|
Leukemia Foundation Of Australia
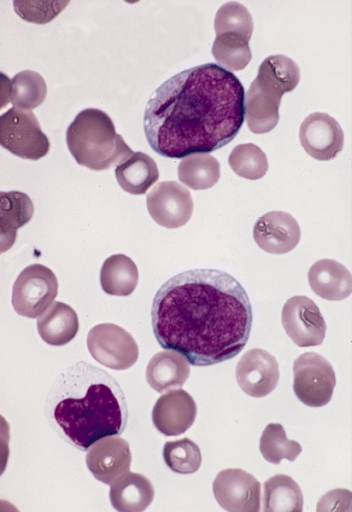
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ''leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia—acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myeloid leukem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright's Stain
Wright's stain is a hematologic stain that facilitates the differentiation of blood cell types. It is classically a mixture of eosin (red) and methylene blue dyes. It is used primarily to stain peripheral blood smears, urine samples, and bone marrow needle aspiration biopsy, aspirates, which are examined under a light microscope. In cytogenetics, it is used to stain chromosomes to facilitate diagnosis of syndromes and diseases. It is named for James Homer Wright, who devised the stain, a modification of the Romanowsky stain, in 1902. Because it distinguishes easily between blood cells, it became widely used for performing differential white blood cell counts, which are routinely ordered when conditions such as infection or leukemia are suspected. The related stains are known as the buffered Wright stain, the Wright-Giemsa stain (a combination of Wright and Giemsa stain, Giemsa stains), and the buffered Wright-Giemsa stain, and specific instructions depend on the solutions being us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle accelerator. Radiation therapy may be cure, curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body, and have not metastasis, spread to other parts. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the canc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics. Overview In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype. The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of the organism's genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholesterol test, are often grouped together into one test panel called a blood panel or blood work. Blood tests are often used in health care to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, pharmaceutical drug effectiveness, and organ function. Typical medicine#Clinical practice, clinical blood panels include a basic metabolic panel or a complete blood count. Blood tests are also used in drug tests to detect drug abuse. Extraction A venipuncture is useful as it is a Invasiveness of surgical procedures, minimally invasive way to obtain cell (biology), cells and extracellular fluid (blood plasma, plasma) from the body for analysis. Blood flows throughout the body, acting as a medium that prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point in the hypothalamus. There is no single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature: sources use values ranging between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle tone, muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes Flushing (physiology), flushed, and may begin to Perspiration, sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral infection, viral, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Pain
Bone pain (also known medically by several other names) is pain coming from a bone, and is caused by damaging stimuli. It occurs as a result of a wide range of diseases or physical conditions or both, and may severely impair the quality of life.Luger, N. Mach, D. Sevcik, M. Mantyh, P. (2005). Bone cancer pain: From mechanism to model to therapy. ''Journal of Pain and Symptom Management''. 29(5): 32-46. Bone pain belongs to the class of deep somatic pain, often experienced as a dull pain that cannot be localized accurately by the patient. This is in contrast with the pain which is mediated by superficial receptors in, e.g., the skin. Bone pain can have several possible causes ranging from extensive physical stress to serious diseases such as cancer.Zwas, T. Elkanovitch, R. George, F. (1987). Interpretation and Classification of Bone Scintigraphic Findings in Stress Fractures. ''Journal of Nuclear Medicine''. 28: 452-457.Mantyh, P. Clohisy, D. Koltzenburg, M. Hunt, S. (2002). Mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precursor Cell
In cell biology, precursor cells—also called blast cells—are partially differentiated, or intermediate, and are sometimes referred to as progenitor cells. A precursor cell is a stem cell with the capacity to differentiate into only one cell type, meaning they are unipotent stem cells. In embryology, precursor cells are a group of cells that later differentiate into one organ. However, progenitor cells are considered multipotent. Due to their contribution to the development of various organs and cancers, precursor and progenitor cells have many potential uses in medicine. There is ongoing research on using these cells to build heart valves, blood vessels, and other tissues by using blood and muscle precursor cells. Cytological types * Oligodendrocyte precursor cell * Myeloblast * Thymocyte * Meiocyte * Megakaryoblast * Promegakaryocyte * Melanoblast * Lymphoblast * Bone marrow precursor cells * Normoblast * Angioblast ( endothelial precursor cells) * Myeloid precursor cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Cell
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Together, these three kinds of blood cells add up to a total 45% of the blood tissue by volume, with the remaining 55% of the volume composed of plasma, the liquid component of blood. Red blood cells Red blood cells or ''erythrocytes'' primarily carry oxygen and collect carbon dioxide through the use of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that gives red blood cells their color and facilitates transportation of oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs to be exhaled. Red blood cells are the most abundant cell in the blood, accounting for about 40–45% of its volume. Red blood cells are circular, biconcave, disk-shaped and deformable to allow them to sque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
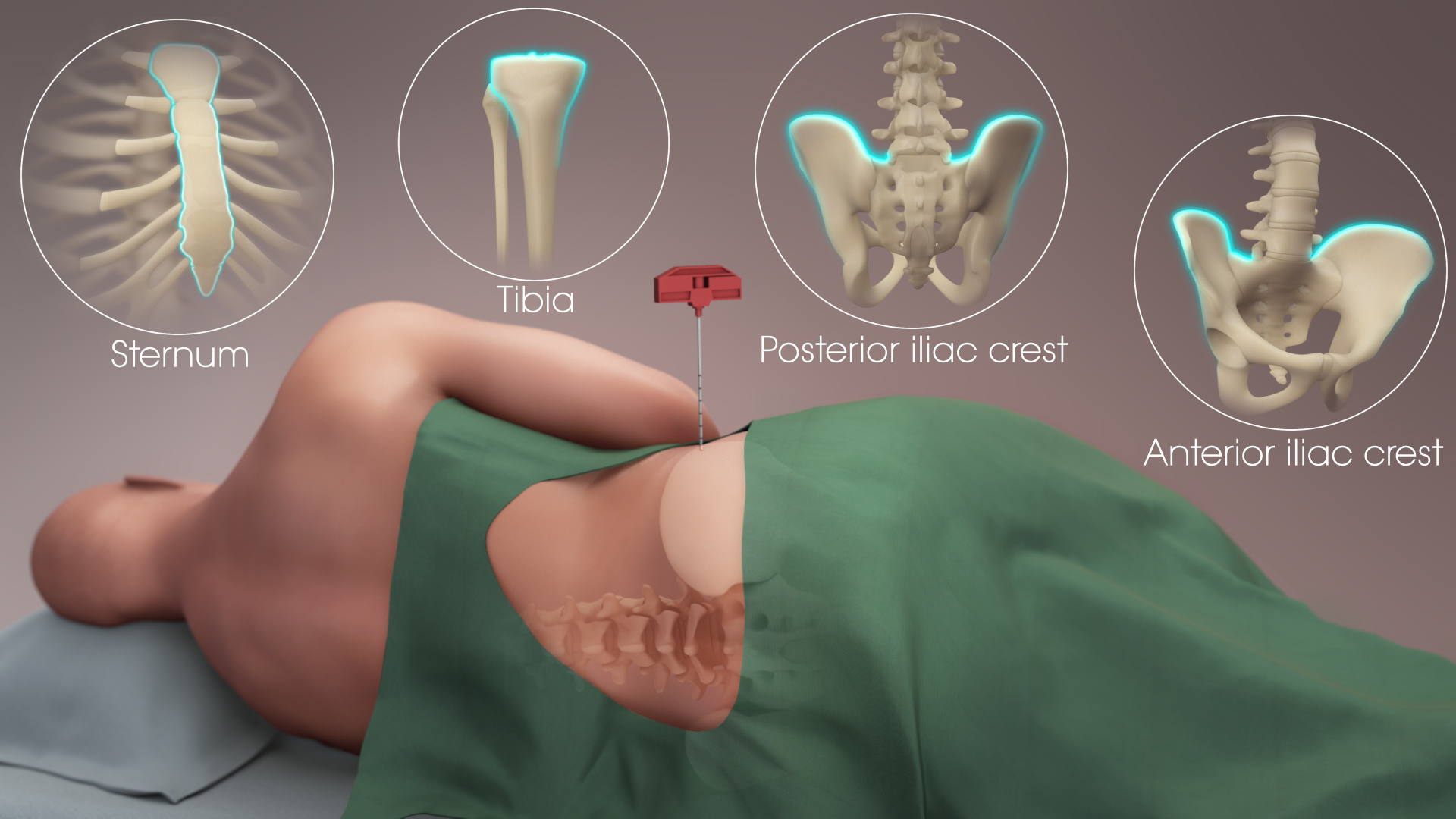
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Cancer
Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (American English) or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (British English) are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are all intimately connected through both the circulatory system and the immune system, a disease affecting one will often affect the others as well, making aplasia, myeloproliferation and lymphoproliferation (and thus the leukemias, myelomas, and the lymphomas) closely related and often overlapping problems. While uncommon in solid tumors, chromosomal translocations are a common cause of these diseases. This commonly leads to a different approach in diagnosis and treatment of hematological malignancies. Hematological malignancies are malignant neoplasms ("cancer"), and they are generally treated by specialists in hematology and/or oncology. In some centers "hematology/oncology" is a single subspecialty of internal medicine while in others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American And British English Spelling Differences
Despite the various list of dialects of English, English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of Comparison of American and British English, the differences between American English, American and British English, British or English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States. A "British standard" began to emerge following the 1755 publication of Samuel Johnson's ''A Dictionary of the English Language'', and an "American standard" started following the work of Noah Webster and, in particular, his ''Webster's Dictionary, An American Dictionary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five-year Survival Rate
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year survival rate. There are absolute and relative survival rates, but the latter are more useful and commonly used. __TOC__ Relative and absolute rates Five-year relative survival rates are more commonly cited in cancer statistics. Five-year absolute survival rates may sometimes also be cited. * Five-year ''absolute'' survival rates describe the percentage of patients alive five years after the disease is diagnosed. * Five-year ''relative'' survival rates describe the percentage of patients with a disease alive five years after the disease is diagnosed, divided by the percentage of the general population of corresponding sex and age alive after five years. Typically, cancer five-year relative survival rates are well below 100%, reflecting exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |