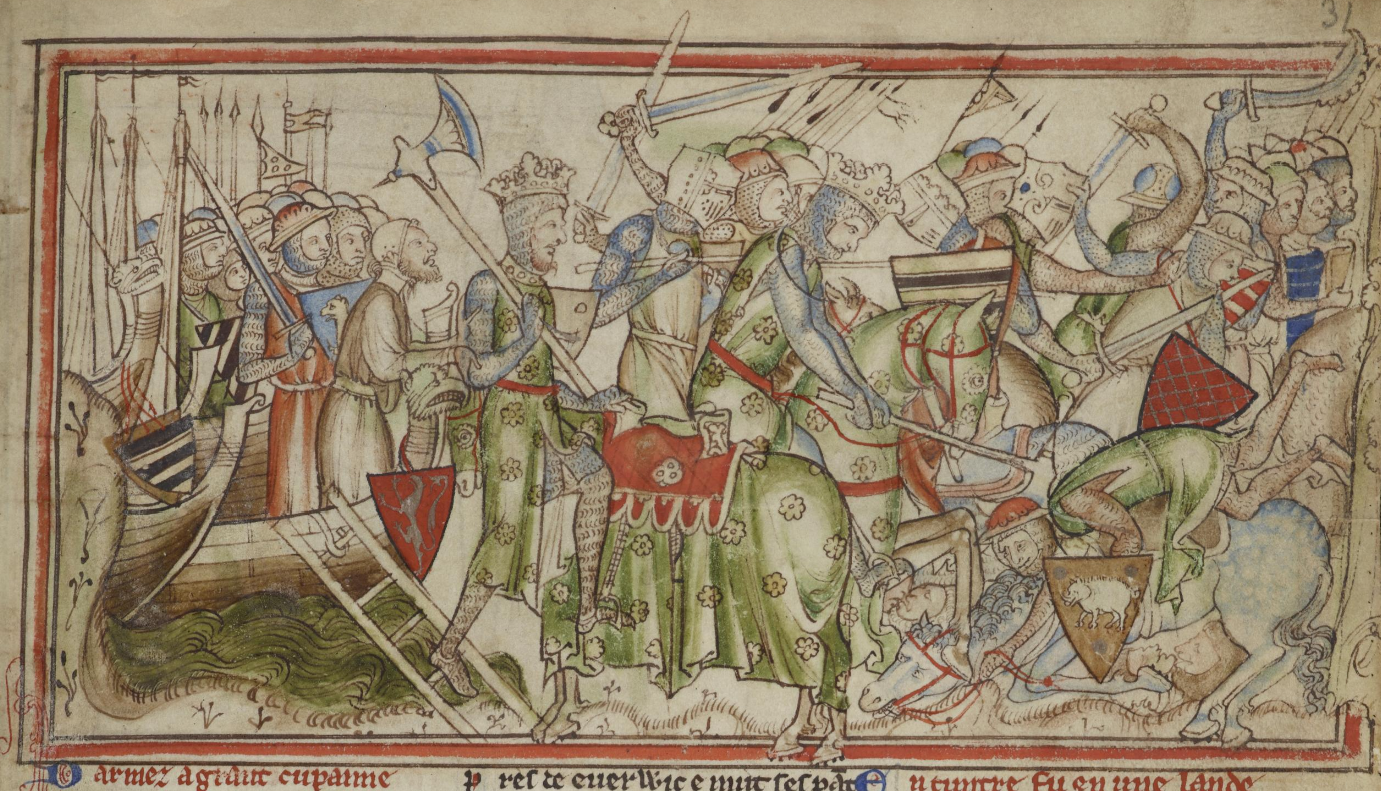
Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda (10 September 1167), also known as Empress Maud, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter and heir of Henry I, king of England and ruler of Normandy, she went to Germany as a child when she was married to the future Holy Roman Emperor Henry V. She travelled with the emperor to Italy in 1116, was controversially crowned empress in St Peter's Basilica, and acted as the imperial regent in Italy. Matilda and Henry V had no children, and when he died in 1125, the imperial crown was claimed by his rival Lothair of Supplinburg. Matilda's younger and only full brother, William Adelin, died in the ''White Ship'' disaster of 1120, leaving Matilda's father and realm facing a potential succession crisis. Upon her widowhood in the Holy Roman Empire, Matilda was recalled to Normandy by her father, who arranged for her to marry Geoffrey of Anjou to form an alliance to protect his southern borders in Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne '' jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England. Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela, daughter of William the Conqueror. His father died as a crusader while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent and Boulogne that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Duchy of Normandy, Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin (the only legitimate son of Henry I of England, Henry I), who drowned in the White Ship disaster, ''White Ship'' disaster of 1120. Henry sought to be succeeded by his daughter, known as Empress Matilda, but was only partially successful in convincing the nobility to support her. On Henry's death in 1135, his nephew Stephen of Blois seized the throne with the help of Stephen's brother Henry of Blois, who was the bishop of Winchester. He was crowned as Stephen, King of England, King Stephen, and his early reign saw fierce fighting with disloyal English barons, rebellious Welsh leaders, and Scottish invaders. Following a major rebellion in the southwest of England, Matilda invaded in 1139 with the help of her half-brother Robert, 1st Earl o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Hickathrift
Tom Hickathrift (or sometimes Jack Hickathrift) is a legendary figure of East Anglian English folklore — a character similar to Jack the Giant Killer. He famously battled a giant, and is sometimes said to be a giant himself, though normally he is just represented as possessing giant-like strength. Life and adventures Various stories of his exploits have grown up. In one version he is fabled to have been a simple labourer at the time of the Norman Conquest and to have killed a giant in the marsh at Tilney, Norfolk armed only with an axle-tree stuck into a cartwheel. When his makeshift weapon broke he grabbed a "lusty rawboned miller" and used him as a weapon instead. This exploit earned him the governorship of Thanet. At the church in Walpole St Peter there is a depression in the ground, where it is said a cannonball landed after he threw it to scare away the devil (in this version Tom is a giant). In the fairy tale as told by Joseph Jacobs, Tom lived in marsh of the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William The Conqueror
William the Conqueror (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), sometimes called William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England (as William I), reigning from 1066 until his death. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy (as William II) from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading a Franco-Norman army to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose. William was the son of the unmarried Duke Robert I of Normandy and his mistress Herleva. His Legitimacy (family law), illegitimate status and youth caused some difficulties for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereward The Wake
Hereward the Wake (Old English pronunciation /ˈhɛ.rɛ.ward/ , modern English pronunciation / ) (also known as Hereward the Outlaw or Hereward the Exile) was an Anglo-Saxon nobleman and a leader of local resistance to the Norman Conquest of England. His base when he led the rebellion against the Norman rulers was the Isle of Ely, in eastern England. According to legend, he roamed the Fens, which covers parts of the modern counties of Cambridgeshire, Lincolnshire and Norfolk, and led popular opposition to William the Conqueror. Primary sources Several primary sources exist for Hereward's life, but the accuracy of their information is difficult to evaluate. They are the version of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' written at Peterborough Abbey (the "E manuscript" or ''Peterborough Chronicle''), the Domesday Book of 1086, the ''Liber Eliensis'' (Latin 'Book of Ely') and, by far the most detailed, the ''Gesta Herewardi''. The texts are sometimes contradictory. For example, ''Gesta'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelwine (Bishop Of Durham)
Æthelwine, also Aethelwine or Ethelwine is an Anglo-Saxon given name meaning "noble friend". Its Old High German equivalent is Adalwin. *Æthelwine of Abingdon (died 1030), abbot of Abingdon *Æthelwine (Bishop of Durham) (died 1071), bishop of Durham *Æthelwine of Lindsey, bishop of Lindsey *Æthelwine of Athelney, Anglo Saxon Saint *Æthelwine of Wells, bishop of Wells * Æthelwine of Sceldeforde Anglo Saxon Saint *Æthelwine, Ealdorman of East Anglia (died 992), son of Æthelstan Half-King *Æthelwine, a son of Æthelweard (son of Alfred), who died in the Battle of Brunanburh (937) *Adalwin (died 816), bishop of Regensburg *Adalwin (died 873), bishop of Salzburg See also *Edwin *Alwin *Alvin (other) {{given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morcar
Morcar (or Morcere) (, ) (died after 1087) was the son of Ælfgār (earl of Mercia) and brother of Ēadwine. He was the earl of Northumbria from 1065 to 1066, when William the Conqueror replaced him with Copsi. Dispute with the Godwins Morcar and his brother Ēadwine, now Earl of Mercia, assisted the Northumbrian rebels to expel Tostig Godwinson. In October 1065 the Northumbrians chose Morcar as earl at York. He at once satisfied the people of the Bernicia by making over the government of the country beyond the River Tyne to Osulf of Bamburgh, the eldest son of Eadwulf IV of Bamburgh, the Bernician earl whom Siward had slain in 1041. Marching southwards with the rebels, Morcar gathered into his forces the men of Nottingham, Derby, and Lincoln, members of the old Danish confederacy of towns, and met Ēadwine, who was at the head of a considerable force at Northampton. There the brothers and their rebel army considered proposals for peace offered to them by Earl Harold G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ely Rebellion
The Ely Rebellion was a rebellion in 1069 or 1070 against the Norman occupation of England, named after the Isle of Ely. It is considered one of the earliest English civil wars. Rebellion The Danish king Sweyn Estrithson sent a small army to try to establish a camp on the Isle of Ely. Hereward the Wake stormed and sacked Peterborough Abbey in company with local men and Sweyn's Danes. While the '' Gesta Herewardi'' says this was after the main battle at Ely, the Peterborough Chronicle says it was before. The historical consensus is that the Chronicle's account is most accurate. His justification is said to have been that he wished to save the Abbey's treasures and relics from the rapacious Normans led by the new Norman abbot who had ousted his uncle Brand. According to the ''Gesta'' he returned the treasures looted from the abbey after having a vision of Saint Peter.Hugh M Thomas, "The Gesta Herewardi, the English and their Conquerors", ''Anglo-Norman Studies 21: Proceedings of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |