|
Leicester Abbey
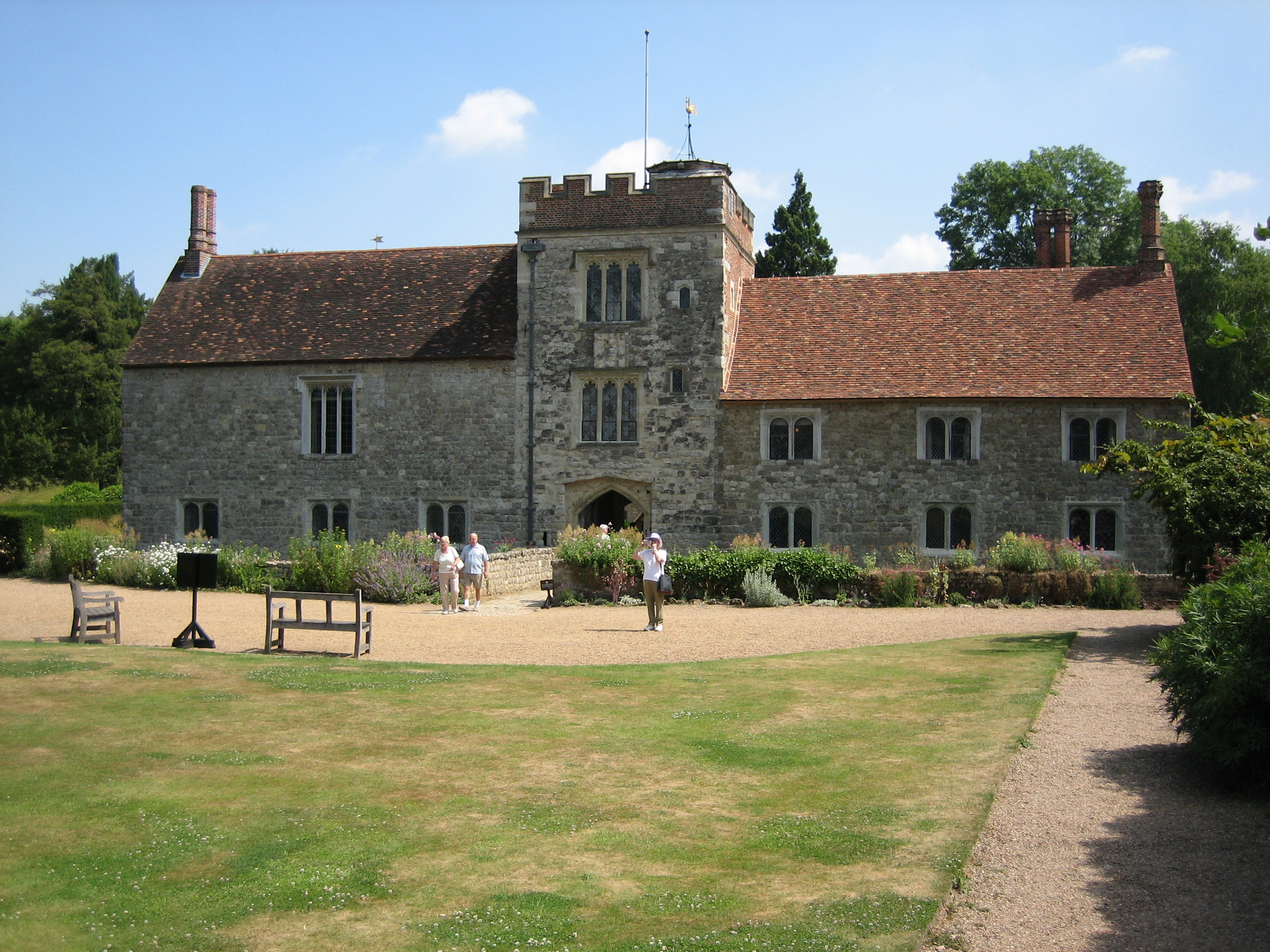
The Abbey of Saint Mary de Pratis, more commonly known as Leicester Abbey, was an Augustinian religious house in the city of Leicester, in the East Midlands of England. The abbey was founded in the 12th century by the Robert de Beaumont, 2nd Earl of Leicester, and grew to become the wealthiest religious establishment within Leicestershire. Through patronage and donations the abbey gained the advowsons of countless churches throughout England, and acquired a considerable amount of land, and several manorial lordships. Leicester Abbey also maintained a cell (a small dependent daughter house) at Cockerham Priory, in Lancashire. The Abbey's prosperity was boosted through the passage of special privileges by both the English Kings and the Pope. These included an exemption from sending representatives to parliament and from paying tithe on certain land and livestock. Despite its privileges and sizeable landed estates, from the late 14th century the abbey began to suffer financiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustinian Canons
The Canons Regular of St. Augustine are Catholic priests who live in community under a rule ( and κανών, ''kanon'', in Greek) and are generally organised into religious orders, differing from both secular canons and other forms of religious life, such as clerics regular, designated by a partly similar terminology. As religious communities, they have laybrothers as part of the community. At times, their Orders have been very popular: in England in the 12th century, there were more houses of canons (often referred to as an abbey or canonry) than monasteries of monks. Preliminary distinctions All canons regular are to be distinguished from secular canons who belong to a resident group of priests but who do not take public vows and are not governed in whatever elements of life they lead in common by a historical rule. One obvious place where such groups of priests are required is at a cathedral, where there were many Masses to celebrate and the Divine Office to be pray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Derbyshire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire (except for North Lincolnshire and North East Lincolnshire), Northamptonshire, Nottinghamshire, and Rutland. The region has a land area of , with an estimated population in . With a Global city#GaWC World Cities, sufficiency-level world city ranking, Nottingham is the only settlement in the region to be classified by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. The main cities in the region are Derby, England, Derby, Leicester, Lincoln, England, Lincoln and Nottingham. The largest towns in these counties are Boston, England, Boston, Chesterfield, Derbyshire, Chesterfield, Coalville, Leicestershire, Coalville, Corby, Glossop, Grantham, Kettering, Loughborough, Newark-on-Trent, Northampton, Mansfield, England, Mansfield, Oakham, Swadlincote and Wellingborough. Physical feature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Habit
A religious habit is a distinctive set of clothing worn by members of a religious order. Traditionally, some plain garb recognizable as a religious habit has also been worn by those leading the religious Hermit, eremitic and Anchorite, anchoritic life, although in their case without conformity to a particular uniform style. Uniformity and distinctiveness by order often evolved and changed over time. Interpretation of terms for clothes in religious rules could change over centuries. Furthermore, every time new communities gained importance in a cultural area the need for visual separation increased for new as well as old communities. Thus, modern habits are rooted in historic forms, but do not necessarily resemble them in cut, color, material, detail or use. In Christian monasticism, Christian monastic orders of the Catholic church, Catholic, Lutheranism, Lutheran and Anglicanism, Anglican Churches, the habit often consists of a tunic covered by a scapular and cowl, with a hood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canons Regular
The Canons Regular of St. Augustine are Catholic priests who live in community under a rule ( and κανών, ''kanon'', in Greek) and are generally organised into Religious order (Catholic), religious orders, differing from both Secular clergy, secular canons and other forms of religious life, such as clerics regular, designated by a partly similar terminology. As religious communities, they have laybrothers as part of the community. At times, their Orders have been very popular: in England in the 12th century, there were more houses of canons (often referred to as an abbey or canonry) than monasteries of monks. Preliminary distinctions All canons regular are to be distinguished from canon (priest), secular canons who belong to a resident group of priests but who do not take religious vows, public vows and are not governed in whatever elements of life they lead in common by a historical rule. One obvious place where such groups of priests are required is at a cathedral, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the head of an independent monastery for men in various Western Christian traditions. The name is derived from ''abba'', the Aramaic form of the Hebrew ''ab'', and means "father". The female equivalent is abbess. Origins The title had its origin in the monasteries of Egypt and Syria, spread through the eastern Mediterranean, and soon became accepted generally in all languages as the designation of the head of a monastery. The word is derived from the Aramaic ' meaning "father" or ', meaning "my father" (it still has this meaning in contemporary Arabic: أب, Hebrew: אבא and Aramaic: ܐܒܐ) In the Septuagint, it was written as "abbas". At first it was employed as a respectful title for any monk, but it was soon restricted by canon law to certain priestly superiors. At times it was applied to various priests, e.g. at the court of the Frankish monarchy the ' ("of the palace"') and ' ("of the camp") were chaplains to the Merovingian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Modern tithes are normally voluntary and paid in money, cash, cheques or via online giving, whereas historically tithes were required and paid in kind, such as agricultural produce. Church tax linked to the tax system are used in many countries to support their national church. Donations to the church beyond what is owed in the tithe, or by those attending a congregation who are not members or adherents, are known as offering (Christianity), offerings, and often are designated for specific purposes such as a building program, debt retirement, or mission work. Many Christian denominations hold Jesus in Christianity, Jesus taught that tithing must be done in conjunction with a deep concern for "justice, mercy and faithfulness" (cf. Matthew 23:23). Tithing was taught at early Christian Church Council, church counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the pope was the sovereign or head of state of the Papal States, and since 1929 of the much smaller Vatican City state. From a Catholic viewpoint, the primacy of the bishop of Rome is largely derived from his role as the apostolic successor to Saint Peter, to whom Petrine primacy, primacy was conferred by Jesus, who gave Peter the Keys of Heaven and the powers of "binding and loosing", naming him as the "rock" upon which the Church would be built. The current pope is Leo XIV, who was elected on 8 May 2025 on the second day of the 2025 papal conclave. Although his office is called the papacy, the ecclesiastical jurisdiction, jurisdiction of the episcopal see is called the Holy See. The word "see" comes from the Latin for 'seat' or 'chair' (, refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of England
This list of kings and reigning queens of the Kingdom of England begins with Alfred the Great, who initially ruled Wessex, one of the heptarchy, seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms which later made up modern England. Alfred styled himself king of the Anglo-Saxons from about 886, and while he was not the first king to claim to rule all of the English people, English, his rule represents the start of the first unbroken line of kings to rule the whole of England, the House of Wessex. Arguments are made for a few different kings thought to have controlled enough Anglo-Saxon kingdoms to be deemed the first king of England. For example, Offa of Mercia and Egbert of Wessex are sometimes described as kings of England by popular writers, but it is no longer the majority view of historians that their wide dominions were part of a process leading to a unified England. The historian Simon Keynes states, for example, "Offa was driven by a lust for power, not a vision of English unity; and what he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated ''Lancs'') is a ceremonial county in North West England. It is bordered by Cumbria to the north, North Yorkshire and West Yorkshire to the east, Greater Manchester and Merseyside to the south, and the Irish Sea to the west. The largest settlement is Preston, Lancashire, Preston, and the county town is the city of Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster. The county has an area of and a population of 1,490,300. Preston is located near the centre of the county, which is urbanised and includes the towns of Blackburn and Burnley; the seaside resort of Blackpool lies to the west, and Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster is in the north. For Local government in England, local government purposes the county comprises a non-metropolitan county, with twelve districts, and two Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas: Blackburn with Darwen and Borough of Blackpool, Blackpool. Lancashire County Council and the two unitary councils collaborate through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockerham Priory
Cockerham Priory was a priory served by Austin Canons in Cockerham, Lancashire, England. St Michael's Church was granted to Leicester Abbey c. 1153–54, with some land.Pastscape Accessed 2014-06-03 The priory was founded in 1207 or 1208 as a cell of the Abbey of St Mary de Pratis ("St Mary in the Meadows") in Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest city in the East Midlands with a popula ... . ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastic Cell
A cell is a small room used by a hermit, monk, nun or anchorite to live and as a devotional space. Cells are often part of larger cenobitic monastic communities such as Catholic, Lutheran, Anglican and Orthodox Christian monasteries, as well as Buddhist vihara, but may also form stand-alone structures in remote locations. The word ''cell'' comes from the Old French ''celle'' meaning a monastic cell, itself from the Latin meaning "room", "store room" or "chamber". Usually, a cell is small and contains a minimum of furnishings. It may be an individual living space in a building or a hermit's primitive solitary living space, possibly a cave or hut in a remote location. A small dependent or daughter house of a major monastery, sometimes housing just one or two monks or nuns, may also be termed a cell. The first cells were in the Nitrian Desert in Egypt following the ministry of Paul of Thebes, Serapion, and Anthony the Great. in the mid 3rd century. In some orders, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Of The Manor
Lord of the manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England and Norman England, referred to the landholder of a historical rural estate. The titles date to the English Feudalism, feudal (specifically English feudal barony, baronial) system. The lord enjoyed Manorialism, manorial rights (the rights to establish and occupy a residence, known as the manor house and demesne) as well as seignory, the right to grant or draw benefit from the estate (for example, as a landlord). The title is not a peerage or title of upper nobility (although the holder could also be a peer) but was a relationship to land and how it could be used and those living on the land (tenants) may be deployed, and the broad estate and its inhabitants administered. The title continues in modern England and Wales as a legally recognised form of property that can be held independently of its historical rights. It may belong entirely to one person or be a moiety title, moiety shared with other people. The title is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |