|
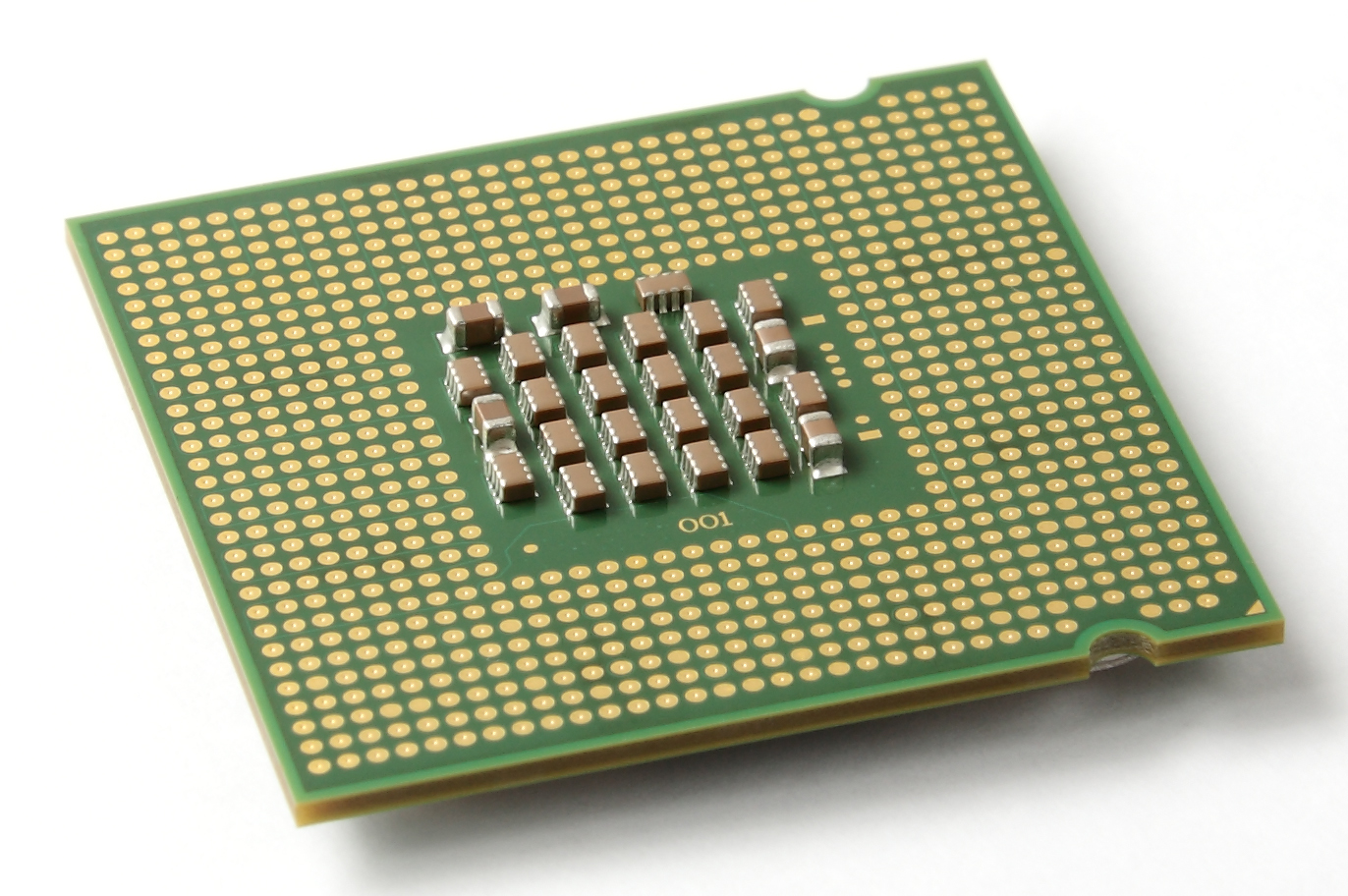
LGA 775
LGA 775 ( land grid array 775), also known as Socket T, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. Unlike PGA CPU sockets, such as its predecessor Socket 478, LGA 775 has no socket holes; instead, it has 775 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor (CPU). Intel started selling LGA 775 (Socket T) CPUs with the 64-bit version of their 90 nm "Prescott"-based Pentium 4 HT. The socket had an unusually long life span, lasting 7 years until the last processors supporting it ceased production in 2011. The socket was superseded by the LGA 1156 (Socket H) and LGA 1366 (Socket B) sockets. LGA 775 processors (Note: Some of the processors listed here might not work on newer Intel based chipsets; see "LGA 775 compatibility" below.) * Pentium 4 * Pentium 4 Extreme Edition * Pentium D * Celeron/ Celeron D * Pentium Dual-Core * Pentium Extreme Edition * Core 2 Duo/ Core 2 Quad * Core 2 Extreme Heatsink design For LGA 775, the distance between the screw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 775 Socket T
LaGuardia Airport ( ) – colloquially known as LaGuardia or simply LGA – is a civil airport in East Elmhurst, Queens, New York City, situated on the northwestern shore of Long Island, bordering Flushing Bay. Covering , the facility was established in 1929, and began operating as a public airport in 1939. It is named after Fiorello H. La Guardia, a former mayor of New York City. The airport accommodates airline service primarily to domestic, but also to limited international destinations. , it was the third-busiest airport in the New York metropolitan area behind Kennedy and Newark airports, and the 19th-busiest in the United States by passenger volume. The airport is located directly to the north of the Grand Central Parkway, the airport's primary access highway. While the airport is a hub for both American Airlines and Delta Air Lines, commercial service is strictly governed by unique regulations including a curfew, a slot system, and a "perimeter rule" prohibiting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Grid Array
The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket (when a socket is used) — as opposed to pins on the integrated circuit, known as a '' pin grid array'' (PGA). An LGA can be electrically connected to a printed circuit board (PCB) either by the use of a socket or by soldering directly to the board. Description The ''land grid array'' is a packaging technology with a grid of contacts, 'lands', on the underside of a package. The contacts are to be connected to a grid of contacts on the PCB. Not all rows and columns of the grid need to be used. The contacts can either be connected by using an LGA socket, or by surface-mount soldering using solder paste. The grid elements found in use can be e.g. circular, triangular or other polygonal shapes and might have even different sizes. Grids might sometimes appear like honey comb patterns. Designs are often optimized for factors like contact likelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1151
LGA 1151, also known as Socket H4, is a type of zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket for Intel desktop processors which comes in two distinct versions: the first revision which supports both Intel's Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs, and the second revision which supports Coffee Lake CPUs exclusively. LGA 1151 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1150 (known as ''Socket H3''). LGA 1151 has 1151 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator, i.e. a voltage regulator which integrated on the CPU's die, introduced with Haswell and Broadwell, has again been moved to the motherboard. Most motherboards for the first revision of the socket support solely DDR4 memory, a lesser number support DDR3(L) memory, and the least number have slots for both DDR4 or DDR3(L) but only one memory type can be installed. Some have UniDIMM support, enabling either type of memory to be placed in the same DIMM, rather than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
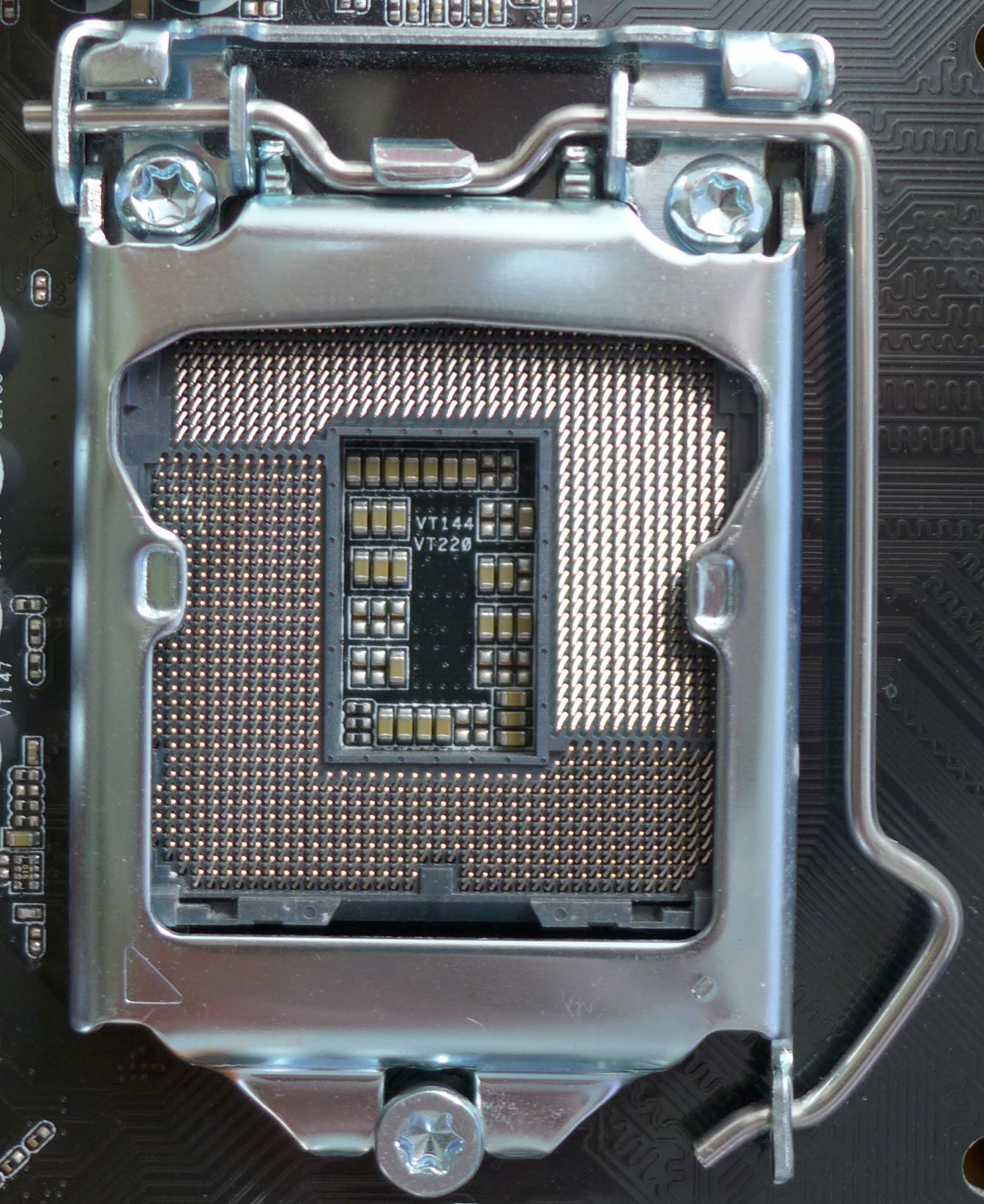
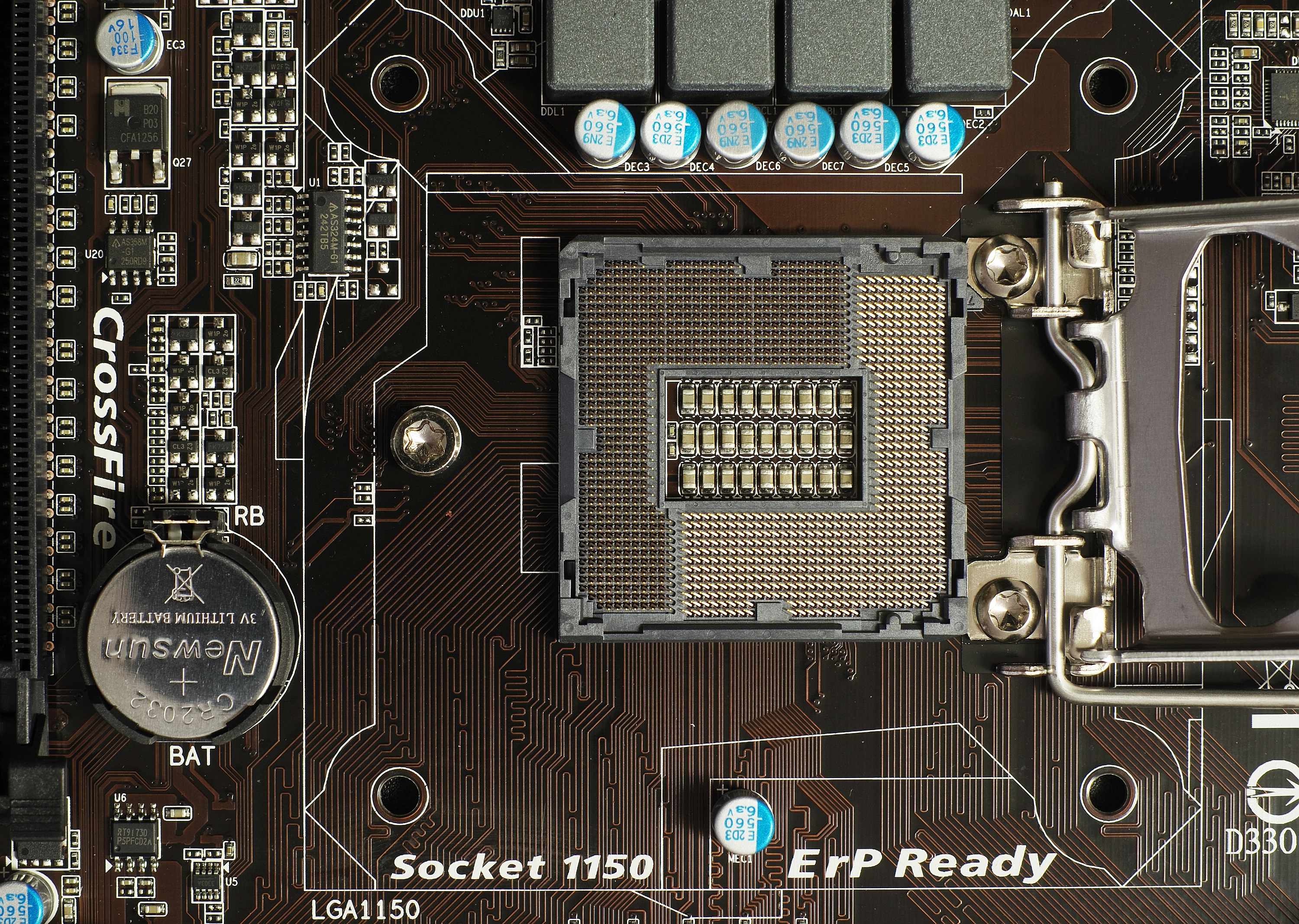
LGA 1150
LGA 1150, also known as Socket H3, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for CPUs built on the Haswell microarchitecture. This socket is also used by the Haswell's successor, Broadwell microarchitecture. It is the successor of LGA 1155 and was itself succeeded by LGA 1151 in 2015. Most motherboards with the LGA 1150 socket support varying video outputs (VGA, DVI or HDMI depending on the model) and Intel Clear Video Technology. Full support of Windows on LGA 1150 platform starts on Windows 7. Official Windows XP support is limited to selected CPUs, chipsets and only for embedded and industrial systems. Intel's Platform Controller Hub (PCH) for the LGA 1150 CPUs is codenamed Lynx Point. Intel Xeon processors for socket LGA 1150 use the Intel C222, C224, and C226 chipsets. Heatsink The 4 holes for fastening the heatsink to the motherboard are placed in a square with a lateral length of 75 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 1155
LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is a zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) CPU socket designed by Intel for their CPUs based on the Sandy Bridge (second generation core) and Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (third generation) microarchitectures. Introduced in 2011, it is the successor of LGA 1156 (known as ''Socket H'') and was itself succeeded by LGA 1150 in 2013. Along with selected variations of LGA 2011 socket, it was the last Intel socket to fully support Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008. LGA 1155 has 1155 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The pins are arranged in a 40×40 array with a 24×16 central void and additional 61 omitted pins (two adjoining the central void, six in each of the four corners, and 35 in groups around the perimeter), yielding the 1600 − 384 − 61 = 1155 pin count. Processors for LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets are not compati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
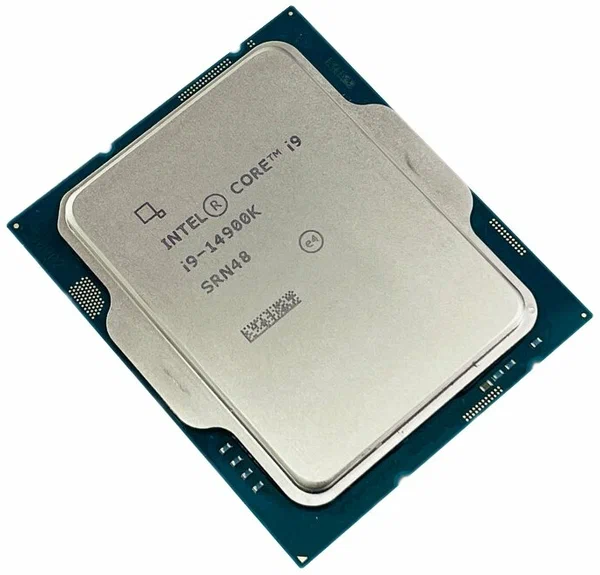
Core 2 Extreme
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors displaced the existing mid- to high-end Pentium processors at the time of their introduction, moving the Pentium to the entry level. Identical or more capable versions of Core processors are also sold as Xeon processors for the server and workstation markets. Core was launched in January 2006 as a mobile-only series, consisting of single- and dual-core models. It was then succeeded later in July by the Core 2 series, which included both desktop and mobile processors with up to four cores, and introduced 64-bit support. Since 2008, Intel began introducing the Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 and Core i9 lineup of processors, succeeding Core 2. A new naming scheme debuted in 2023, consisting of Core 3, Core 5, and Core 7 for mainstream processors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core 2 Duo
Intel Core is a line of multi-core (with the exception of Core Solo and Core 2 Solo) central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors displaced the existing mid- to high-end Pentium processors at the time of their introduction, moving the Pentium to the entry level. Identical or more capable versions of Core processors are also sold as Xeon processors for the server and workstation markets. Core was launched in January 2006 as a mobile-only series, consisting of single- and dual-core models. It was then succeeded later in July by the Core 2 series, which included both desktop and mobile processors with up to four cores, and introduced 64-bit support. Since 2008, Intel began introducing the Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 and Core i9 lineup of processors, succeeding Core 2. A new naming scheme debuted in 2023, consisting of Core 3, Core 5, and Core 7 for mainstream processo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium Extreme Edition
Pentium D is a range of desktop 64-bit x86-64 processors based on the NetBurst microarchitecture, which is the dual-core variant of the Pentium 4 manufactured by Intel. Each CPU comprised two cores. The brand's first processor, codenamed Smithfield and manufactured on the 90 nm process, was released on May 25, 2005, followed by the 65 nm Presler nine months later. The core implementation on the 90 nm Smithfield and later 65 nm Presler are designed differently but are functionally the same. The 90 nm Smithfield contains a single die, with two adjoined but functionally separate CPU cores cut from the same wafer. The later 65 nm Presler utilized a multi-chip module package, where two discrete dies each containing a single core reside on the CPU substrate. Neither the 90 nm Smithfield nor the 65 nm Presler were capable of direct core to core communication, relying instead on the northbridge link to send information between the two cores. By 2004, the NetBurst processors reached a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celeron D
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessors targeted at low-cost personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023. The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, 1998, and was based on the Pentium II. Celeron-branded processors released from 2009 to 2023 are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed compared to flagship Intel CPU lines, such as the Pentium or Core brands. They often have less cache or intentionally disabled advanced features, with variable impact on performance. While some Celeron designs have achieved strong performance for their segment, the majority of the Celeron line has exhibited noticeably degraded performance. This has been the primary justification for the higher cost of other Intel CPU brands versus the Celeron range. In September 2022, Intel announced that the Celeron brand, along with Pentium, were to be replaced with the new "Intel Processor" branding for lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium 4 Extreme Edition
Pentium 4 is a series of single-core CPUs for desktops, laptops and entry-level servers manufactured by Intel. The processors were shipped from November 20, 2000 until August 8, 2008. All Pentium 4 CPUs are based on the NetBurst microarchitecture, the successor to the P6. The Pentium 4 Willamette (180 nm) introduced SSE2, while the Prescott (90 nm) introduced SSE3 and later 64-bit technology. Later versions introduced Hyper-Threading Technology (HTT). The first Pentium 4-branded processor to implement 64-bit was the Prescott (90 nm) (February 2004), but this feature was not enabled. Intel subsequently began selling 64-bit Pentium 4s using the ''"E0" revision'' of the Prescotts, being sold on the OEM market as the Pentium 4, model F. The E0 revision also adds eXecute Disable (XD) (Intel's name for the NX bit) to Intel 64. Intel's official launch of Intel 64 (under the name EM64T at that time) in mainstream desktop processors was the N0 stepping Presc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |